Descriptive Statistics Test Bank: Questions & Answers
advertisement

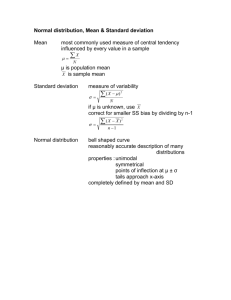
CHAPTER THREE Descriptive Statistics C 1. E Term C E Term Statistical measures used to yield information about the middle of a group of numbers are called _______. A. averages B. measures of variability C. measures of central tendency D. Z scores 2. Which of the following is NOT a measure of central tendency? A. mean B. median C. variance D. mode 69 Test Bank 70 A 3. E Term A A. mode B. mean C. median D. coefficient of variation 4. E Term C 5. 6. E Term The lowest appropriate level of measurement for the mean is _________. A. nominal B. ordinal C. interval D. ratio 7. E Term A Which of the following is an appropriate measure of central tendency for ordinal data? A. standard deviation B. mean C. median D. coefficient of variation E Term B Which of the following is an appropriate measure of central tendency for nominal data? A. mode B. mean C. median D. coefficient of variation E Term C The most frequently occurring value in a set of data is called the _______. The lowest appropriate level of measurement for the median is _________. A. nominal B. ordinal C. interval D. ratio 8. The lowest appropriate level of measurement for the mode is _________. A. nominal B. ordinal C. interval D. ratio Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics C 9. The middle value in an ordered array of numbers is called the _______. E Term A. mode B. mean C. median D. coefficient of variation B Another term for average is _______. 10. E Term C 11. E Term A 12. A. mode B. mean C. median D. variance The Greek letter usually refers to the _______. A. population standard deviation B. sample variance C. population mean D. sample mean The Greek letter usually refers to the _________. E Term A. population standard deviation B. sample variance C. population mean D. sample mean D The notation X usually refers to the _______________. 13. E Term A. population standard deviation B. sample variance C. population mean D. sample mean B The notation S2 usually refers to the _______________. 14. E Term A. population standard deviation B. sample variance C. population mean D. sample mean 71 Test Bank 72 D 15. Which of the following is NOT a commonly used measure of variability? M Term A. variance B. standard deviation C. mean absolute deviation D. average deviation A The sum of deviations about the arithmetic mean is always equal to _______. 16. E Term C 17. A. zero B. the variance C. the mean absolute deviation D. the standard deviation The average of the squared deviations from the arithmetic mean is called the _______. M Term A. standard deviation B. mean absolute deviation C. variance D. coefficient of variation B The sample variance is found by taking the square root of _______. 18. E Term A. the sample mean B. the sample variance C. the coefficient of variation D. the mean absolute deviation C The lowest appropriate level of measurement for standard deviation is _________. 19. E Term A. nominal B. ordinal C. interval D. ratio B The lowest appropriate level of measurement for the Interquartile Range is _________. 20. E Term A. nominal B. ordinal C. interval D. ratio Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics D 21. The number of standard deviations that a value (X) is above or below the mean is the _________________. M Term A. B. C. D. D If the mean of a distribution is greater than the median, then the distribution is ______. 22. M Term C 23. absolute deviation coefficient of variation interquartile range Z score A. not skewed B. symmetrical about its mean C. skewed to the left D. skewed to the right If the median of a distribution is greater than mean, then the distribution is _________. M Term A. B. C. D. D The interquartile range is _____________. 24. not skewed symmetrical about its mean skewed to the left skewed to the right E Term A. B. C. D. B The five numbers used to construct a box and whisker plot are _______. 25. the largest value minus the least value the ratio of the mean to the standard deviation negative if the distribution is skewed to the left Q3 - Q1 M Term A. B. C. D. D Which of the following is a measure of relative dispersion? 