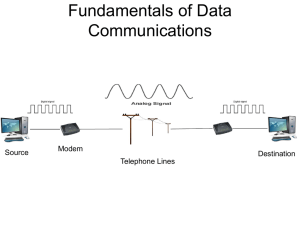
Modems and Other Communications Devices
advertisement

Modems and Other Communications Devices Guide to Operating Systems Third Edition Objectives After reading this chapter and completing the exercises you will be able to: • Explain analog modem architecture • Use the classic Hayes AT modem command set with computer communications applications • Describe digital modem architecture for highspeed communications through IDSN, cable, DSL, and satellites Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 2 Objectives (continued) After reading this chapter and completing the exercises you will be able to: • Explain the basics of telephone-line data communications • Configure modem and internet communications in different operating systems Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 3 Analog Modem Architecture • Modem – hardware and software that connects two incompatible systems • Plain old telephone service (POTS) lines – old term • Public switched telephone network (PSTN) lines - modern term Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 4 Analog Modem Hardware Basics • Components: – data pump, controller, and UART • Data pump – component that performs modulation/demodulation Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 5 Analog Modem Hardware Basics (continued) • Controller – provides the modem’s identity – interprets Attention (AT) commands • Protocol – specifies how networked data is formatted – how it is transmitted – how it is interpreted at the receiving end Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 6 Analog Modem Hardware Basics (continued) • International Telecommunications Union (ITU) – establishes modem protocol standards – compose the ITU-T standards • Latest standards define a 56 Kbps to 64 Kbps protocol Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 7 Analog Modem Hardware Basics (continued) • Data terminal equipment (DTE) – data transfer rate Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 8 Analog Modem Hardware Basics (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 9 Analog Modem Hardware Basics (continued) • Modem is called the data communications equipment (DCE) • Speed is the DCE communications rate • UART – electronic chip – the Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter – converts data from the computer Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 10 Analog Modem Hardware Basics (continued) • Asynchronous communication – most common method for today’s desktop computers – uses fairly accurate clocks (timers) at both ends of the connection to synchronize data • Synchronous communication – sends information in blocks (frames) of data that include embedded clock signals Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 11 Software-Based Modems • Winmodems – software-based modems – controllerless modem that retains a hardware data pump (Digital Signal Processor (DSP) – implements the controller functions in software Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 12 Software-Based Modems (continued) • Host Signal Processor (HSP) modems – dispense with the controller and data pump hardware entirely Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 13 Software-Based Modems (continued) • Disadvantage – software takes up memory and processor cycles • Advantage – their dependence on particular operating systems – cost savings and upgradeability Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 14 Hayes AT Command Set for Analog Modems • Hayes command or Attention (AT) commands – created by Dennis Hayes – begin with the letters AT – tells the modem to interpret the next character string as a command Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 15 Hayes AT Command Set for Analog Modems (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 16 Hayes AT Command Set for Analog Modems (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 17 Digital Modems • Digital modems – digital devices that use digital transmission media – network or serial devices – connect via Point-to-Point (PPP) • Telecommunications networks: – ISDN – Cable networks – DSL – Satellite Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 18 ISDN • Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) – uses standard copper telephone line pair – digital equipment on either end of the connection – ISDN router to route the transmission to the right place – terminal adapter (TA), a type of digital modem Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 19 ISDN (continued) • Basic rate interface (BRI) – aggregate data rate of 144 Kbps – three channels • Primary rate interface (PRI) – supports faster data rates – aggregate bandwidth equal to 1.544 Mbps Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 20 ISDN (continued) • PRI – used for LAN-to-LAN connectivity – ISP sites – videoconferencing – corporate sites that support telecommuters Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 21 Cable Modems • Cable modem – used to attach to cable data services – external device – plugs into a USB port or network interface card – connected to the coaxial cable used for the cable TV system Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 22 Cable Modems (continued) • Data Over Cable Service interface Specifications (DOCSIS) – DOCSIS 1.0 – DOCSIS 1.1 – DOCSIS 2.0 Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 23 DSL Modems • Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) – high-speed digital data communications service – challenging ISDN and cable modems – digital technology that works over copper wire – must install an intelligent adapter in your computer Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 24 DSL Modems (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 25 DSL Modems (continued) • Dedicated