Today: 1. Classifiers 2. 5 Sentences signed
advertisement

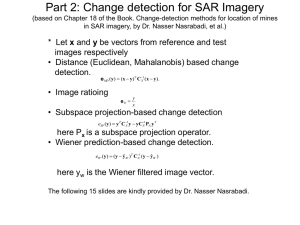
+ http://ww w.youtube. com/watch ?v=202hHdEyeM Multiple Meanings + Classifiers in ASL Part 2 of ASL 2 lecture, May 3, 2012 2011 + Iconic signs and Classifier Descriptions Many non-signers believe signing is “gestures in the air”no!!! There are some elements of ASL that are more iconic than others, and appear “gesture-like”- such as classifiers- but they are a part of the grammar ASL has a complex grammatical system and has a structure more similar to spoken Chinese than English One examples is the classifier system + What are classifiers? Classifiers have no meaning on their own- they must be used in conjunction with their noun English has very few classifiers- (tons=? Stack=?) example: tons of homework, stacks of paper (and we can avoid using classifiers if we choose to do so) In spoken Chinese: Flat objects (table, paper, bed) vs. thin objects, etc. In ASL, we have a similar system Classifiers show, for example, the shape, description, and number of items In ASL, classifiers (classifier predicates) are required for certain expressions + Predicates “The boy is sick.” Subject In ASL: _______t__ BOY Verb can lead the predicate In this case, however, the adjective is the predicate (no verb “to be”) Predicate IX SICK ASL also has CLASSIFIER predicates CAR CL (3): “drive up hill” = “The car is driving up the hill.” + Classifier Predicates (classifiers)a type of verbs (Valli) Use the 5 parameters (handshape, movement, location, palm orientation, nonmanual signals) Nonmanuals Classifier The If such as “thin”, “cha”, etc. predicates have a location (3-d space) location tells where the object is the handshape moves, it shows the object’s destination (where it goes) + Classifier Predicates (aka Classifiers): Handshapes that represent a concept (size, shape, function, etc.) Glossed with a CL before the item The handshape is after the : ---example: CL:3 The description in English is in “ “ Example: CL:3 “car rolls over” + Classifier types in ASL: Entity (semantic classifiers)- items,- types of nouns- CL:1 “person walking fast”, CL:bent-V “row of chairs”, CL:3 “car parks” Instrumental- tools, such as scalpel, chisel (use your hand or part of body) – CL “play checkers”, CL “light match”, CL “garbage dump out” Size and Shape Specifiers (descriptive classifiers): Depth and width -Perimeter shape, etc. Locative classifiers- placement, spatial information- CL (5) “leaf floating on the ground”; CL:C, CL:B “place cup on napkin” Body Part Classifiers -BPCL:F “look at”, BPCL “cross legs”, BPCL: flat C “grin” Classifier Predicates- Examples: + CL:F-small, round- e.g. polkadots, button, thin tube CL:B- flat items-e.g. shelves, door, window CL:1- linear items- eg.sticks, pencils, worm, person walking CL-3- vehicles CL:U- flat and rectangular items-e..g. diving board, tongue depressor, ribbon CL: bent-V - crouching animal, people sitting, etc. CL (5 spread)- e.g. windy, ripples in a lake, etc. Size and Shape Specifiers (Valli + p.81) + Movement shows: eg. speed (Valli p. 91) Other variations: up hill, two cars passing each other, surface pass person, etc. + Test Question: Classifiers are— Classifiers are: A. Signs that are similar to adjectives B. Predicate Verbs that have no meaning on their own, but must be used with a noun C. Signs that are just gestures D. Predicate gestures that have no meaning + Test Question: Which of the following English expressions use classifiers to sign in ASL? A. B. C. D. E. A. A person walking down the street B. A stack of papers C. A barrell D. A scalpel (surgical tool) E. all of the above + Test question: What are SASS (descriptive classifiers)? A. A. Shape and Smoothness Signs B. B. Size and Sharpness of Signs C. C. Signs that are Surrounded by Shape D. D. Size and Shape Specifiers + The End!