26. M Term 73 A. B. C. D. the mean, standard deviation, Q1, Q3, and the coefficient of variation Q1, Q2, Q3, the least value of X, and the largest value of X the mean, standard deviation, least value of X, largest value of X, and Q2 the coefficient of variation, IQR, mean, Q2, and mean absolute deviation standard deviation interquartile range mean absolute deviation coefficient of dispersion Test Bank 74 A 27. The empirical rule says that approximately what percentage of the values would be within 2 standard deviations of the mean in a bell shaped set of data? M Term A. 95% B. 68% C. 50% D. almost all B The empirical rule says that approximately what percentage of the values would be within 1 standard deviation of the mean in a bell shaped set of data? 28. M Term A 29. H Calc D A. at least 75% B. at least 68% C. at least 95% D. at least 89% 30. M Calc B M Calc A. 95% B. 68% C. 50% D. almost all Chebyshev's Theorem says that how many values will be within 2 standard deviations of the mean? Chebyshev's Theorem says that the number of values within 3 standard deviations of the mean will be _______. A. at least 75% B. at least 68% C. at least 95% D. at least 89% 31. A statistics student made the following grades on 5 tests: 84, 78, 88, 78, and 72. What is the mean grade? A. 78 B. 80 C. 72 D. 84 Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics C 32. M Calc A 33. 34. E Calc A commuter travels many miles to work each morning. She has timed this trip 5 times during the last month. The time (in minutes) required to make this trip was 34, 39, 41, 35, and 41. The mean time required for this trip was _______. A. B. C. D. 35. M Calc B A statistics student made the following grades on 5 tests: 84, 78, 88, 78, and 82. What is the mode? A. 78 B. 80 C. 88 D. 84 M Calc A A statistics student made the following grades on 5 tests: 84, 78, 88, 72, and 72. What is the median grade? A. 88 B. 72 C. 78 D. 80 E Calc D 75 A commuter travels many miles to work each morning. She has timed this trip 5 times during the last month. The time (in minutes) required to make this trip was 34, 39, 41, 35, and 41. The median time required for this trip was _______. A. B. C. D. 36. 35 41 37.5 38 39 41 37.5 38 A commuter travels many miles to work each morning. She has timed this trip 5 times during the last month. The time (in minutes) required to make this trip was 34, 39, 41, 35, and 41. The modal time required for this trip was _______. A. B. C. D. 39 41 37.5 38 Test Bank 76 B 37. H Calc A A. B. C. D. 38. H Calc D 39. M BCalc 3.32 2.97 1.73 11 A commuter travels many miles to work each morning. She has timed this trip 5 times during the last month. The time (in minutes) required to make this trip was 44, 39, 41, 35, and 41. The mean time required for this trip was 40 minutes. What is the mean absolute deviation for this sample data? A. B. C. D. 40. 8.8 11 0 3 A commuter travels many miles to work each morning. She has timed this trip 5 times during the last month. The time (in minutes) required to make this trip was 44, 39, 41, 35, and 41. The mean time required for this trip was 40 minutes. What is the standard deviation for this sample data? A. B. C. D. H Calc D A commuter travels many miles to work each morning. She has timed this trip 5 times during the last month. The time (in minutes) required to make this trip was 44, 39, 41, 35, and 41. The mean time required for this trip was 40 minutes. What is the variance for this sample data? 0 12 3 2.4 Abel Alonzo, Director of Human Resources, is exploring employee absenteeism at the Batesville Bottling during the last operating year. A sample of six personnel records produced the following data: 0, 2, 4, 7, 2, 9. The mean number absences per employee is ____________. A. B. C. D. 3 2 5.5 4 Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics B 41. 77 Abel Alonzo, Director of Human Resources, is exploring employee absenteeism at the Batesville Bottling during the last operating year. A sample of six personnel records produced the following data: 0, 2, 4, 7, 2, 9. The modal number absences per employee is ____________. E BCalc A. B. C. D. A Abel Alonzo, Director of Human Resources, is exploring employee absenteeism at the Batesville Bottling during the last operating year. A sample of six personnel records produced the following data: 0, 2, 4, 7, 2, 9. The median number absences per employee is ____________. 42. 3 2 5.5 4 M BCalc A. B. C. D. A Abel Alonzo, Director of Human Resources, is exploring employee absenteeism at the Batesville Bottling during the last operating year. A sample of six personnel records produced the following data: 0, 2, 4, 7, 2, 9. The variance of the number absences per employee is ____________. 