Standard Operating Procedures - Environmental Health & Safety
advertisement

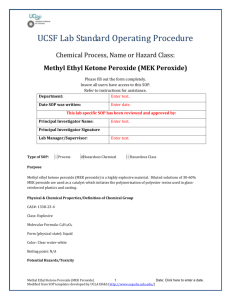
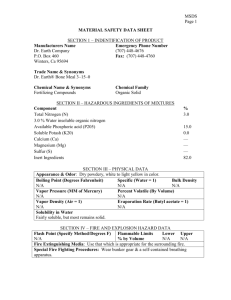
Standard Operating Procedures Laboratory Specific Chemical: MEK peroxide Please fill out the form completely. Print a copy and insert into your Laboratory Safety Manual and Chemical Hygiene Plan. Refer to instructions for assistance. _____________________________________________________________________________ Department:________________________ Date when SOP was written:_______ Date when SOP was approved by the lab supervisor: ___________________ Principal Investigator:___________________________________________________ Internal Laboratory Safety Coordinator/Lab Manager:___________________________________ Laboratory Phone:____________________ Office Phone:_____________________ Emergency Contact:____________________________________________________ (Name and Phone Number) Location(s) covered by this SOP:__________________________________________ (Building/Room Number) _____________________________________________________________________________ Type of SOP: Process Hazardous Chemical Hazardous Class Purpose Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEK peroxide) is an organic peroxide, a high explosive material similar to acetone peroxide. MEK peroxide is a colorless, oily liquid whereas acetone peroxide is a white powder. MEK peroxide is slightly less sensitive to shock and temperature, and more stable in storage. Dilute solutions of 30 to 60% MEK peroxide are used in industry and by hobbyists as the catalyst which initiates the polymerization of polyester resins used in glass-reinforced plastic, and casting. For this application, MEK peroxide is dissolved in dimethyl phthalate, cyclohexane peroxide, or diallyl phthalate to reduce sensitivity to shock. Benzoyl peroxide can be used for the same purpose. MEK peroxide is a severe skin irritant and can cause progressive corrosive damage or blindness. MEK peroxide and acetone peroxide have been reported to be the explosives used in the alleged 2006 transatlantic aircraft plot. 1 Physical & Chemical Properties/Definition of Chemical Group CAS#: 1338-23-4 Class: Explosive Molecular formula: C8H16O4 Boiling Point: Not available Melting Point: 110 deg C (explosive decomposition) Decomposition Temperature: 110 deg C (explodes) Potential Hazards/Toxicity EMERGENCY OVERVIEW: Extremely destructive to tissue of the mucous membranes, upper respiratory tract, eyes, and skin. MEK peroxide is a strong oxidizing agent. May be ignited by heat, sparks or flame and undergoes self-accelerating decomposition. Explosive decomposition occurs at 230° F or 110° C. Sensitive to sunlight. Ignition and/or explosion may occur if mixed with readily oxidizable materials. Reacts with combustible materials such as wood, cloth or organic materials, with chlorine, and with metals (iron, copper and their alloys and aluminum and its alloys). Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents, natural rubbers, synthetic rubbers and chemical accelerators. Incompatible with heavy metals, acids and bases. Target Organs: Mucous membranes, upper respiratory tract, eyes, and skin 2 Potential Health Effects: Eye: May cause blindness. Skin: May cause skin irritation. If absorbed, causes symptoms similar to those of ingestion. May cause sensitization by skin contact. Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. May cause liver and kidney damage. May cause headache. May cause tremors and convulsions. May cause unconsciousness. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. May cause burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis, shortness of breath, headache, nausea, and vomiting Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Eyes: Wear appropriate protective eyeglasses or chemical safety goggles as described by OSHA's eye and face protection regulations in 29 CFR 1910.133 Skin: Viton gloves must be worn while handling MEK peroxide Clothing: Wear long pants, closed toed shoes and a lab coat Respirators: Follow the OSHA respirator regulations found in 29 CFR 1910.134. Always use a NIOSH approved respirator when necessary. Engineering Controls: Use process enclosure, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to control airborne levels below recommended exposure limits. First Aid Procedures Eyes: First check the victim for contact lenses and remove if present. Flush victim's eyes with water or normal saline solution for 20 to 30 minutes while simultaneously calling a hospital or poison control center. Do not put any ointments, oils, or medication in the victim's eyes without specific instructions from a physician. Immediately transport the victim after flushing eyes to a hospital even if no symptoms (such as redness or irritation) develop. Skin: Immediately flood affected skin with water while removing and isolating all contaminated clothing. Gently wash all affected skin areas thoroughly with soap and water. If symptoms such as redness or irritation develop, immediately call a physician and be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital for treatment. Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting. Corrosive chemicals will destroy the membranes of the mouth, throat, and esophagus and, in addition, have a high risk of being aspirated into the victim's lungs during vomiting which increases the medical problems. If the victim is conscious and not convulsing, give 1 or 2 glasses of water to dilute the chemical and immediately call a hospital or poison control center. Immediately transport the victim to a hospital. If the victim is convulsing or unconscious, do not give anything by mouth, ensure that the victim's airway is open and lay the victim on his/her side with the head lower than the body. Do not induce vomiting. Transport the victim immediately to a hospital. 