AXILLA - By Dr Nand Lal Dhomeja ( Anatomy Department )
advertisement

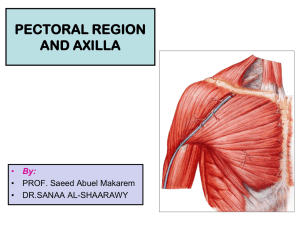
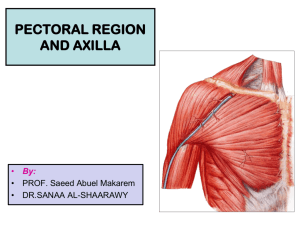
AXILLA LEARNING OBJECTIVES • • • • Know the position, shape of axilla Mention the boundaries and muscle forming the boundaries of axilla Discuss the formation, course and relations of axillary vessels Describe arrangement and groups axillary lymph nodes Axilla Area of transition between neck and arm An irregularly shaped pyramidal space with: 4 sides An inlet A base or floor Axillary inlet is connected with neck superiorly and with arm inferiorly Axillary Inlet Margins of inlet are completely formed by bone Medially - lateral border of rib1 Anterior - posterior Surface of clavicle Posterior - superior border of scapula Anterior wall Lateral part of Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Subclavius Clavipectoral fascia Medial Wall Upper rib Serratus Anterior Long thoracic nerve Lateral Wall Narrow Formed completely by intertubercular sulcus of humerus Posterior Wall Costal surface of scapula and subscapularis muscle Latissimus dorsi and Teres Major Gaps between posterior wall forms aperatures Floor Fascia Dome of skin connecting inferior margins of walls Supported by clavipectoral fascia Contents Axillary artery and its branches Axillary vein and its tributaries Brachial plexus Nerves - long thoracic nerve, and intercostobrachial nerve Collection of lymph nodes Connection of the breast with axilla Proximal parts of biceps brachii and coracobrachialis Axillary Artery first portion: Outer border 1st rib to medial edge of pectoralis minor Second portion: behind pectoralis minor Third portion: lateral edge of pectoralis minor to lower border of teres major Branches Of The Axillary Artery first part – Highest Thoracic second part – Thoracoacromial Lateral Thoracic Third part – Subscapular. Posterior Humeral Circumflex. Anterior Humeral Circumflex Axillary Vein Origin: basilic vein (lower border of Teres major) Outflow: subclavian vein (outer border of first rib) Tributaries: brachial veins cephalic vein Venae commitantes to correspond with branches of axillary artery Course: It lies on medial side of artery between two vessels are medial cord of brachial plexus, median, ulnar, and medial anterior thoracic nerves. Valves: A pair of valves opposite the lower border of subsacpularis At ends of cephlaic vein and subscapular vein (the venae commitantes of subscapular artery) Brachial Plexus Each trunk divides into anterior and posterior divisions behind middle of clavicle at apex of axilla Three posterior divisions join to form posterior cord Anterior divisions of upper and middle trunks form lateral cord Anterior division of lower trunk continues as medial cord Cords lie around axillary artery Posterior cord - axillary and radial nerves. Lateral cord - musculocutaneous and lateral head of median nerves Medial cord - ulnar and medial head of median nerves Nerves Long thoracic nerve: supplies serratus anterior arises by three roots from C5-C7 descends behind brachial plexus and axillary vessels, resting on outer surface of serratus anterior. It extends along side of thorax to lower border of serratus anterior giving its branches. Injury: during surgery for breast cancer, specifically radical mastectomies involving removal of axillary lymph nodes from a blow to ribs on an outstretched arm gives rise to “winged scapula” Intercostobrachial nerve: pierces external intercostals and Serratus anterior, crosses axilla to medial side of arm joins with a branch from medial brachial cutaneous nerve. supplies skin of upper half of medial and posterior part of arm, communicating with posterior brachial cutaneous branch of radial nerve. Injury: During lymphectomy eg in breast surgery Hypothesia of skin covering axilla and medial side of arm Axillary Lymph Nodes They drain upper limb, upper abdominal wall and pectoral region and receive most of lymphatic drainage of breast. Arranged in five groups: anterior group - deep to pectoralis major and drain lateral and anterior chest wall, breast and upper abdominal wall. lateral group - lateral wall of axilla. Drain whole arm with exception of that portion whose vessels accompany cephalic vein posterior group - lateral edge of subscapularis muscle on posterior wall of axilla. Drain skin and muscles of lower part of back of neck and of posterior thoracic wall central group - arranged around axillary vessels in axillary fat. Drains the above 4 groups apical group (median) - apex of axilla immediately behind clavicle, they are continuous with inferior deep cervical nodes. Receive drainage from all preceding groups. Connection Of Breast With Axilla Lymphatic drainage of breast Breast cancer and its staging Surgery of breast cancer Lymph node biopsy Lymphectomy Damage to the nerves during surgery (Long thoracic nerve, Intercostobrachial nerve) CLINICALLY ORIENTED ANATOMY OF K.L.M SIXTH EDITION