Chapter 10 - Continents
advertisement

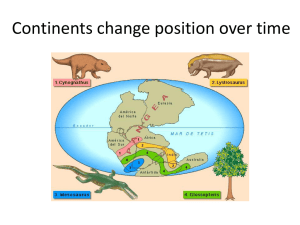
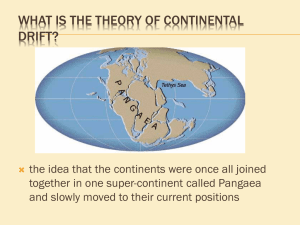
Grotzinger • Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 10: HISTORY OF THE CONTINENTS © 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 10: History of the Continents About Evolution of the Continents • Nearly two-thirds of the Earth’s surface – all of the oceanic crust – was formed over the past 200 million years. • However, rocks of the continents are much older, as old as 4 billion years. • Studying the continents tells us how the continental lithosphere formed and evolved. Lecture Outline 1. The structure of North America 2. Tectonic provinces around the world 3. How continents grow 4. How continents are modified 5. The origin of cratons 6. The deep structure of the continents 1. The Tectonics of North America ● The stable interior ● Canadian shield ● interior platform ● basins and uplifts 1. The Tectonics of North America ● The Appalachian fold belt ● Valley and ridge province ● Blue ridge province ● Piedmont ● Coastal Plain 1. The Tectonics of North America ● The North American cordillera ● uplift and orogeny ● rejuvenation ● crustal stretching 2. Tectonic Provinces around the World ● Types of tectonic provinces ● shield ● platform ● continental basin ● orogen ● extended crust 2. Tectonic Provinces around the World ● Ages of tectonic provinces ● Archean ● Early Proterozoic ● Middle Proterozoic ● Late Proterozoic ● Paleozoic ● Mesozoic and Cenozoic Thought questions for this chapter Figure 10.8b shows more continental crust of MesozoicCenozoic tectonic age than continental crust of any geologic period. Does this contradict the hypothesis that most of the continental crust was differentiated from the mantle in the first half of Earth’s history? 3. How Continents Grow ● Modes of growth ● Magmatic addition ● Continental accretion ● accreted terrains ● exotic terrains Terrain accretion Terrain accretion Aleutian Trench Wrangellia Subduction margin (convergent boundary) Cascadia Trench NORTH AMERICA San Andreas Fault Spreading center (divergent boundary) Transform fault Island arc Submarine deposits Ancient ocean floor Displaced continental fragments Wrangellia was transported from 5000 km away … to the Southern Hemisphere! Much of western North America is made up of exotic terranes accreted over the past 200 million years. Aleutian Trench Wrangellia Subduction margin (convergent boundary) Cascadia Trench NORTH AMERICA San Andreas Fault Spreading center (divergent boundary) Transform fault Island arc Submarine deposits Ancient ocean floor Displaced continental fragments Thought questions for this chapter How would you recognize an accreted terrane? How could you tell if it originated far away or nearby? 4. How Continents are Modified ● Modification by plate collision ● Alpine-Himalayan orogeny ● Assembly of Pangaea ● The Wilson Cycle Alpine-Himalayan Orogeny Alpine-Himalayan Orogeny Alpine-Himalayan Orogeny Alpine-Himalayan Orogeny Alpine-Himalayan Orogeny Wilson Cycle Geologic Time Scale of Events in the History of Earth’s Continents 4. How Continents are Modified ● Modification by epeirogeny ● cooling and heating of lithosphere ● weight of accumulating sediments or glacial ice Thought questions for this chapter How would you recognize an accreted terrane? How could you tell if it originated far away or nearby? How would you identify a region where active orogeny is taking place today? Give an example. Would you prefer to live on a planet with orogenies or without them? Why? 5. Origin of Cratons ● Archean cratons ● granite-greenstone terrains ● high-grade metamorphic terrains Thought questions for this chapter Why are the ocean basins just about the right size to contain all the water on Earth’s surface? 6. Deep Structure of the Continents ● Structure of the craton ● continental crust ● cratonic keel Thought questions for this chapter What would happen at the surface if the cold keel beneath a craton suddenly heated up? How might this effect be related to the formation of the Colorado Plateau? Key terms and concepts Accreted terrane Accretion Active margin Craton Cratonic keel Epeirogeny Glacial rebound Magmatic addition Orogen Orogeny Passive margin Rejuvenation Shield Tectonic age Key terms and concepts Tectonic province Wilson cycle