Chapter 4: Of Tests and Testing (Norms, Correlation, & Inference)
advertisement

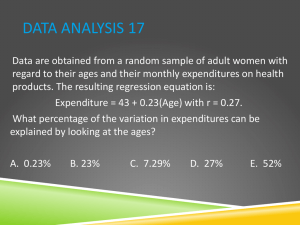
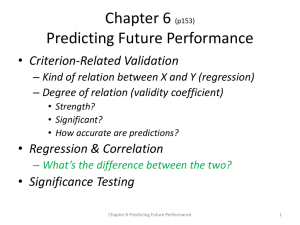
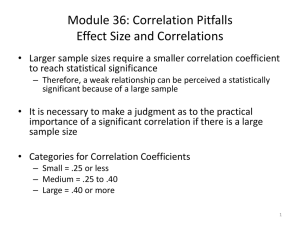
Chapter 4: Of Tests and Testing 12 Assumptions in Psychological Testing and Assessment • Assumption 1: Psychological traits and states exist • Assumption 2: Psychological traits and states can be quantified and measured • Assumption 3: Various approaches to measuring aspects of the same thing can be useful • Assumption 4: Assessment can provide answers to some of life’s most momentous questions • 12 Assumptions in Psychological Testing and Assessment • Assumption 5: Assessment can pinpoint phenomena that require further attention or study. • Assumption 6: Various sources of data enrich and are part of the assessment process. • Assumption 7: Various sources of error are part of the assessment process. • 12 Assumptions in Psychological Testing and Assessment • Assumption 8: Tests and other measurement techniques have strengths and weaknesses • Assumption 9: Test-related behavior predicts non–test-related behavior • Assumption 10: Present-day behavior sampling predicts future behavior • 12 Assumptions in Psychological Testing and Assessment • Assumption 11: Testing and assessment can be conducted in a fair and unbiased manner • Assumption 12: Testing and assessment benefit society Most Controversial Assumption? • Why? What are Norms? • Derived typical test performance of a standardization sample • The test score distribution that provides the average or typical (normal) score level on a test Standardization (normative) Sample • The normative sample is a representative subset drawn from the broader target population • Typically, a large random sample • Sample size should be large enough to obtain stable values. Sampling Techniques • Randomization – every case has an equal chance of selection • Stratified – representative proportions of groups – e.g. age, socioeconomic level, ethnicity • Incidental – Convenience sampling – Not a desired procedure Types of Norms • Developmental Norms • Indicates developmental level attained • Age equivalent norms (Mental Age) • • • e.g., a 7 year old who scores the same mean obtained by 10 year old children has a mental age of 10. Grade equivalent norms e.g., average score of 4th graders is 23, a child with a raw score of 23 is given a 4th grade age equivalence. Norm-Referenced (Within group) Norms • Individual performance is evaluated in reference to a standardization group • The same test is used to compare other groups of test-takers • Deviation IQs What is Correlation? • Index of linear association between two variables (X and Y) • Does not suggest cause and effect • Computed value is called a coefficient • Best example is the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (r) Pearson Formula (definitional) • Co-variation between X and Y • Ratio of the variability between X and Y Values of r • Coefficient values range between -1 and + 1 • What does 0 mean? – The closer the coefficient value is to 0, the weaker the association between two variables • The further a coefficient moves from 0, the stronger the association between two variables – Coefficients of -1 and +1 have the same magnitude of association Coefficient of Determination (r2) • Correlation coefficient squared • The value indicates the proportion of the variation in Y scores that is a function of the X scores • i.e., the variance in X explained by Y Graphing Correlation • Correlations between two variables can be displayed in a scatterplot • Individual scores are plotted on two-dimensional axes – X scores plotted on horizontal axis (abscissa) – Y scores plotted on vertical axis (ordinate) Positively Correlated • As X increases, Y increases Negatively Correlated • As X increases, Y decreases No Correlation • No relationship between X and Y Curvilinear Relationship • Non-linear relationship between two variables • The scatterplot has a significant curve • U-shaped curve • Umbrella-shaped curve • S-shaped curve Other Correlation Coefficients • Spearman rho – Used in rank-order correlation • ordinal scales • Evaluate the differences (or agreement) between rankings of two variables – Students’ scores on a mid-term 1 and mid-term 2 are ranked from lowest to highest; the rankings are correlated Point Biserial • Comparison of one continuous variable and one dichotomous variable • Dichotomous variables include Yes/No or True/False scales – Correlation between Age (continuous) and Active Class Participation (Yes or No) Phi • Correlation between two dichotomous variables – Correlation between Active Class Participation (Yes or No) and Mid-term results (Pass or Fail) Biserial r • Comparison of one continuous variable and one artificially dichotomized variable • An artificially dichotomized variable is a continuous variable that is transformed to dichotomous variable – e.g., Age in years converted to age groups • 18-25, 26-30, 31-40, 40-50, 51-60, etc. Tetrachoric • Correlation between two artificially dichotomized variables – Correlation between age groups and mid-term score Roles of Correlations in Testing • Test-retest reliability – Correlation between scores on the same test at two different times • Correlation of GRE in the Fall and Spring semesters • • • Criterion (predictive) validity coefficients – Correlation between test scores and results of an independent criterion Correlation between SAT and College GPA Convergent validity coefficients – Correlation between scores on two conceptually similar tests • Correlation between self-esteem and self-concept Regression • Degree of predictability between two variables • Extends the concept of correlation to the prediction of a test score (Y) based on a another test score (X) Regression Equation • • • • Y’ = a + bX X = predictor (test score) Y’ = criterion (predicted score) a = y-intercept (criterion score if the predictor score is 0) b = slope (correlation between the predictor and criterion) Regression Line • Line drawn through the scatter of scores • The regression line represents the Principle of Least Squares • least squared deviation from the line • The line demonstrates the best fit for all data points Slope • Essentially, the correlation coefficient Y-Intercept • Where the regression line crosses the Y-axis • Criterion score if the predictor score is 0 a = Y – bX • • Y is the mean of the Y scores X is the mean of the X scores Regression Example Y’ = 2 + 0.67X • What is the predicted score (Y’) if X is 10? Regression Line • Line drawn through the scatter of scores • The regression line represents the Principle of Least Squares – least squared deviation from the line • The line demonstrates the best fit for all data points • Regression Line Example Residuals • Difference between the predicted (Y’) and observed criterion (Y) values • Y – Y’ • Principle of Least Squares • Minimize the deviation between Y and Y’ Standard Error of Estimate • Error in the prediction estimate – Standard deviation of the residuals • The square root of the residual variance • The lower the standard deviation, the lower the degree of error in the regression equation Inference from Measurement • Meta-Analysis – Statistical combination of studies • Culture and Inference – Individualists vs. collectivists