sFlt-1 expression in trophoblast - eScholarShare
advertisement
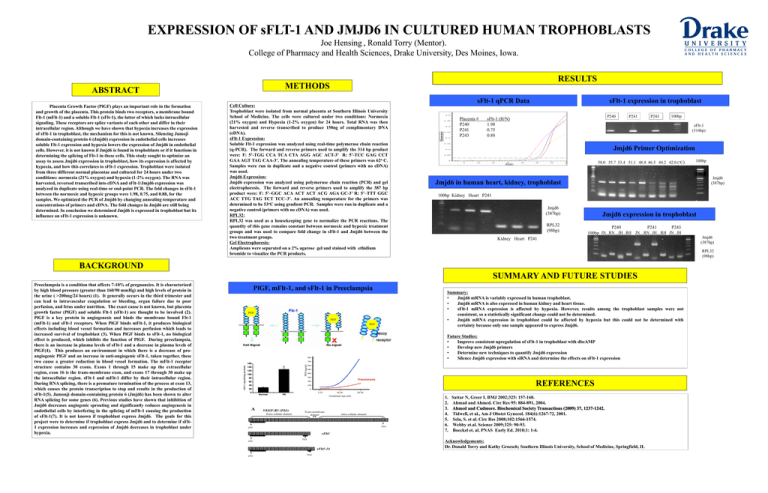
EXPRESSION OF sFLT-1 AND JMJD6 IN CULTURED HUMAN TROPHOBLASTS Joe Hensing , Ronald Torry (Mentor). College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Drake University, Des Moines, Iowa. METHODS ABSTRACT Placenta Growth Factor (PlGF) plays an important role in the formation and growth of the placenta. This protein binds two receptors, a membrane bound Flt-1 (mFlt-1) and a soluble Flt-1 (sFlt-1), the latter of which lacks intracellular signaling. These receptors are splice variants of each other and differ in their intracellular region. Although we have shown that hypoxia increases the expression of sFlt-1 in trophoblast, the mechanism for this is not known. Silencing Jumoji domain-containing protein 6 (Jmjd6) expression in endothelial cells increases soluble Flt-1 expression and hypoxia lowers the expression of Jmjd6 in endothelial cells. However, it is not known if Jmjd6 is found in trophoblasts or if it functions in determining the splicing of Flt-1 in these cells. This study sought to optimize an assay to assess Jmjd6 expression in trophoblast, how its expression is affected by hypoxia, and how this correlates to sFlt-1 expression. Trophoblast were isolated from three different normal placentae and cultured for 24 hours under two conditions: normoxia (21% oxygen) and hypoxia (1-2% oxygen). The RNA was harvested, reversed transcribed into cDNA and sFlt-1/Jmjd6 expression was analyzed in duplicate using real-time or end-point PCR. The fold changes in sFlt-1 between the normoxic and hypoxic groups were 1.98, 0.75, and 0.88, for the samples. We optimized the PCR of Jmjd6 by changing annealing temperature and concentrations of primers and cDNA. The fold changes in Jmjd6 are still being determined. In conclusion we determined Jmjd6 is expressed in trophoblast but its influence on sFlt-1 expression is unknown. RESULTS Cell Culture: Trophoblast were isolated from normal placenta at Southern Illinois University School of Medicine. The cells were cultured under two conditions: Normoxia (21% oxygen) and Hypoxia (1-2% oxygen) for 24 hours. Total RNA was then harvested and reverse transcribed to produce 150ng of complimentary DNA (cDNA). sFlt-1 Expression: Soluble Flt-1 expression was analyzed using real-time polymerase chain reaction (q-PCR). The forward and reverse primers used to amplify the 314 bp product were: F: 5’-TGG CCA TCA CTA AGG AGC ACT-3’ R: 5’-TCC GAG CCT GAA AGT TAG CAA-3’. The annealing temperature of these primers was 62o C. Samples were run in duplicate and a negative control (primers with no cDNA) was used. Jmjd6 Expression: Jmjd6 expression was analyzed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and gel electrophoresis. The forward and reverse primers used to amplify the 387 bp product were: F: 5’–GGC ACA ACT ACT ACG AGA GC-3’ R: 5’–TTT GGC ACC TTG TAG TCT TCC–3’. An annealing temperature for the primers was determined to be 53oC using gradient PCR. Samples were run in duplicate and a negative control (primers with no cDNA) was used. RPL32: RPL32 was used as a housekeeping gene to normalize the PCR reactions. The quantity of this gene remains constant between normoxic and hypoxic treatment groups and was used to compare fold change in sFlt-1 and Jmjd6 between the two treatment groups. Gel Electrophoresis: Amplicons were separated on a 2% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide to visualize the PCR products. sFlt-1 qPCR Data Placenta # P240 P241 P243 sFlt-1 expression in trophoblast P240 sFlt-1 (H/N) 1.98 0.75 0.88 P241 P243 100bp sFlt-1 (314bp) Jmjd6 Primer Optimization 58.0 55.7 53.4 51.1 48.8 46.5 44.2 42.0 (oC) Jmjd6 (387bp) Jmjd6 