3 Inhalation: Immediately leave the contaminated area; take deep breaths of fresh air. Immediately call a physician and be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital even if no symptoms (such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or burning in the mouth, throat, or chest) develop. Provide proper respiratory protection to rescuers entering an unknown atmosphere. Whenever possible, Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA) should be used; if not available, use a level of protection greater than or equal to that advised under Protective Clothing. Special Handling and Storage Requirements Handling: Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. Avoid shock and friction. Keep away from sources of ignition - No smoking. Storage: Store in a tightly closed container. Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible substances, heat, sparks, flames or other ignition sources. 4 Spill and Accident Procedure Chemical Spill Dial 911 and x59797 Spill – Ventilate area of spill. Eliminate all sources of ignition. Remove all non-essential personnel from area. Clean-up personnel should wear proper protective equipment and clothing. Absorb material with suitable absorbent and containerize for disposal. Small (<1 L) – If you have training, you may assist in the clean-up effort. Use appropriate personal protective equipment and clean-up material for chemical spilled. Double bag spill waste in clear plastic bags, label and take to the next chemical waste pick-up. Large (>1 L) – Dial 911 (or 310-825-1491 from cell phone) and EH&S at x59797 for assistance. Chemical Spill on Body or Clothes – Remove clothing and rinse body thoroughly in emergency shower for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention. Notify supervisor and EH&S at x59797 immediately. Chemical Splash Into Eyes – Immediately rinse eyeball and inner surface of eyelid with water for 15 minutes by forcibly holding the eye open. Seek medical attention. Notify supervisor and EH&S at x59797 immediately. Medical Emergency Dial 911 or x52111 Life Threatening Emergency, After Hours, Weekends And Holidays – Dial 911 (or 310-825-1491 from cell phone) or contact the Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center (emergency room) directly at x52111 (located at 757 Westwood Plaza, enter from Gayley Avenue). Note: All serious injuries must be reported to EH&S at x59797 within 8 hours. Non-Life Threatening Emergency– Go to the Occupational Health Facility (OHF), x56771, CHS room 67-120 (This is on the 6th floor, 7th corridor, room 120. Enter through the School of Dentistry on Tiverton Drive and proceed to the “O” elevator to the 6th floor.)Hours: M F, 7:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. At all other times report to Ronald Regan UCLA Medical Center (emergency room) at x52111. Note: All serious injuries must be reported to EH&S at x59797 within 8 hours. Needle stick/puncture exposure (as applicable to chemical handling procedure)– Wash the affected area with antiseptic soap and warm water for 15 minutes. For mucous membrane exposure, flush the affected area for 15 minutes using an eyewash station. Page the needle stick nurse by dialing 231 from a campus phone, enter 93333 when prompted and then enter your extension. Hours: M – F, 8:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. At all other times report to Ronald Regan UCLA Medical Center (emergency room) at x52111. Note: All needle stick/puncture exposures must be reported to EH&S at x59797 within 8 hours. 5 Decontamination/Waste Disposal Procedure Waste disposal procedures General hazardous waste disposing guidelines: Labeling Requirements for Hazardous Waste Containers: • A UCLA Hazardous Waste Tag must be placed on each hazardous waste container upon start of accumulation. • The On-Line Tag Program (OTP) can be used to print hazardous waste tags right from your printer. • One account on the On-Line Tag Program (OTP) can be used for the entire lab. See the OnLine Tag Program1 more information and to get your lab signed up. Hazardous Waste Storage: • Hazardous waste must be transferred to EH&S for disposal within 90 days of being generated. • Waste containers must be in secondary containment at all times to adequately contain the contents of the container/spilled materials. • Hazardous waste must always be appropriately labeled with a UCLA waste tag at all times. • Containers must be closed when not in use. • Storage of hazardous waste in fume hoods or under sinks is not recommended. • Hazardous waste that meets the quantity threshold of 55 gallons of hazardous waste or 1 quart of extremely hazardous waste1 must be transferred to EH&S for disposal within 3 days of reaching these set volumes. • Report damaged containers to EH&S. EH&S can provide assistance to transfer the contents to an appropriate container. • Mark storage areas according to the type of chemicals kept there (e.g. “Corrosive”, “Flammable”, etc.). • Containers should be inspected weekly for signs of leaks, corrosion, or deterioration. Hazardous Waste Disposal: • Don't dispose of chemicals down the drain! • Don't dispose of chemicals via trashcans. • Don't use hoods to intentionally evaporate chemicals. • Transport the hazardous waste to your designated pick-up location using a sturdy cart and secondary containment. • Consult the hazardous waste pick-up schedule1 for the building specific times and locations of disposal. Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) Location (State the location of MSDS) Hardcopy or electronic copy must be available. Online MSDS can be accessed at http://msds.ehs.ucla.edu. Protocol/Procedure (Add specific description of procedure.) Note: Any deviation from this SOP requires written approval from PI. 6 Documentation of Training (signature of all users is required) I have read and understand the content of this SOP: Name Signature 7 Date