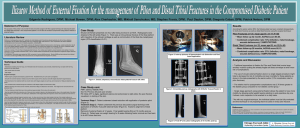
Conclusions: The Ilizarov method produces a good clinical outcome
advertisement

Bilaga ansökan Skaraborgs FoU 2011-10-01 Telmo Ramos ”Om behandling av tibiafrakturer med Ilizarov extern fixation” I Ilizarov external fixation or Intramedullary Nailing for treatment of diaphyseal tibial fractures – a randomized prospective study. Telmo Ramos, Carl Ekholm, Jón Karlsson, Lars Nistor. All datainsamling är klar sommaren 2011 inkl 1 års-uppföljning av samtliga patienter. Analys har påbörjats och under oktober kommer jag att gå igenom detta med statistiker Salmir Nasic. Utkast till artikel avseende Inledning, metod och preliminär diskussion har påbörjats. Vi kommer att välja tidskrift när vi ser resultaten. Eftersom det rör sig om en prospektiv randomiserad undersökning inom frakturkirurgi (där sådana är ovanliga) räknar vi med att få acceptans av någon av de “tunga” internationella tidskrifterna. II The Ilizarov external fixator a useful alternative treatment for proximal tibial fractures. A prospective observational study of 30 patients. Telmo Ramos, Carl Ekholm, Jón Karlsson, Lars Nistor. IN MANUSKRIPT- Archives of Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery hösten 2011 Abstract Introduction The purpose of the treatment of proximal tibial fractures is to obtain a stable, painfree knee joint with a restored range of motion and enough congruence to avoid post-traumatic osteoarthritis. The most frequently used treatment is ORIF with screws and plates. Minimallyinvasive techniques using external fixation are an alternative. The aim of this study was to analyse the results using the Ilizarov technique in both uni- and bicondylar tibia fractures. Methods Thirty consecutive patients with isolated fractures of the proximal tibia were treated with the Ilizarov technique, 11 Schatzker I-IV with 2-3 rings and 19 Schatzker V-VI with 3-4 tibial rings and a femoral hinged two-ring extension. Unrestricted weight bearing was allowed. Post-operatively conventional radiographs, CT scans, postoperative pain assessment and complications were evaluated. The knee function was evaluated with the EQ-5D, NHP and KOOS scores and self-appraisal as well. Results All the fractures healed. Twenty-five patients achieved a range of motion better than 10100º. The type I-IV fractures had a shorter operating time and hospital stay, as well as better knee flexion and the self-appraisal indicated that they tolerated the treatment better. Pin infections ocurred in 4% of the pin sites, however, only two patients needed debridement. Two patients developed compartment syndrome and underwent fasciotomy. Three patients had unstable knees at follow-up. Two patients underwent a total knee arthroplasty because of residual pain. The overall result was satisfactory in twenty-six patients. Conclusions The Ilizarov method produces a good clinical outcome and can be recommended in proximal tibial fractures of all types. III Treatment of distal tibial fractures with the Ilizarov external fixator. Telmo Ramos, Carl Ekholm, Jón Karlsson, Lars Nistor. IN MANUSKRIPT - Archives of Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery hösten 2011 Abstract Background and purpose: The most frequently used treatment for distal tibial fractures is ORIF with screws and plates, which, however, has a relatively high complication rate, why a staged protocol is often recommended. Minimally invasive techniques with external fixation have been introduced as an alternative and allows for immediate reduction and stabilization. The aim of this prospective study was to analyze the outcome using the Ilizarov technique in patients with distal metaphyseal peri- and intra-articular tibia fractures. Patients and methods: Thirty consecutive patients with isolated fractures were followed prospectively for one year. Depending on the type of fracture, 4-5 rings were used, sometimes with a foot extension. Unrestricted weight-bearing was allowed. Post-operatively conventional radiographs, postoperative pain assessment and complications were evaluated. The function was evaluated clinically and using self-appraisal with the EQ-5D, NHP and FAOS. Results: All the fractures healed. No patient developed compartment syndrom or deep venous thrombosis (DVT). The pin