in human heart, kidney, trophoblast 100bp Kidney Heart P241 Jmjd6 (387bp) RPL32 (98bp) Jmjd6 expression in trophoblast P240 P241 P243 100bp JN RN JH RH JN RN JH RH JN JH Kidney Heart P241 SUMMARY AND FUTURE STUDIES PlGF, mFlt-1, and sFlt-1 in Preeclampsia PlGF PlGF PlGF Jmjd6 (387bp) RPL32 (98bp) BACKGROUND Summary: • Jmjd6 mRNA is variably expressed in human trophoblast. • Jmjd6 mRNA is also expressed in human kidney and heart tissue. • sFlt-1 mRNA expression is affected by hypoxia. However, results among the trophoblast samples were not consistent, so a statistically significant change could not be determined. • Jmjd6 mRNA expression in trophoblast could be affected by hypoxia but this could not be determined with certainty because only one sample appeared to express Jmjd6. Future Studies: • Improve consistent upregulation of sFlt-1 in trophoblast with dbcAMP • Develop new Jmjd6 primers • Determine new techniques to quantify Jmjd6 expression • Silence Jmjd6 expression with siRNA and determine the effects on sFlt-1 expression sFlt-1 (ng/ml/mg protein) Preeclampsia is a condition that affects 7-10% of pregnancies. It is characterized by high blood pressure (greater than 160/90 mmHg) and high levels of protein in the urine ( >200mg/24 hours) (1). It generally occurs in the third trimester and can lead to intravascular coagulation or bleeding, organ failure due to poor perfusion, and fetus under nutrition. The exact cause is not known, but placenta growth factor (PlGF) and soluble Flt-1 (sFlt-1) are thought to be involved (2). PlGF is a key protein in angiogenesis and binds the membrane bound Flt-1 (mFlt-1) and sFlt-1 receptors. When PlGF binds mFlt-1, it produces biological effects including blood vessel formation and increases perfusion which leads to increased survival of trophoblast (3). When PlGF binds to sFlt-1, no biological effect is produced, which inhibits the function of PlGF. During preeclampsia, there is an increase in plasma levels of sFlt-1 and a decrease in plasma levels of PlGF(4). This produces an environment in which there is a decrease of proangiogenic PlGF and an increase in anti-angiogenic sFlt-1, taken together, these two cause a greater reduction in blood vessel formation. The mFlt-1 receptor structure contains 30 exons. Exons 1 through 15 make up the extracellular region, exon 16 is the trans-membrane exon, and exons 17 through 30 make up the intracellular region. sFlt-1 and mFlt-1 differ by their intracellular region. During RNA splicing, there is a premature termination of the process at exon 13, which causes the protein transcription to stop and results in the production of sFlt-1(5). Jumonji domain-containing protein 6 (Jmjd6) has been shown to alter RNA splicing for some genes (6). Previous studies have shown that inhibition of Jmjd6 decreases angiogenic sprouting and significantly reduces angiogenesis in endothelial cells by interfering in the splicing of mFlt-1 causing the production of sFlt-1(7). It is not known if trophoblast express Jmjd6. The goals for this project were to determine if trophoblast express Jmjd6 and to determine if sFlt1 expression increases and expression of Jmjd6 decreases in trophoblast under hypoxia. 100bp REFERENCES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Sattar N, Greer I. BMJ 2002;325: 157-160. Ahmad and Ahmed. Circ Res 95: 884-891, 2004. Ahmed and Cudmore. Biochemical Society Transactions (2009) 37, 1237-1242. Tidwell, et al., Am J Obstet Gynecol. 184(6):1267-72, 2001. Sela, S. et al. Circ Res 2008;102:1566-1574. Webby et.al. Science 2009;325: 90-93. Boeckel et. al. PNAS Early Ed. 2010;1: 1-6. Acknowledgements: Dr. Donald Torry and Kathy Groesch; Southern Illinois University, School of Medicine, Springfield, IL