Linear Equation Lesson Plan - PD-ROM
advertisement

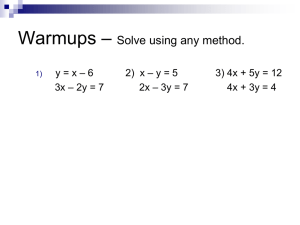
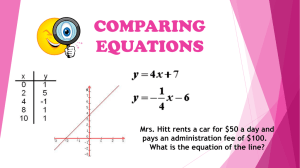
Linear Equation Exploration Lesson Plans L Laasstt 1155 m miinnuutteess ooff ccllaassss bbeeffoorree ssttaarrttiinngg uunniitt,, rreevviieew w tthhee ccoooorrddiinnaattee ppllaannee aanndd vvooccaabbuullaarryy.. H Hoom meew woorrkk ppaaggee 117700;; 11--2211 ooddddss.. PPrreennttiiccee HHaalll TToooollss ffoorr SSuucccceessss PPrree--R Reeqquuiissiitteess: The students will need to know the names of the parts of equations (constant, coefficient, variable) and how to create tables of values for equations. D Daayy 11 ~~ C Coooorrddiinnaattee PPllaaiinn R Reevviieew w ~~ B Booookk ((44--11)) PPrreennttiiccee HHaalll TToooollss ffoorr SSuucccceessss Materials Needed: • Floor taped off with a coordinate plane, mark the +y, -y, +x, -x. • Ordered pairs on card stock for student seats. (Sample ordered pairs are attached) • Timer or timer program on computer • Coordinate plane review worksheet Find Your Ordered Pair Seat ~ While they line up outside class explain they will get a card with an ordered pair printed on it. The ordered pair corresponds to a seat that follows the coordinate plain taped to the floor. They are to find their seat from the card for that day. Keep track of the time it takes each period. Continue the ordered pair seats for a week, keeping track of the times. Use the seats during the de-briefs and during the lessons to reinforce the topics and ideas of linear equations. Debrief ~ What do you notice with the coordinate plain? (Positives are to the top and to the right, negatives to the bottom and to the left) Where do you start to find your seat? Raise your hand if you are in the _____ quadrant? Coordinate Plain and tables review worksheet Worksheet Master #1 Homework ~ Make a table of values for the following 5 equations for x ~ -2 to +2. y=x-2 y = -3x + 1 y = 2x + 2 y=3 y = -½x + (-4) B Beeggiinnnniinngg L Leevveell ~~ D Daayy 22 Objective: Using a graphing calculator or computer-graphing program to discover the characteristics of linear equations. Beginners will discover what parts of the equations makes “uphill/downhill” lines, horizontal lines, lines that cross above/below the x-axis and through the origin. This is just the first introduction to linear equations, so it will start with investigation. Materials Needed: • One graphing calculator or Green Globs program/GraphCalc program • LCD for overhead for calculator or projector system • Overhead projector if using calculator • PowerPoint presentation ~ Drawing Linear Equations Find Your Ordered Pair Seat ~ De-brief by having students stand up in quadrants or positive/negative x/y coordinates. WARM UP: PowerPoint slide #3 In the equation y = x + 11 a) What is the coefficient? b) Is the coefficient positive or negative? c) What is the constant? d) Is the constant positive or negative? e) What is an improper fraction? Give an example? ACTIVITY: Have the Attention PowerPoint slide (Slide 1) showing as the students come into the room. Explain that there are several steps to learning linear equations, today they are at the beginner level and go to the beginner level slide (slide 2) and explain what the beginner level means. 1) Have the students quickly sketch 8 Cartesian planes on the front of their paper or use the premade handout. 2) Type in an equation on the graphing calculator and show on the LCD or use computer-graphing program. 3) Have students copy the equation on their first plane. 4) Show the graph of the equation on the overhead and have students draw a quick sketch on their first plane. NOTE: Make sure they have the intercept in roughly the correct place. Make sure the slope is roughly the correct “steepness”. Remind them that they are just beginners and in a couple of days they will be experts, so just do a rough sketch of the line. Encourage them to analyze the equations and their lines. 5) When all sketches are complete have students complete the Beginner Level worksheet in pairs. (Each partner should complete their own paper, which will become their notes). EQUATIONS: The following are some sample equations to use for their sketches. Homework Finish the beginner level notes. 1) 2) 3) 4) y y y y 3x 2 / 5 x 6 6x 3 2 5) 6) 7) 8) y y y y 4 x 6 3 / 7x 4 16 / 3 x 5 1 / 4x 2 N Noovviiccee L Leevveell ~~ D Daayy 33 Objective: Using a computer-graphing program to discover the characteristics of linear equations. Today the students will discover the y-intercept is where the line crosses the y-axis and it is the constant in the equation. Materials Needed: • Projector system and computer • PowerPoint presentation ~ Drawing Linear Equations • Novice Level Notes Handout, 8 coordinate planes handout, graph paper • Rulers Have the Attention PowerPoint slide (Slide 1) showing as the students come into the room. Explain, again, that there are several steps to learning linear equations, today they will be leaving the beginner level and going to the novice level (slide 6) and explain what the novice level means. Find Your Ordered Pair Seat ~ De-brief by having students stand up in "uphill", "downhill", steep, flat, horizontal lines. WARM UP: Beginner Quiz ~ PowerPoint slide #7, then to #8. Answers on slide #9. ACTIVITY: 1) Pass out novice level notes and rulers. 2) Explain that they are going to start to notice specifics in the equations and their lines. PowerPoint slide #6 3) Show each PowerPoint slide with the equations graphed, have them draw a rough sketch as before. Starting at slide #14 NOTE: Make sure they have the intercept in roughly the correct place. Make sure the slope is roughly the correct “steepness” and going in the correct "uphill"/"downhill" direction. Remind them that they are just 1 step beyond a beginner, so they will not be perfect yet, but in two days they will be. 4) The students will answer the questions next to the graph and make a prediction for the equation. Again remind them that they will get better by the end of today’s lesson. 