infections were mostly superficial and were treated with antibiotics or/and removal of isolated pins. Two patients had pin tract infections treated with debridement of the soft tissues. The fixator was removed after a median period of 16 (range 12-30) weeks. One patient had a pin-tract infection after the removal of the fixator, which required reoperation. Residual malunion was observed, but in most of patients less than 0.5 cm. Two patients had major residual deformities, one painful with deep infection, and were reoperated. The overall result was satisfactory in twenty eight patients. Conclusions: The Ilizarov method produces a good clinical outcome and can be recommended to these difficult-to-treat fractures. IV Postoperative impact of daily life after primary treatment of proximal/distal tibia fracture with the Ilizarov external fixator. Marina Modin, Telmo Ramos, Margareta Warrén Stomberg. J Clin Nurs 2009, 18:3498-3506 Abstract Aims and objectives. To describe patients’ experience of the impact of their health-related life situation on their daily life two and four weeks after primary fracture treatment with Ilizarov external fixation. Background. A few studies have been conducted postoperatively focussing on fracture treatment with Ilizarov fixation. Design. A prospective descriptive research design. Method. Patients who had been treated for a proximal/distal tibial fracture were invited to participate in the study. Data were collected with a semi-structured questionnaire where 20 patients described in their own words their situation at home two and four weeks postoperatively. The process used when analysing the data was similar to content analysis. Results. Four key themes were identified: ‘limitations in the home environment’, ‘limitations outside the home’, ‘limitations to social relations’ and ‘experience of having an Ilizarov fixation’. The patient’s life situation was strongly affected during the first postoperative month. This took the form of clear limitations on activities outside the home and a degree of limitation on coping with household chores and personal hygiene. These limitations became less severe after between 2–4 weeks and were very much a consequence of using crutches. Conclusion. This study points to limitations in the patient’s daily life situation in the home. The results from the study make it obvious that the information given to patients prior to discharge, concerning the value of putting weight on the leg, had not been clear or that the patients had not understood it. This had a negative impact on the patient’s daily life after discharge. Further data are needed to uncover the extent of the issue to be able to optimise patient outcomes. Relevance to clinical practice. There is a need for clearer and more active information from the nurse before discharge but also a need to follow up how the information given is understood. V Gait analysis with insoles in diaphyseal tibial fractures treated with the Ilizarov external fixator or Intramedullary Nailing – a prospective randomized comparison. Telmo Ramos, Katarina Hjältman, Tom Köhler, Lars Nistor (?). Gait Posture 2012 (?) Datainsamlingen är klar. Den fortsatta analysen har diskuterats vid två dagars besök med Tom Köhler, gånganalytiker i Berlin. Vi håller på att med hjälp av honom konstruera en ny parameter – gångeffektivitet - där man väger in gånghastighet, belastning, steglängd, effektiv fotlängd (hur foten avvecklas i steget) och justerar för kroppslängd och vikt. Vi räknar med att sedan kunna presentera jämförelsen mellan de olika behandlingsmetoderna med utgångspunkt från denna parameter och grundparametrar. Dataanalysen har påbörjats och under oktober kommer vi att ha telefonkonferenser för att diskutera utvärderingen. I detta delarbete kommer dels mätmetoden, dels resultaten att diskuteras. VI Gait analysis with insoles in isolated proximal and distal metaphyseal tibial fractures treated with the Ilizarov external fixator. Telmo Ramos, Katarina Hjältman, Tom Köhler, Lars Nistor (?). Gait & Posture 2012 (?) Jfr V. Informationen blir så omfattande att vi inte räknar med att kunna få acceptans om allt läggs in i en artikel vilket vore det bästa men vi får istället diskutera resultaten från denna del i förhållande till föregående artikel.