43. 3 2 5.5 4 H BCalc A. B. C. D. C Abel Alonzo, Director of Human Resources, is exploring employee absenteeism at the Batesville Bottling during the last operating year. A sample of six personnel records produced the following data: 0, 2, 4, 7, 2, 9. The standard deviation of the number absences per employee is ____________. 44. H BCalc A. B. C. D. 11.6 9.67 3.41 3.11 11.6 9.67 3.41 3.11 Test Bank 78 A 45. The mean life of a particular brand of light bulb is 1000 hours and the standard deviation is 50 hours. It can be concluded that at least 75% of the bulbs will last between _______. H BCalc A. B. C. D. C The mean life of a particular brand of light bulb is 1000 hours and the standard deviation is 50 hours. It can be concluded that at least 89% of the bulbs will last between _______. 46. 900 and 1100 hours 950 and 1050 hours 850 and 1150 hours 800 and 1200 hours H BCalc A. B. C. D. B The mean life of a particular brand of light bulb is 1000 hours and the standard deviation is 50 hours. Tests show that the life of the bulb is approximately normally distributed. It can be concluded that approximately 68% of the bulbs will last between _______. 47. M Calc A A. B. C. D. 48. M BCalc 900 and 1100 hours 950 and 1050 hours 850 and 1150 hours 800 and 1200 hours 900 and 1100 hours 950 and 1050 hours 850 and 1150 hours 800 and 1200 hours Jessica Salas, president of Salas Products, is reviewing the warranty policy for her company's new model of automobile batteries. Life tests performed on a sample of 100 batteries indicated: (1) an average life of 75 months, (2) a standard deviation of 5 months, and (3) battery life is approximately normally distributed. Approximately 68% of the batteries will last between ________________. A. B. C. D. 70 and 80 months 60 and 90 months 65 and 85 months 55 and 95 months Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics C 49. 79 Jessica Salas, president of Salas Products, is reviewing the warranty policy for her company's new model of automobile batteries. Life tests performed on a sample of 100 batteries indicated: (1) an average life of 75 months, (2) a standard deviation of 5 months, and (3) battery life is approximately normally distributed. Approximately 95% of the batteries will last between ________________. M BCalc A. B. C. D. B Jessica Salas, president of Salas Products, is reviewing the warranty policy for her company's new model of automobile batteries. Life tests performed on a sample of 100 batteries indicated: (1) an average life of 75 months, (2) a standard deviation of 5 months, and (3) battery life is approximately normally distributed. Approximately 99% of the batteries will last between ________________. 50. 70 and 80 months 60 and 90 months 65 and 85 months 55 and 95 months M BCalc A. B. C. D. C Jessica Salas, president of Salas Products, is reviewing the warranty policy for her company's new model of automobile batteries. Life tests performed on a sample of 100 batteries indicated: (1) an average life of 75 months, (2) a standard deviation of 5 months, and (3) battery life is approximately normally distributed. What percentage of the batteries will fail within the first 65 months of use? 51. 70 and 80 months 60 and 90 months 65 and 85 months 55 and 95 months H BCalc A. B. C. D. B The average starting salary for graduates at a university is $25,000 with a standard deviation of $2,000. If a histogram of the data shows the it takes on a mound shape, the empirical rule says that approximately 95% of the graduates would have a starting salary between _______. 52. M BCalc A. B. C. D. 0.5% 1% 2.5% 5% 23,000 and 27,000 21,000 and 29,000 19,000 and 31,000 24,000 and 26,000 Test Bank 80 A 53. The average starting salary for graduates at a university is $25,000 with a standard deviation of $2,000. If a histogram of the data shows the it takes on a mound shape, the empirical rule says that approximately 68% of the graduates would have a starting salary between _______. M BCalc A. B. C. D. A The average starting salary for graduates at a university is $25,000 with a standard deviation of $2,000. A histogram of the data shows the shape to be very erratic so Chebyshev's Theorem should be used. How many of the graduates would have a starting salary between 21,000 and 29,000? 54. 