Johann Holzmann
advertisement
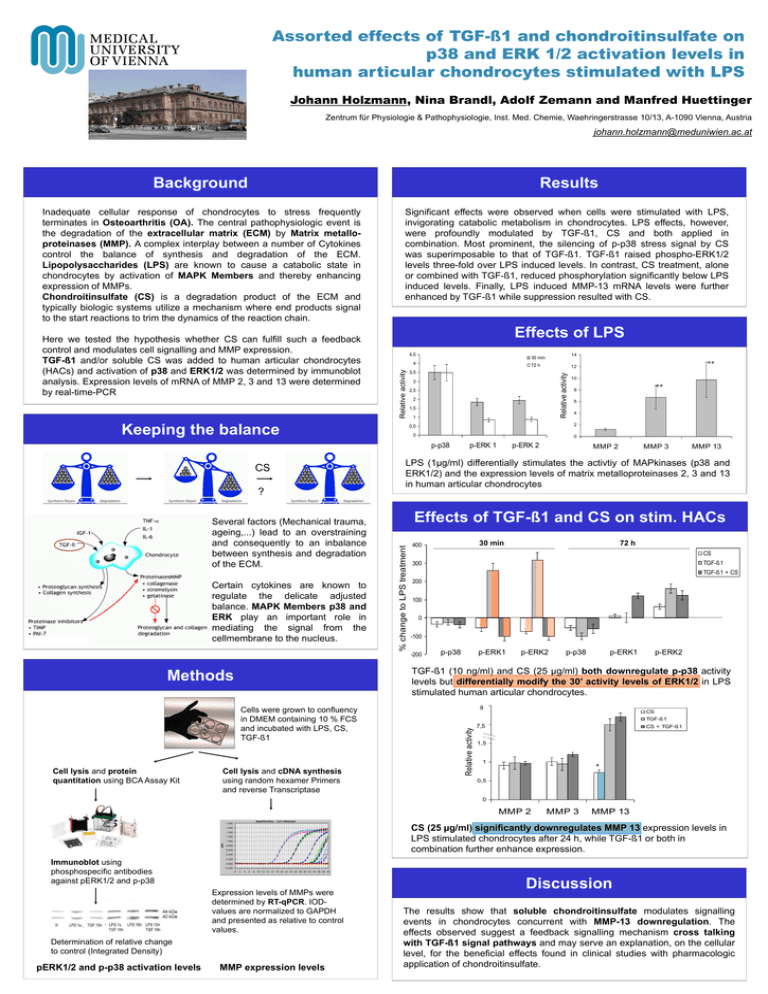
Assorted effects of TGF-ß1 and chondroitinsulfate on p38 and ERK 1/2 activation levels in human articular chondrocytes stimulated with LPS Johann Holzmann, Nina Brandl, Adolf Zemann and Manfred Huettinger Zentrum für Physiologie & Pathophysiologie, Inst. Med. Chemie, Waehringerstrasse 10/13, A-1090 Vienna, Austria johann.holzmann@meduniwien.ac.at Background Results Inadequate cellular response of chondrocytes to stress frequently terminates in Osteoarthritis (OA). The central pathophysiologic event is the degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) by Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP). A complex interplay between a number of Cytokines control the balance of synthesis and degradation of the ECM. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are known to cause a catabolic state in chondrocytes by activation of MAPK Members and thereby enhancing expression of MMPs. Chondroitinsulfate (CS) is a degradation product of the ECM and typically biologic systems utilize a mechanism where end products signal to the start reactions to trim the dynamics of the reaction chain. Significant effects were observed when cells were stimulated with LPS, invigorating catabolic metabolism in chondrocytes. LPS effects, however, were profoundly modulated by TGF-ß1, CS and both applied in combination. Most prominent, the silencing of p-p38 stress signal by CS was superimposable to that of TGF-ß1. TGF-ß1 raised phospho-ERK1/2 levels three-fold over LPS induced levels. In contrast, CS treatment, alone or combined with TGF-ß1, reduced phosphorylation significantly below LPS induced levels. Finally, LPS induced MMP-13 mRNA levels were further enhanced by TGF-ß1 while suppression resulted with CS. 4,5 Keeping the balance 72 h Relative activity 3 2,5 2 1,5 1 Several factors (Mechanical trauma, ageing,...) lead to an overstraining and consequently to an inbalance between synthesis and degradation of the ECM. Certain cytokines are known to regulate the delicate adjusted balance. MAPK Members p38 and ERK play an important role in mediating the signal from the cellmembrane to the nucleus. 6 4 2 0 0 p-ERK 2 MMP 2 MMP 3 MMP 13 Effects of TGF-ß1 and CS on stim. HACs 30 min 400 72 h CS TGF-ß1 300 TGF-ß1 + CS 200 100 0 -100 -200 p-p38 p-ERK1 p-ERK2 p-p38 p-ERK1 p-ERK2 TGF-ß1 (10 ng/ml) and CS (25 µg/ml) both downregulate p-p38 activity levels but differentially modify the 30’ activity levels of ERK1/2 in LPS stimulated human articular chondrocytes. Cells were grown to confluency in DMEM containing 10 % FCS and incubated with LPS, CS, TGF-ß1 Cell lysis and cDNA synthesis using random hexamer Primers and reverse Transcriptase 2,5 8 8 CS TGF-ß1 Relative activity Methods Cell lysis and protein quantitation using BCA Assay Kit ** 8 LPS (1µg/ml) differentially stimulates the activtiy of MAPkinases (p38 and ERK1/2) and the expression levels of matrix metalloproteinases 2, 3 and 13 in human articular chondrocytes % change to LPS treatment ? 10 0,5 p-ERK 1 ** 12 3,5 p-p38 CS 14 30 min 4 Relative activity Here we tested the hypothesis whether CS can fulfill such a feedback control and modulates cell signalling and MMP expression. TGF-ß1 and/or soluble CS was added to human articular chondrocytes (HACs) and activation of p38 and ERK1/2 was determined by immunoblot analysis. Expression levels of mRNA of MMP 2, 3 and 13 were determined by real-time-PCR Effects of LPS 7,52 CS + TGF-ß1 1,5 1 * 0,5 0 MMP 2 MMP 3 MMP 13 CS (25 µg/ml) significantly downregulates MMP 13 expression levels in LPS stimulated chondrocytes after 24 h, while TGF-ß1 or both in combination further enhance expression. Immunoblot using phosphospecific antibodies against pERK1/2 and p-p38 Expression levels of MMPs were determined by RT-qPCR. IODvalues are normalized to GAPDH and presented as relative to control values. Determination of relative change to control (Integrated Density) pERK1/2 and p-p38 activation levels MMP expression levels Discussion The results show that soluble chondroitinsulfate modulates signalling events in chondrocytes concurrent with MMP-13 downregulation. The effects observed suggest a feedback signalling mechanism cross talking with TGF-ß1 signal pathways and may serve an explanation, on the cellular level, for the beneficial effects found in clinical studies with pharmacologic application of chondroitinsulfate.











