Nasal trauma Skeletal injury of the head and neck are not unusual
advertisement

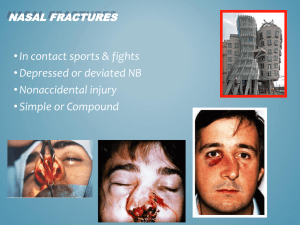
Nasal trauma Skeletal injury of the head and neck are not unusual and may arise from ►personal insult :blow to the nose from the side or infront ►►personal accident ►►►sport injury ►►►►RTA Aetiology Pathogenesis ◙ no fracture Just oedema and bleeding.this occur in low velocity trauma but could lead to septal deviation due to displacement of maxillary crest ◙ Class 1 fracture Usually due to frontal or fronto-lateral blow result in vertical fracture of the septum-chevallet fracture- with depressed or distal portion of the nasal bone ◙ Class II fracture It is nearly always due to lateral trauma,result in horizontal fracture of the septum-Jarjavay fracture- or C shape fracture of the septum involving the perpendicular plate of ethmoid and septal cartilage with fracture of upper nose or frontal process of maxilla,here the velocity is more than class I ◙ Class III fracture The force is foreward ,the velocity is very high like RTA and here all facial bones could be involved even ethmoid labrynth,cribriform plate of ethmoid, can lead to CSF rhinorrhea,this fracture produce a pig like nose,i.e elevation of the nostrils and suddeling of nose with widening of nasal bridge so increase space between eyes(telecanthus) All types of fractures could be seen and in addition to soft tissue damage like nasalacrimal duct damage. Management How and when the injury was sustained-- time and mechanism of trauma Other injuries may also be present and may have been overlooked There will be certain degree of nasal obstruction Diplopia,visual disturbance and epiphora suggest orbital trauma Loose teeth and altered bite or trismus indicate the need of dental opinion Watery rhinorrhea ,loss of smellthough uncommon,signall possible skull base damage and need more detailed evaluation Examination may be difficult in the acute situation when swelling may hide an underlying abnormality ,a second inspection afew days later 5-7 days may be necessary Gently palpate the nasal bones for a step deformity ,any surgical emphysema that could suggest a more serious injury. Look if there is any soft tissue laceration. Inspect the nasal cavities and check for the presence of septal haematoma or deviation Then don’t forget to make a thorough general ENT /head &neck examination. Treatment If no fracture or deformity just conservative like manage the epistaxis properly ,analgesia and reassurance If fracture seen early and there is nooedema and swelling so do close reduction under LA or short acting GA disimpaction & realignment can usually be achieved with digital pressure or walsham`s forceps : elevation of fractured bones then packing and P.O.P splint for one week If fracture seen later then will be much swelling ,so manipulation should be delayed for 5-7 days ,manipulation should never be delayed more than 2 weeksbecause the bones should be fixed ,calus formation and reduction should be difficult if not impossible There are two treatment modalities for the broken nose ,the closed reduction method which involves repositioning the dislocated parts of the nasal bone&can be achieved under local or general anaesthesia as mentioned above Or Open reduction in which the the septum is also explored and injuries corrected After 2 weeks reduction is difficult ,so leave until the condition is settled then do septorhinoplasty after 6 months ☻you have to distinguish between recent trauma and old deformity especially in patient with frequent injury likr sportman and frequent fighters Septal haematoma It is due to collection of blood beneath the mucoprechondrium of the nasal septum this collection interfere with the vitality of the cartilage ,the cartilage remain viable for 3 days more than 3 days the chondrocyte die lead to absorption of the cartilage Clinical pictures ruction---complete bilateral nasal obstruction Discomfort Septal swelling soft red in colour Complication Septal abcess Cartilage necrosis Nasal suddle deformity Treatment Simple aspiration ---if haematoma is small Incision and drainage Packing to obliterate dead space with or without quilting suture Systemic AB Septal abcess Mostly due to trauma 75% Infective –measle,scarlet fever,furenculosis,AIDS. Complicate ethmoid and sphenoid sinus infection Complication Spread infection to orbit,meningies,brain,cavernous sinus Clinical pictures Sever pain Septal swelling Nasal obstruction Pyrexia Treatment Immediate drainage Systemic AB Reconstruction of the defect in the acute phase will reduce growth impactionies