23,000 and 27,000 21,000 and 29,000 19,000 and 31,000 24,000 and 26,000 H BCalc A. B. C. D. B The average starting salary for graduates at a university is $25,000 with a standard deviation of $2,000. A histogram of the data shows the shape to be very erratic so Chebyshev's Theorem should be used. How many of the graduates would have a starting salary between 19,000 and 31,000? 55. at least 75% at least 89% at least 68% at least 95% H BCalc A. B. C. D. B The ages of students in a class have been put into the frequency distribution below. Age Number of Students 18 3 19 5 20 28 21 4 What is the average age of these students? M Calc 56. A. B. C. D. at least 75% at least 89% at least 68% at least 95% 19.50 19.85 20.00 28.00 Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics B 57. H Calc D A. B. C. D. 58. M Calc C E Calc The ages of students in a class have been put into the frequency distribution below. Age Number of Students 18 3 19 5 20 28 21 4 What is the standard deviation for this (population) set of data? The ages of students in a class have been put into the frequency distribution below. Age Number of Students 18 3 19 5 20 28 21 4 What is the median age of these students? A. B. C. D. 59. 0.494 0.703 1.12 1.25 18 19 19.5 20 The ages of students in a class have been put into the frequency distribution below. Age Number of Students 18 3 19 5 20 28 21 4 What is the modal age of these students? A. B. C. D. 18 19 20 21 81 Test Bank 82 A 60. M App C The mean, median, and mode for the following set of data are all the same value (20). Data: 18, 19, 20, 20, 21, 22. If the highest number were changed from 22 to 322, which of the following would be most affected? A. B. C. D. 61. mean median mode sample size In its Industry Norms and Key Business Ratios, Dun & Bradstreet reported that Q1, Q2, and Q3 for 577 motorcycle dealers' current ratios were 1.3, 1.6 and 2.9, respectively. From this we can conclude that __________________. M BApp A. B. C. D. C An instructor is evaluating the performance of students on a test. He records the number of points that each student missed and created a frequency distribution. This is provided below: Points missed Number of students 0-under 10 2 10-under 20 4 20-under 30 10 30-under 40 8 40-under 50 6 What is the mean number of points missed? H Calc 62. A. B. C. D. 68% of these dealers had current ratios between 1.3 and 2.9 95% of these dealers had current ratios between 1.3 and 2.9 50% of these dealers had current ratios between 1.3 and 2.9 75% of these dealers had current ratios between 1.3 and 2.9 20 25 29 30 Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics C 63. H Calc D An instructor is evaluating the performance of students on a test. He records the number of points that each student missed and created a frequency distribution. This is provided below: Points missed Number of students 0-under 10 2 10-under 20 4 20-under 30 10 30-under 40 8 40-under 50 6 What is the variance for this population? A. B. C. D. 64. 83 11.43 135.17 130.67 200 In its Industry Norms and Key Business Ratios, Dun & Bradstreet reported that Q1, Q2, and Q3 for 577 motorcycle dealers' current ratios were 1.3, 1.6 and 2.9, respectively. From this we can conclude that __________________. M BApp A. B. C. D. A An instructor is evaluating the performance of students on a test. He records the number of points that each student missed and created a frequency distribution. This is provided below: Points missed Number of students 0-under 10 2 10-under 20 4 20-under 30 10 30-under 40 8 40-under 50 6 What is the standard deviation for this population? H Calc 65. A. B. C. D. 68% of these dealers had current ratios of 1.6 or less 95% of these dealers had current ratios of 2.9 or less 50% of these dealers had current ratios of 2.9 or more 75% of these dealers had current ratios of 1.3 or more 11.43 14.14 11.63 135.17 Test Bank 84 C 66. H Calc D An instructor is evaluating the performance of students on a test. He records the number of points that each student missed and created a frequency distribution. This is provided below: Points missed Number of students 0-under 10 2 10-under 20 4 20-under 30 10 30-under 40 8 40-under 50 6 If this is considered a sample, what is the standard deviation? A. B. C. D. 67. 