to a single user • Employs the full bandwidth • Connected by means of a combined DSL adapter and router • Router – device that can be used to direct network traffic and create a firewall Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 26 DSL Modems (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 27 DSL Modems (continued) • DSL services: – Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) – G.lite Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (G.lite ADSL) – Integrated Services Digital Network Digital Subscriber Line (IDSL) – Rate Adaptive Digital Subscriber Line (RADSL) – High Bit-Rate Digital Subscriber Line (HDSL) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 28 DSL Modems (continued) • DSL services (continued): – Symmetric high Bit-Rate Digital Subscriber Line (SHDSL) – Very High Bit-Rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) – Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) • ADSL is the most commonly used version of DSL Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 29 DSL Modems (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 30 Satellite • Available – more and more rural areas – metropolitan areas • 500 Kbps for downloading speeds • 50 Kbps for uploading Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 31 Satellite Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 32 Data Communications Techniques • Flow control – way to halt and resume the flow of data Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 33 Software Flow Control • Xon-Xoff – uses Ctrl+S character (ASCII 19) to stop the flow of data (Xoff) – Ctrl+Q (ASCII 17) to resume (Xon) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 34 Hardware Flow Control • Halts and resumes the movement of data – changing the voltage on specific pins in the serial interface – eliminates the problem of the modem confusing data with control signals Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 35 Hardware Flow Control (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 36 Error Correction • Possible errors – a bit can be lost – an extraneous bit can be introduced – a bit can be flipped Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 37 Error Correction • Basic error correction – start and stop bits – each eight-bit byte is framed by a start bit and a stop bit Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 38 Error Correction (continued) • Parity checking – data verification process – ensures data integrity – system of data bit comparisons between the sending and receiving computer Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 39 Error Correction (continued) • Link Access Protocol for Modems (LAPM) – used to construct data into discrete frame-like units for transmission over communications lines Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 40 Data Compression • Modems compress data sent • Data compression routine for a picture with a lot of blue – the “compressed” representation of the screen shows a blue dot and a number that represents the number of times the blue dot is repeated – does it “on the fly,” compressing the data while you send it Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 41 Data Compression (continued) • Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) compression method – compresses data as it is sent – can detect when the data is already compressed Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 42 Modems and the Operating System • Available in all operating systems • Installation CD-ROMs shipped with most all modems Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 43 Configuring Dial-up Connections in Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003 • See page 352 for setup information on Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 44 Configuring Dial-up Connections in UNIX/Linux • Two purposes – dial-in device – dial-out device • For dial-in connectivity, UNIX uses a daemon – an internal, automatically running program called getty Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 45 Configuring Dial-up Connections in UNIX/Linux (continued) • Minicom – create a modem configuration – see Figure 7-8 Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 46 Configuring Dial-up Connections in UNIX/Linux (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 47 Configuring Dial-up Connections in UNIX/Linux (continued) • UUCP – UNIX to UNIX Copy Protocol – found on almost all UNIX versions Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 48 Configuring Modems and Scripts in NetWare 6.x • Components for Novell Internet Access Server – WMDMMGR.EXE – MOEDMMGR.DLL – Modem configuration files – A sample PPP login script Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 49 Configuring Modems and Scripts in NetWare 6.x (continued) • See page 357-358 – recommended steps for modifying a modem configuration file or PPP login script Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 50 Configuring Modems in Mac OS X • Provide information to configure the device – telephone number for the ISP – user name for the ISP account – password for the ISP account Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 51 Configuring Modems in Mac OS X (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 52 Configuring Modems in Mac OS X (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 53 Summary • Modems open WAN communications • Most PCs have a built-in analog modem • Analog modem architecture • Hayes AT modem command set • Digital versus analog modems Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 54 Summary (continued) • See Table 7-4 for a review of analog and digital remote access speeds Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 55 Summary (continued) Guide to Operating Systems, Third Edition 56