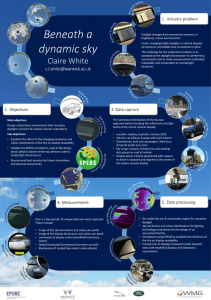
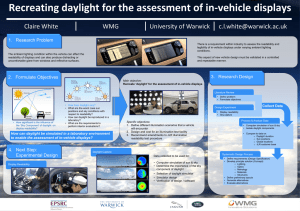
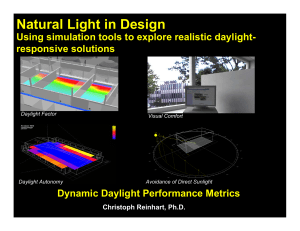
Daylight Calculations
advertisement

Daylight Calculations Daylight or natural light is provided directly by the sunlight and/or the sky. Sunlight is so variable that it is not of much use in lighting design of interiors. Illuminance from the sky is also variable; it varies during the day and through the year. In countries like Britain where the climate is not reliable, an overcast sky is considered to be the main source of daylight. It also represents the worst type of daylight. Daylight factor The daylight factor is defined as the ratio of the natural illuminance at a particular point on a horizontal plane to the simultaneously occurring external illuminance of the unobstructed overcast sky. In Britain, the standard sky is assumed to give at least 5000 lx of illuminance on the ground. Daylight factor (DF) = Internal illuminanc e 100 External illuminanc e The daylight reaching any point inside a room is usually made up of three components: Sky component Externally reflected component Internally reflected component If there is no external obstruction like trees, buildings etc. the externally reflected component is omitted. Several techniques, manual as well as computerised, may be used to calculate these components for a building. In side-lit rooms, the maximum DF is near the windows, and it is mainly due to the sky component. In the early stages of building design, the average daylight factor may be used to assess the adequacy of daylight: Average DF = W Tθ 2 A (1 - R ) where: W is the area of the windows (m2) A is the total area of the internal surfaces (m2) T is the glass transmittance corrected for dirt θ is visible sky angle in degrees from the centre of the window R is the average reflectance of area A. The values of these quantities are determined from the given data and W, T and R are corrected by using factors given in the BS Daylight Code and other publications. Example: Find the average daylight factor for a room – 5.0 m × 4.0 m × 2.4 m high with one 2.4 m × 1.3 m high double-glazed window. Assume that the surfaces of the room are light in colour; there is an obstruction as shown in Figure App 9.1. Solution: The emphasised figures are approximate correction factors Average DF = W Tθ 2 A (1 - R ) Window area = 2.4 × 1.3 = 3.12 m2 W = 3.12 × 0.7 = 2.18 m2 T = 0.6 (approx.) for double-glazed windows in clean environment θ = 73º A = 2 × (5.0 × 2.4 + 4.0 × 2.4) + 5.0 × 4.0 + 5.0 × 4.0 = 83.2 m2 R = 0.6 (considering light coloured room surfaces) 5.0 m 2.4 m PLAN 4.0 m Visible sky angle ° 73 SECTION Obstruction Figure App 9.1 Average DF = 0.6 73 2.18 83.2 (1 0.6 2 ) = 95.484 83.2 0.64 = 1.8 %