11.43 14.14 11.63 135.17 Which of the following is always true? E Term A. B. C. D. A Pinky Bauer, Chief Financial Officer of Harrison Haulers, Inc., suspects irregularities in the payroll system, and orders an inspection of "each and every payroll voucher issued since January 1, 1993." Each payroll voucher was inspected and the following frequency distribution was compiled. Errors Per Voucher Number of Vouchers 0-under 2 500 2-under 4 400 4-under 6 300 6-under 8 200 8-under 10 100 The mean number of errors per voucher is __________. 68. H BCalc A. B. C. D. the median is always one-half of the mean the mode is always greater than the mean the mean is always equal to the median the standard deviation is always the square root of the variance 3.67 5 750 300 Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics A 69. Pinky Bauer, Chief Financial Officer of Harrison Haulers, Inc., suspects irregularities in the payroll system, and orders an inspection of "each and every payroll voucher issued since January 1, 1993." Each payroll voucher was inspected and the following frequency distribution was compiled. Errors Per Voucher Number of Vouchers 0-under 2 500 2-under 4 400 4-under 6 300 6-under 8 200 8-under 10 100 The distribution of errors per voucher is __________. M BApp A. B. C. D. C A sales manager has sampled past sales records to determine how many refrigerators are sold each day. Daily records for a sample of 10 days have been selected. The sales on these days are: 0, 4, 4, 2, 1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 7. What is the mean daily sales? 70. symmetrical with respect to its mean skewed to the right not skewed negatively skewed M BCalc A. B. C. D. C A sales manager has sampled past sales records to determine how many refrigerators are sold each day. Daily records for a sample of 10 days have been selected. The sales on these days are: 0, 4, 3, 2, 1, 3, 5, 5, 2, 5. What is the median daily sales? 71. M BCalc A. B. C. D. 2 4 3.2 10 3.5 2 3 4 85 Test Bank 86 D 72. E BCalc B 73. A sales manager has sampled past sales records to determine how many refrigerators are sold each day. Daily records for a sample of 10 days have been selected. The sales on these days are: 0, 4, 4, 2, 1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 7. The mode of data set is ______. A. 3.5 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 A sales manager has sampled past sales records to determine how many televisions are sold each day. Daily records for a sample of 5 days have been selected. The sales on these days are: 2, 4, 5, 2, 7. What is the mean for this set of data? E BCalc A. B. C. D. A A sales manager has sampled past sales records to determine how many televisions are sold each day. Daily records for a sample of 5 days have been selected. The sales on these days are: 2, 4, 5, 2, 7. What is the mode for this set of data? 74. 2 4 5 4.5 E BCalc A. B. C. D. A In its Industry Norms and Key Business Ratios, Dun & Bradstreet reported that Q1, Q2, and Q3 for 577 motorcycle dealers' current ratios were 1.3, 1.6 and 2.9, respectively. From this we can conclude that __________________. 75. E BApp A. B. C. D. 2 4 5 4.5 50% of these dealers had current ratios of 1.6 or less 68% of these dealers had current ratios of 1.3 or less 50% of these dealers had current ratios of 2.9 or more 95% of these dealers had current ratios of 1.3 or more Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics C 76. 87 A sales manager has sampled past sales records to determine how many televisions are sold each day. Daily records for a sample of 5 days have been selected. The sales on these days are: 2, 4, 5, 2, 7. What is the standard deviation for this set of sample data? M BCalc A. B. C. D. B A sales manager has sampled past sales records to determine how many televisions are sold each day. Daily records for a sample of 5 days have been selected. The sales on these days are: 2, 4, 5, 2, 7. What is the variance for this set of sample data? 77. 2 0 2.12 4.5 M BCalc A. B. C. D. B A sales manager has sampled past sales records to determine how many televisions are sold each day. Daily records for a sample of 5 days have been selected. The sales on these days are: 2, 4, 5, 2, 7. What is the median for this set of data? 78. 