Topics to Disccuss for Co
advertisement

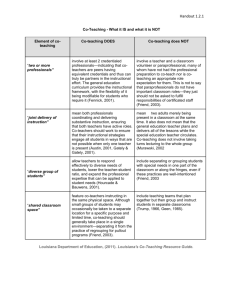
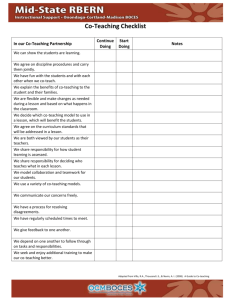
Co-Teaching Roles of Special Education/General Education Teachers in the Classroom Topics to Discuss for Co-Teachers Topic to Discuss Gen Ed Teacher’s Thoughts Special Ed Teacher’s Thoughts Planning: How, when, where, and what will you plan to increase effectiveness of this partnership? Instructional Format: (refer to page 3-6) Which co-teaching format(s) will you use? Which do you feel uncomfortable with? Equality: How will you help students understand that you are BOTH teachers with authority in the classroom? Space: Where will teachers be located in the room? Students? Adapted from “Aiming for the Ideal: Co-Teaching Approaches” by Lynne Cook, Ph.D. and Marilyn Friend, 2009 Co-Teaching Roles of Special Education/General Education Teachers in the Classroom Topics to Discuss for Co-Teachers Topic to Discuss Gen Ed Teacher’s Thoughts Special Ed Teacher’s Thoughts Classroom Management: What is your tolerance level for noise, behavior, and disruptions? How do you handle discipline? Help: How do you define “help” for a student? Grades: Who will do the grading? Will this be a shared responsibility? What/How will this be shared? Other: What else do you need to inform the other teacher about? Adapted from “Aiming for the Ideal: Co-Teaching Approaches” by Lynne Cook, Ph.D. and Marilyn Friend, 2009 Co-Teaching Roles of Special Education/General Education Teachers in the Classroom Topics to Discuss for Co-Teachers Approach One Teach, One Observe One Teach, One Assist Advantages Focused observation on student engagement Decide in advance the focus of that day’s observation Observations can be discussed to make adjustments to next lesson(s) Help and observe each other to become better teachers Gives individual help to students without being obtrusive in the lesson Allows each teacher to maximize their strengths (Caveat: this approach is often overused. It is the “fallback” approach and isn’t used for an instructional purpose but as a default.) When? New co-teaching situations When questions arise about students To check student progress To compare target students to others in class Planning LOW When the lesson lends itself to one teacher delivery When one teacher has particular expertise In new coteaching situations: get to know each other In lessons about a process in which student work needs close monitoring LOW Samples Which students initiate conversations in groups? Which students begin/do not begin work promptly? Is Anne’s inattentive behavior less than others? What does James do when he is confused? “This is my favorite lesson!” How well do students understand the steps of…? Are all students following as they take notes? Adapted from “Aiming for the Ideal: Co-Teaching Approaches” by Lynne Cook, Ph.D. and Marilyn Friend, 2009 Co-Teaching Roles of Special Education/General Education Teachers in the Classroom Topics to Discuss for Co-Teachers Approach Parallel Teaching Advantages Gives students more time to ask questions and explore Gives teachers closer supervision of the class (This approach has both teachers conducting the SAME lesson simultaneously. Then, the class comes back together for a review.) Station Teaching Allows difficult material to be taught in three different ways Allows for more one-on-one time with students Gives students movement, rather than sit-and-get When? When a lower adult-student ratio is needed to improve instruction To foster student participation in discussions For drill and practice, reteaching, and test review When content is complex but not hierarchical In lessons in which part of the planned instruction is review When several topics comprise one lesson Planning MEDIUM MEDIUM Samples More students would have a chance to share their alternative endings to a story. Each teacher present a lesson from a different view to encourage a debate when they come back together In science class to closely monitor use of special materials One station addresses a recently-read story, one focuses on editing a writing, and one has an activity teaching a new skill Examine geography, economics, and culture of a region Adapted from “Aiming for the Ideal: Co-Teaching Approaches” by Lynne Cook, Ph.D. and Marilyn Friend, 2009 Co-Teaching Roles of Special Education/General Education Teachers in the Classroom Topics to Discuss for Co-Teachers Approach Alternative Teaching Advantages Can give a small group extra instruction on the same lesson without missing anything Can be used for an entire block or just a few minutes Team Teaching Each teacher speaks freely during the largegroup lesson Sends a clear message to students that both teachers know the material Instruction becomes a conversation between two experts When? In situations where students’ mastery of concepts varies greatly When extremely high levels of mastery are expected for all students When enrichment is desired for high-achievers When some students are working in a parallel curriculum When experience is comparable When conversation may be more engaging than lecture Both teachers have high comfort and experience To model goal interaction for students Planning HIGH HIGH Samples Large group completes a practice exercise; small group receives additional direct instruction Large group checks homework; small group is pretaught vocab for today’s lesson Large group works on projects in small groups; small group takes a test. One explains experiment; other demonstrates Teachers debate US foreign policy Act out a story’s scene One teaches; other models desired “thinking” aloud One teaches; other takes model notes Adapted from “Aiming for the Ideal: Co-Teaching Approaches” by Lynne Cook, Ph.D. and Marilyn Friend, 2009