5) Display the next slide, which has the correct equation, and have them write it down. 6) After the first 4 lines, start to ask if anyone notices anything about the lines and where the lines cross the y-axis. Homework ~ PowerPoint slide #26 Students are to predict, make a table of values, and graph 6 different equations. A Addvvaanncceedd L Leevveell ~~ D Daayy 44 Objective: Using a computer-graphing program to discover the characteristics of linear equations. Today the students will discover the slope is rise over run, and the vocabulary of slope and y-intercept. Materials Needed: • Green Globs program or GraphCalc program • Projector system and computer • PowerPoint presentation ~ Drawing Linear Equations • Advanced Level Notes Handout • Rulers Have the Attention PowerPoint slide (Slide 1) showing as the students come into the room. Explain, again, that there are several steps to learning linear equations, today they will be leaving the novice level and going to the advanced level (slide 27) and explain what the advanced level means. Find Your Ordered Pair Seat ~ De-brief by having students stand up in lines and check what the constant will be. WARM UP: Create equations that satisfy certain requirements ~ PowerPoint slide #28. Use the computer-graphing program to test students’ equations. Make it a point to show various equations on the same graph. Have them realize that the bigger a number’s absolute value is the steeper the line and the smaller the absolute value is the flatter the line. ACTIVITY: 1) Pass out novice level notes and rulers. Explain that they are going to start to get pretty good at writing the equations after today’s lesson. 2) Show the lines of the equations directly on the white board. Starting at PowerPoint slide #29 3) Have the students draw an exact line in each grid. 4) The students will answer the questions next to the graph and ask for a prediction of the equation. Again remind them that they will get it exactly by the end of today’s lesson. NOTE: They should know part of the equation, the constant. They discovered the constant yesterday and how to find it. Point out that the coefficient is found by knowing how many up or down from the y-intercept over how many to the right to the next point on the line. If they went up, equals positive coefficient, if they go down, negative coefficient. 5) Introduce the vocabulary for the parts of the linear equation, coefficient is the slope and the constant is the y-intercept. Homework ~ PowerPoint slide #45 Students find the slope of several linear equation lines. E Exxppeerrtt L Leevveell ~~ D Daayy 55 Objective: Using a computer-graphing program to discover the characteristics of linear equations. Today the students will learn and appreciate the expert way of graphing linear equation, which is by plotting the y-intercept first and then using the slope to plot the next point. The students will struggle with graphing 2 equation by using a table of values and then they will learn the expert way. Materials Needed: • Projector system and computer • PowerPoint presentation ~ Drawing Linear Equations • Binder paper and graph paper • Rulers Have the Attention PowerPoint slide (Slide 1) showing as the students come into the room. Explain, again, that there are several steps to learning linear equations, today they will be experts and experts use their knowledge to graph equations smarter (slide 46). Find Your Ordered Pair Seat ~ De-brief by having students stand up in lines and check what the steepness or flatness of the slope is. WARM UP: Create table of values and graphs for equations ~ PowerPoint slide #47. ACTIVITY: 1) Pass out graph paper and rulers. Explain that they are going to get their equations exactly after today’s lesson without the teacher’s help. 2) The students will write the y-intercept and the slope on binder paper, then use that information to write the linear equation. Check that they understand the different parts of the equation and what it does to the graph. 3) Then have the student create a table of values, using –2 to +2 for x, on binder paper and draw the lines on graph paper for the 2 equations. PowerPoint slide #52 Have them struggle with the fraction data values. 4) Once the students have struggled with the graphs, explain what an expert would do to graph the lines. Slide #53 ~ plotting the y-intercept first and then using the slope to plot the next point. Draw a line through the two points. 5) Use the blank coordinate plane (Slide #54) to show how to graph the equations quickly and accurately. Homework ~ Practice 4-4 worksheet Students use the expert method to graph several linear equations. Reinforcing linear equation characteristics and vocabulary M Miinndd//W Woorrdd M Maapp Objective: Using word mind maps to have the students deepen their knowledge of linear equations in a graphical form. Materials Needed: Word/Mind Map Word list ACTIVITY: 1) Pass out mind map and word list. 2) The students will use the word list to fill in the mind/word map, so the characteristics are presented in a graphic organized form. 3) De-brief mind/word map. F Fiinnddiinngg yy--iinntteerrcceepptt Objective: Using linear equations students will deepen their knowledge of linear equations and yintercept in a fun, game form. Materials Needed: • Graphs on hard-stock • Small white boards and markers • 1 binder paper and pencil per group ~ it is for keeping score • Prizes for winners of the game, a prize per group ACTIVITY: 1) Get students into groups of 3. 2) Explain the rules… • 1 student will get a stack of graphs on hard-stock paper along with the equations on a separate sheet of paper. There is a number at the top of each graph. That number corresponds to the answer number on the answer sheet. • The other 2 students will get white boards and markers. • The student with the equations will show 1 at a time and the other students will write the equation on the white board and sketch the equation. Students will also be asked to identify the points and y-intercept of the line. • The first student with the correct equation gets 1 point. • After a set number of equations shown, students will rotate roles ~ therefore, everyone will get a chance to show the graphs and compete against another. • The student with the most points at the end gets a prize.