4 4.5 2 0 E BCalc A. B. C. D. C A sales manager has sampled past sales records to determine how many televisions are sold each day. Daily records for a sample of 5 days have been selected. The sales on these days are: 2, 4, 5, 2, 7. What is the mean absolute deviation for this set of data? 79. M BCalc A. B. C. D. 2 4 5 4.5 0 2 1.6 4 Test Bank 88 D 80. M App C Consider the following 3 numbers: 10, 20, 30. In calculating measures of central tendency and variability for this set of data, which of the following is true? A. you can calculate the mean only if you know if this is a sample or a population B. you can calculate the median only if you know if this is a sample or a population C. you can calculate the mode only if you know if this is a sample or a population D. you can calculate the variance only if you know if this is a sample or a population 81. Liz Chapa manages a portfolio of 250 common stocks. Her staff compiled the following performance statistics for two new stocks. Rate of Return Stock Mean Standard Deviation Salas Products, Inc. 15% 5% Hot Boards, Inc. 20% 5% The coefficient of variation for Salas Products, Inc. is __________. E BCalc A. B. C. D. B The following box and whisker plot was constructed for the age of accounts receivable. 82. 300% 100% 33% 5% The box and whisker plot reveals that the accounts receivable ages are _______. E BApp A. B. C. D. skewed to the left skewed to the right not skewed normally distributed Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics A 83. 89 The following box and whisker plot was constructed for the age of accounts receivable. The box and whisker plot reveals that the accounts receivable ages are _______. E BApp A. B. C. D. A The following frequency distribution was constructed for the age of accounts receivable. 84. skewed to the left skewed to the right not skewed normally distributed The frequency distribution reveals that the accounts receivable ages are _______. E BApp A. B. C. D. B The following frequency distribution was constructed for the age of accounts receivable. 85. skewed to the left skewed to the right not skewed normally distributed The frequency distribution reveals that the accounts receivable ages are _______. E BApp A. B. C. D. skewed to the left skewed to the right not skewed normally distributed Test Bank 90 B 86. Liz Chapa manages a portfolio of 250 common stocks. Her staff compiled the following performance statistics for two new stocks. Rate of Return Stock Mean Standard Deviation Salas Products, Inc. 15% 5% Hot Boards, Inc. 20% 5% The coefficient of variation for Salas Products, Inc. is __________. M BCalc A. B. C. D. D David Desreumaux, VP of Human Resources of American First Banks (AFB), is reviewing the employee training programs of AFB banks. His staff compiled the following table of regional statistics on teller training hours. Southeast Region Southwest Region Mean 20 28 Median 20 20 Mode 20 21 Standard Deviation 5 7 What can David conclude from these statistics? 87. M BApp A. B. C. D. equal to the coefficient of variation for Hot Boards greater than the coefficient of variation for Hot Boards less than the coefficient of variation for Hot Boards 25% the Southeast distribution is skewed to the left the Southeast distribution is skewed to the right the Southwest distribution is skewed to the left the Southwest distribution is skewed to the right Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics A 88. 91 David Desreumaux, VP of Human Resources of American First Banks (AFB), is reviewing the employee training programs of AFB banks. His staff compiled the following table of regional statistics on teller training hours. Southeast Region Southwest Region Mean 20 28 Median 20 20 Mode 20 21 Standard Deviation 5 7 What can David conclude from these statistics? M BApp A. B. C. D. D David Desreumaux, VP of Human Resources of American First Banks (AFB), is reviewing the employee training programs of AFB banks. His staff compiled the following table of regional statistics on teller training hours. Southeast Region Southwest Region Mean 20 28 Median 20 20 Mode 20 21 Standard Deviation 5 7 What can David conclude from these statistics? 