Cost Accounting Variances: Material & Labor Analysis
advertisement

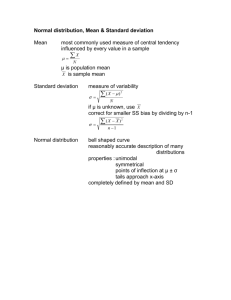
Required 1. Compute a material price variance for the plates purchased last month and a material quantity variance for the plates used last month. Materials price variance = actual quantity purchased x difference between actual and standard costs per unit of input purchased = 12,000 plates x ($2.35 - $2.50) = $1,800 F For the material price variance, the result is favorable because the actual price purchased is lower than the standard costs. Materials quantity variance = difference between actual quantity used and standard quantity allowed x standard cost per unit = = = = [10,500 plates - (2 plates x (1,800 + 2,400))] x $2.50/plate (10,500 plates - 8,400 plates) x $2.50/plate 2,100 plates x $2.50/plate $5,250 U For the material quantity variance, the result is unfavorable because the actual quantity used is higher than the standard quantity allowed. 2. For labor cost in the lab: a. Compute a labor rate variance and a labor efficiency variance. Labor rate variance = actual hours worked x difference between actual cost per hour and standard cost per hour = 1,150 hr x ($12 - $14) = 1,150 hr x -$2/hr = $2,300 F For the labor rate variance, the result is favorable because the actual cost per hour is lower than the standard cost per hour. For standard hours allowed, it can be calculated for each blood and smear tests as follows: (1,800 x 0.30 hr) + (2,400 x 0.15 hr) = 900 hours Labor efficiency variance = difference between actual hours worked and standard hours allowed per hour x standard cost = (1150 hr - 900 hr) x $14/hr = 250 hr x $14/hr = $3,500 U For the labor efficiency variance, the result is unfavorable because the actual hours worked are higher than the standard quantity allowed. b. In most hospitals, one half of the workers in the lab are senior technicians and one-half are assistants. In an effort to reduce costs, Valley View Hospital employs only onefourth senior technicians and three fourths assistants. Would you recommend that this policy be continued? Explain I would not recommend Valley View Hospital continue this policy. We could see that the Valley View does save some cost for labor rate in the labor rate variance which gives the result of $2,300 favorable. However, with the assistants, the job is probably not being done as effectively as the senior technicians. As a result, it would require more hours to complete the lab tests and result in an unfavorable position in the labor efficiency variance. Also, it requires more material which shows with the unfavorable material quantity variance. 3. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiently variances. Is there any relation between the variable overhead efficiency variance and the labor efficiency variance? Explain. Variable overhead spending variance = actual hours worked x difference between actual cost per hour and standard cost per hour = 1,150 hr x ($6.80 - $6.00) = 1,150 hr x $0.80/hr = $920 U For the variable overhead spending variance, the result is unfavorable because the actual cost per hour is higher than the standard cost per hour. Variable overhead efficiency variance = difference between actual hours worked and standard hours allowed per hour x standard cost = (1,150 hr - 900 hr) x $6.00/hr = 250 hr x $6.00/hr = $1,500 U For the variable overhead efficiency variance, the result is unfavorable because the actual hours worked is higher than the standard quantity allowed. This shows that both the variable overhead efficiency variance and the labor efficiency variance are in the unfavorable position for the hospital. This is due to the fact that the assistants need more time to complete the lab tests. Therefore, they will incur higher lab variable overhead expenses accordingly.