Part 1 of 1 -
advertisement

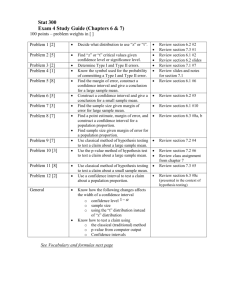
Part 1 of 1 Question 1 of 18 5.0 Points A numerical finding computed from sample data is called a: A. sampling frame B. margin of error C. confidence interval D. statistic E. parameter F. standard error G. quota Mark for Review Question 2 of 18 5.0 Points A numerical finding that is valid for the entire population is a:: A. standard error B. confidence interval C. quota D. margin of error E. parameter F. statistic G. sampling frame Mark for Review Question 3 of 18 5.0 Points The range (from lowest to highest) within which the sample statistic might vary from the population parameter is called the A. margin of error B. sampling frame C. parameter D. standard error E. statistic F. quota G. confidence interval Mark for Review Question 4 of 18 5.0 Points Which is equal to half a margin of error: A. statistic B. parameter C. confidence interval D. margin of error E. sampling frame F. standard error G. quota Mark for Review Question 5 of 18 5.0 Points Which is used in a form of non-probability sampling: A. statistic B. parameter C. confidence interval D. margin of error E. sampling frame F. standard error G. quota Mark for Review Question 6 of 18 5.0 Points We can be 95% sure that our sample finding is within one _____________ of the true population number. A. statistic B. parameter C. confidence interval D. margin of error E. sampling frame F. standard error G. quota Mark for Review Question 7 of 18 5.0 Points If we divide the population into subgroups of interest and take random samples of each subgroup we have a A. simple random sample B. multistage cluster sample C. stratified sample D. systematic sample E. quota sample F. subsample Mark for Review Question 8 of 18 5.0 Points If we do not have a list of the population, so we sample subgroups such as blocks or census tracts and then sample individuals within selected blocks or census tracts we have a A. simple random sample B. multistage cluster sample C. stratified sample D. systematic sample E. quota sample F. subsample Mark for Review Question 9 of 18 5.0 Points If we go down an alphabetized list of names and take every twentieth name we have a A. simple random sample B. multistage cluster sample C. stratified sample D. systematic sample E. quota sample F. subsample Mark for Review Question 10 of 18 10.0 Points A survey has 600 respondents. What is the margin of error? Give the answer as a percent with one number to the right of the decimal.For example 6.9% or 12.2% 1. Mark for Review Question 11 of 18 5.0 Points A researcher needs a margin of error of 5% in a survey. How large a sample is needed? 1. Mark for Review Question 12 of 18 5.0 Points A researcher is studying the Hispanic, African American and white populations in a county with 300,000 residents. 250,000 are white, 50,000 are Hispanic and 50,000 are African Americans. The researcher wants a margin of error of 5% for each of the groups. How large a sample is needed? 1. Mark for Review Question 13 of 18 10.0 Points A survey is conducted with 437 respondents in a city with 160,000 residents. The mean income reported for the sample is $25,321 with a standard deviation of $270. What is the margin of error for this mean score. Report the results with a dollar sign and two numbers after the decimal point, e.g., $72.35 1. Mark for Review Question 14 of 18 5.0 Points Nonprobability sampling: A. always produces samples that possess distorted characteristics relative to the population B. denies the researcher the use of statistical theory to estimate the probability of correct inferences C. should never be used under any circumstances D. includes stratified sampling E. requires the use of sampling frames Mark for Review Question 15 of 18 5.0 Points In general, as sample size increases: A. the standard error decreases in size B. the standard error increases in size C. the standard error will remain the same regardless of changes in sample size D. the standard error is a constant E. the standard error fluctuates in size Mark for Review Question 16 of 18 5.0 Points Stratifying a population prior to drawing a sample: A. generally occurs when the variables used to stratify are known to be associated with the dependent variable B. eliminates the need for simple random sampling C. is most useful for studying a homogeneous population D. eliminates the need for probability sampling E. is an alternative systematic sampling Mark for Review Question 17 of 18 5.0 Points This illustration represents a: A. simple random sample B. multistage cluster sample C. stratified sample D. systematic sample E. quota sample F. subsample Mark for Review Question 18 of 18 5.0 Points This illustration represents a: A. simple random sample B. multistage cluster sample C. stratified sample D. systematic sample E. quota sample F. subsample Mark for Review