89. M BApp A. B. C. D. the Southwest distribution has the greater dispersion the Southwest distribution is skewed to the left the Southeast distribution has the greater dispersion the Southeast distribution is skewed to the left the Southwest distribution has the greater relative dispersion the Southwest distribution is skewed to the left the Southeast distribution has the greater relative dispersion the Southeast distribution is not skewed Test Bank 92 D 90. Manuel Banales, Marketing Director of Plano Power Plants, Inc.’s Electrical Division, is leading a study to assess the relative importance of product features. Two items on a survey questionnaire distributed to 100 of Plano’s customers asked them to rate the importance of “ease of maintenance” and “efficiency of operation” on a scale of 1 to 10 (with 1 meaning “not important” and 10 meaning “highly important”). His staff assembled the following statistics on these two items. Ease of Maintenance Efficiency of Operation Mean 7.5 6.0 Median 8.5 5.5 Mode 9.0 4.5 Standard Deviation 1.5 2.5 What can Manuel conclude from these statistics? M BApp A. B. C. D. B Manuel Banales, Marketing Director of Plano Power Plants, Inc.’s Electrical Division, is leading a study to assess the relative importance of product features. Two items on a survey questionnaire distributed to 100 of Plano’s customers asked them to rate the importance of “ease of maintenance” and “efficiency of operation” on a scale of 1 to 10 (with 1 meaning “not important” and 10 meaning “highly important”). His staff assembled the following statistics on these two items. Ease of Maintenance Efficiency of Operation Mean 7.5 6.0 Median 8.5 5.5 Mode 9.0 4.5 Standard Deviation 1.5 2.5 What can Manuel conclude from these statistics? 91. M BApp A. B. C. D. the Ease of Maintenance distribution is skewed to the right the Ease of Maintenance distribution is not skewed the Efficiency of Operation distribution is skewed to the left the Efficiency of Operation distribution is positively skewed the Ease of Maintenance distribution has more relative dispersion the Ease of Maintenance distribution has less dispersion the Efficiency of Operation distribution is skewed to the left the Efficiency of Operation distribution has less dispersion Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics A 92. 93 Manuel Banales, Marketing Director of Plano Power Plants, Inc.’s Electrical Division, is leading a study to assess the relative importance of product features. Two items on a survey questionnaire distributed to 100 of Plano’s customers asked them to rate the importance of “ease of maintenance” and “efficiency of operation” on a scale of 1 to 10 (with 1 meaning “not important” and 10 meaning “highly important”). His staff assembled the following statistics on these two items. Ease of Maintenance Efficiency of Operation Mean 7.5 6.0 Median 8.5 5.5 Mode 9.0 4.5 Standard Deviation 1.5 2.5 What can Manuel conclude from these statistics? M BApp A. B. C. D. B In its Industry Norms and Key Business Ratios, Dun & Bradstreet reported that Q1, Q2, and Q3 for 2,037 gasoline service stations' sales to inventory ratios were 20.8, 33.4, and 53.8, respectively. From this we can conclude that ____________. 93. E BApp A 94. H BCalc Ease of Maintenance is more important than Efficiency of Operation Efficiency of Operation is more important than Ease of Maintenance Efficiency of Operation and Ease of Maintenance are equally important the Efficiency of Operation distribution has less dispersion A. 68% of these service stations had sales to inventory ratios of 20.8 or less B. 50% of these service stations had sales to inventory ratios of 33.4 or less C. 50% of these service stations had sales to inventory ratios of 53.8 or more D. 95% of these service stations had sales to inventory ratios of 20.8 or more Albert Abbasi, VP of Operations at Ingleside International Bank, is evaluating the service level provided to walk-in customers. Accordingly, his staff prepared the following distribution of waiting time for walk-in customers. Waiting Time Number of Customers (in minutes) 0-under 2 60 2-under 4 30 4-under 6 10 The mean waiting time for this sample of walk-in customers is _________. A. B. C. D. 2 minutes 66.67 minutes 33.33 minutes 3 minutes Test Bank 94 B 95. Albert Abbasi, VP of Operations at Ingleside International Bank, is evaluating the service level provided to walk-in customers. Accordingly, his staff prepared the following distribution of waiting time for walk-in customers. Waiting Time Number of Customers (in minutes) 0-under 2 60 2-under 4 30 4-under 6 10 The standard deviation of waiting time for this sample of walk-in customers is ______. H BCalc A. B. C. D. C David Desreumaux, VP of Human Resources of American First Banks (AFB), is reviewing the employee training programs of AFB banks. His staff reports several statistics for teller training hours. The mean is 20 hours, the standard deviation is 5 hours, the median is 15 hours, and mode is 10 hours. The Pearsonian coefficient of skewness for teller training hours is __________. 