Simpson`s 1/3 Rule for Integration
advertisement
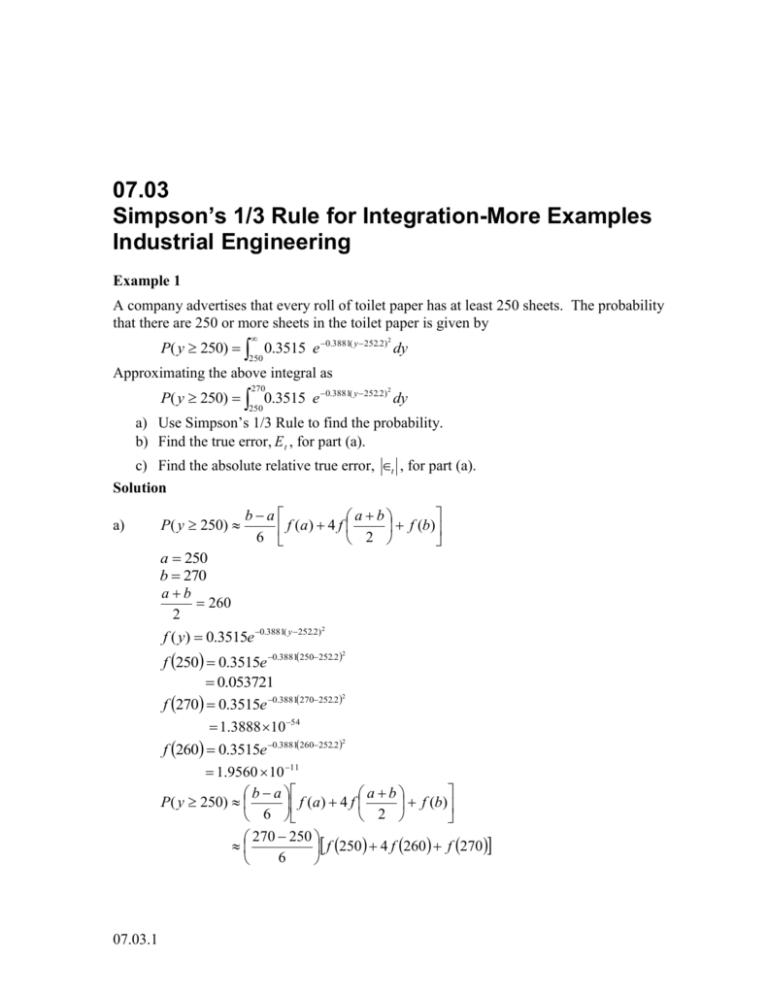
07.03 Simpson’s 1/3 Rule for Integration-More Examples Industrial Engineering Example 1 A company advertises that every roll of toilet paper has at least 250 sheets. The probability that there are 250 or more sheets in the toilet paper is given by P( y 250) 0.3515 e 0.3881( y 252.2) dy 2 250 Approximating the above integral as 270 P( y 250) 0.3515 e 0.3881( y 252.2) dy 2 250 a) Use Simpson’s 1/3 Rule to find the probability. b) Find the true error, E t , for part (a). c) Find the absolute relative true error, t , for part (a). Solution a) P( y 250) ba ab f (a) 4 f f (b) 6 2 a 250 b 270 ab 260 2 2 f ( y) 0.3515e 0.3881( y 252.2) f 250 0.3515e 0.3881250252.2 0.053721 2 f 270 0.3515e 0.3881270252.2 1.3888 10 54 2 f 260 0.3515e 0.3881260252.2 1.9560 10 11 b a ab P( y 250) f (a) 4 f f (b) 6 2 270 250 f 250 4 f 260 f 270 6 2 07.03.1 07.03.2 Chapter 07.03 20 0.053721 41.9559 10 11 1.3888 10 54 6 0.17907 b) The exact value of the above integral cannot be found. For calculating the true error and relative true error, we assume the value obtained by adaptive numerical integration using Maple as the exact value. 270 P( y 250) 0.3515 e 0.3881( y 252.2) dy 2 250 0.97377 So the true error is, Et True Value Approximat e Value 0.97377 0.17907 0.79470 Absolute Relative true error, True Error t 100 % True Value 0.79470 100 % 0.97377 81.611 % Example 2 A company advertises that every roll of toilet paper has at least 250 sheets. The probability that there are 250 or more sheets in the toilet paper is given by P( y 250) 0.3515 e0.3881( y252.2) dy 2 250 Approximating the above integral as 270 P( y 250) 0.3515 e 0.3881( y 252.2 ) dy 2 250 a) Use four segment Simpson’s 1/3 Rule to find the probability. b) Find the true error, E t , for part (a). c) Find the absolute relative true error for part (a). Solution a) Using n segment Simpson’s 1/3rd Rule, n 1 n2 ba P( y 250) f ( y 0 ) 4 f ( y i ) 2 f ( y i ) f ( y n ) 3n i 1 i 2 i odd i even n4 a 250 b 270 ba h n Simpson’s 1/3 Rule for Integration-More Examples: Industrial Engineering 270 250 4 5 f ( y) 0.3515e 0.3881( y 252.2) 2 So n 1 n2 ba P( y 250) f ( y 0 ) 4 f ( y i ) 2 f ( y i ) f ( y n ) 3n i 1 i 2 i odd i even 3 2 270 250 f 250 4 f y i 2 f y i f 270 34 i 1 i 2 i odd i even 20 f 250 4 f y1 4 f y3 2 f y 2 f 270 12 10 f (250) 4 f (255) 4 f (265) 2 f (260) f (270) 6 29 10 0.053721 40.016769 48.5260 10 6 21.9560 10 11 1.3888 10 54 0.20133 Since f y0 f 250 0.3515e 0.3881250252.2 0.053721 2 f y1 f 250 5 f 255 0.3515e 0.3881255252.2 0.016769 2 f y2 f 255 5 f 260 0.3515e 0.3881260252.2 1.9560 10 11 2 f y3 f 260 5 f 265 0.3515e 0.3881265252.2 8.5260 10 29 2 f y4 f yn 07.03.3 07.03.4 Chapter 07.03 f 270 0.3515e 0.3881270252.2 1.3888 10 54 2 b) The exact value of the above integral cannot be found. For calculating the true error and relative true error, we assume the value obtained by adaptive numerical integration using Maple as the exact value. 270 P( y 250) 0.3515 e 0.3881( y 252.2) dy 2 250 0.97377 So the true error is Et True Value Approximate Value 0.97377 0.20133 0.77244 Absolute Relative true error, True Error t 100 % True Value 0.77244 100 % 0.97377 79.325 % Table 1 Values of Simpson’s 1/3 Rule for Example 2 with multiple segments. Approximate Value n Et t % 2 4 6 8 10 0.17907 0.20133 1.0090 1.2042 1.0954 0.79470 0.77244 0.035226 0.23042 0.12167 81.611 79.325 3.6175 23.663 12.495