96. 2 minutes 1.35 minutes 1.82 minutes 1.80 minutes M BCalc A. B. C. D. C The following box and whisker plot was constructed for the age of accounts receivable. 97. 6 1 3 4 The box and whisker plot reveals that the accounts receivable ages are _______. E BApp A. B. C. D. skewed to the left skewed to the right not skewed normally distributed Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics C 98. 95 The following frequency distribution was constructed for the age of accounts receivable. The frequency distribution reveals that the accounts receivable ages are _______. E BApp A. B. C. D. A Which Excel function returns the second quartile? 99. skewed to the left skewed to the right not skewed positively skewed E Term A. B. C. D. median() mode() max() quart2() B 100. Which Excel function returns the population standard deviation? M Term A. B. C. D. C 101. Which Excel function returns the sample standard deviation? M Term A. B. C. D. D 102. Which Excel function returns the arithmetic mean? M Term A. B. C. D. pstdev() stdevp() stdev() stdevpop() sstdev() stdevs() stdev() stdevsample() amean() meana() mean() average() 96 Test Bank 103. Albert Abbasi, VP of Operations at Ingleside International Bank (IIB), is evaluating the service level provided to walk-in customers. Accordingly, his staff prepared the following distribution of waiting time for walk-in customers. Waiting Time Number of Customers (in minutes) 0-under 2 120 2-under 4 40 4-under 6 25 6-under 8 10 8-under 10 5 In a recent survey, 70% of the walk-in customers indicated that waiting four minutes (or more) was unacceptable. Presently, IIB has no direct competitors, but a competing bank is under construction across the street. Discuss the managerial and business implications of this situation. What alternatives should Albert consider? What graphic depiction should he choose for his presentation to the bank’s board of directors? M BApp _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics 104. 97 Angelina Arnott, Director of National Industrial Sales, is concerned by a deteriorating sales trend. Specifically, the number of customers is stable at 1,500, but they are purchasing less each year. She orders her staff to search for causes of the downward trend by surveying all 1,500 industrial customers. One question on the survey asked the customers to rate “Merchandise is delivered on time” on a scale of 1 to 5, with 1 meaning “never” and 5 meaning “always”. Merchandise Delivered On Time Number of Customers 1 100 2 200 3 300 4 700 5 100 No Response 100 Discuss the managerial and business implications of Angelina’s situation. Identify some possible causes of the trend. What corrective actions are available for each cause? What graphic depiction(s) should she choose for her report to the VP of Marketing? M BApp _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 98 Test Bank 105. Annualized rates of return were calculated from closing prices of Caterpillar (CAT) and General Mills (GIS) common stock. Descriptive statistics of these rates of return presented in the following table. CAT GIS Mean 0.233621705 0.139744793 Standard Error 0.162775427 0.097267227 Median 0.194367839 0.122108626 Mode #N/A 0 Standard Deviation 1.091930758 0.652488394 Sample Variance 1.19231278 0.425741105 Kurtosis 6.478114897 -0.59713571 Skewness 1.647492156 0.058132445 Range 6.669350226 2.710777183 Minimum -1.770866463 -1.256246317 Maximum 4.898483762 1.454530866 Sum 10.51297674 6.288515695 Count 45 45 Describe what these descriptive statistics reveal about the market performance of these two stocks. M BApp Chapter 3: Descriptive Statistics 106. Descriptive statistics of daily sales ($'s) were calculated for two Bob's Quick Shops -- the Southside store, and the Midcity store. Southside Mean 5025.622 Standard Error 118.306 Median 5110.73 Mode #N/A Standard Deviation 916.394 Sample Variance 839778 Kurtosis -0.64387 Skewness -0.05517 Range 3949.172 Minimum 3133.362 Maximum 7082.534 Sum 301537.3 Count 60 Midcity 2733.333 249.1417 2000 1000 1929.843 3724294 -0.49322 0.860968 6000 1000 7000 164000 60 Describe what these descriptivie statistics indicate about daily sales at these two stores. M BApp 99 100 Test Bank