31-Analytical Tools in Surveillance_2011
Analysis & graphical display of surveillance data
EPIET Introductory Course
October 2010
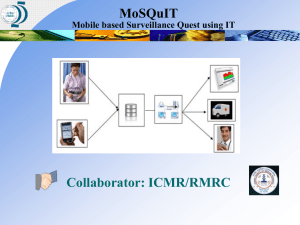
Surveillance system
Health Care Services
Indicator
Public Health Authority
Reporting
Collection
Data
Intervention
Collation,
Analysis,
Interpretation
& Presentation
Information
Dissemination
2
Purpose of surveillance
Monitor trends (PPT)
Monitor control programmes
Detect unusual events
Objectives
Define steps in surveillance analysis
Perform descriptive analysis
Use surveillance data for alert
Understand mechanisms of more complex analysis
Knowledge of surveillance system / surveillance data
– Changes over time
– Multiple sources of information
– Data entry and validation
– Problem of quality and completeness
Evaluation of the system
Surveillance indicators & Denominator issues
Choice of indicator according to availability of denominator :
• no denominator available:
crude number of cases
proportional morbidity
• denominator available:
calculation of rates
standardisation
Denominators
Albanian and refugee populations,
Albania, week 16/1999
Surveillance indicators
Distribution of attendance at health facility by diagnosis
Albania, Week 19 (10-16/05/1999)
Diarrhoea by age groups, weeks 15-19, 1999, Albania
1400
Number of notified cases
1200
< 5 years
5 years and +
1000
800
600
400
200
0
15 16 17
Week
18 19
Notifying healh-care centres and notified out-patients
Albania, weeks 15-19, 1999
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
15
NGO
Number of health centres
MoH
16 17
Week
18 19
Number of out-patients
30000
25000
20000
15000
10000
5000
0
15 16 17
Week
18 19
800
600
400
Number of notified cases
1400
1200
< 5 years
5 years and +
Diarrhoea by age groups, weeks 15-19, 1999, Albania
30
Proportional morbidity
< 5 years
5 years and +
20
1000 10
0
2
15 16 17 18
Diarrhoea / cardiovasc.
19
1
200
0
15 16 17
Week
18 19
0
15 16 17 18 19
Surveillance indicators
& denominator issues
Choice of indicator according to availability of denominator :
• no denominator available:
crude number of cases
proportional morbidity
• denominator available:
calculation of rates
standardisation
Incidence Rate of Disease =
XX.X / 1000
Incidence Rate of Disease =
YY.Y / 1000
Compare XX.X to YY.Y
Disease frequency varies according to age
Age structure of the 2 populations is different
Standardisation
Descriptive Analysis of Person Characteristics
Frequency distributions
– Tables
– Histograms for quantitative classification: age…
– Bars for ordinal or nominal qualitative classification: uneven age-groups, suspectconfirmed…
– Pie for nominal qualitative classification: sex, strain, region
14
Descriptive analysis
- Place -
Mapping
– Dot/Spot map
– Chloropleth map
Choice of
– Colors
– Scale
Asthma cases in Barcelona by district
January 21, 1986 l l l l l l l 7
4 l
5 l l l l
3 l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
2 l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
1 l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
6 l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
9 l
10
Mediterranean sea
8 l
H1N1 Map by number of confirmed cases
Wikipedia May 9, 2009
50 000+ confirmed cases
5 000+ confirmed cases
500+ confirmed cases
50+ confirmed cases
5+ confirmed cases
1+ confirmed cases
17
Combination?
18
• Equal amplitude scale : (120 / 4)
INCIDENCE | Freq Percent Cum
--------------+---------------------
1 – 30 | 10 33.3% 33.3%
31 – 60 | 16 53.3% 86.6%
61 – 90 | 2 6.7% 93.3%
91 – 120 | 2 6.7% 100.0%
--------------+---------------------
Total | 30 100.0%
• Equal frequency scale : (30 / 3)
INCIDENCE | Freq Percent Cum
--------------+---------------------
1 – 30 | 10 33.3% 33.3%
31 – 39 | 10 33.3% 66.6%
40 – 120 | 10 33.3% 100.0%
--------------+---------------------
Total | 30 100.0%
•
Convenience scale
INCIDENCE | Freq Percent Cum
--------------+---------------------
< 100 | 28 93.3% 93.3%
>= 100 | 2 6.7% 100.0%
--------------+---------------------
Total | 30 100.0%
Seasonal influenza: incidence rate (%) by region
France, January-March 2003
Incidence Rate (%)
0,00 – 2,85
2,86 – 5,69
5,70 – 8,54
Equal amplitude scale
Incidence Rate (%)
0,00 – 1,02
1,03 – 2,52
2,53 – 8,54
Equal frequency scale
Diarrhoea, week 40, 2008
Estimated number of cases / 100,000
Descriptive analysis
- Time -
Descriptive analysis of time
Graphical analysis
Requires aggregation on appropriate time unit
Choice of time variable
Date of onset
Date of notification
Use rates when denominator changes over time
Describe trend, seasonality
25
20
15
10
5
0
37
Descriptive analysis – Time –
Graphical analysis
Number of cases
Foodborne Intoxications Clusters
19
17 17
12
11
12
9
6
5
66
16
15
12 12
9
8 8
6
8 8
7
3
2
5
44
55
44
2
3
4
2
44
3
1
3
2
4
6
12
11
7
14
13
12
11
6
0
14 14
7
6
7 7
4
5
6
7
8
12
10
1
10
2
77
6
333
2
5
44
5
1
4
3
2
3
4
9
8
3
4
5
6
12
10 10
11
12
11
12
10
11
10
6
7
6
8
7
3
9
50 11 24 11 24 37 37
Weeks
50
24
Descriptive analysis – Time –
Graphical analysis
15
10
5
25
Number of cases
20
0
37 50 11 24 37
Weeks
50 11 24 37
100
80
60
40
20
0
50
25
0
50
25
-25
0
50
25
0
Descriptive Analysis of Time
Components of Surveillance Data
Signal
Trend
Seasonality
Residuals
Smoothing techniques:
Moving average
Notifications
Moving average of 12 weeks
Moving average of 52 weeks
30 -
Number of notified cases
25 2005 2006 2007 2008
20 -
15 -
10 -
5 -
0 -
26 39 52 13 26 39 52 13 26 39 52 13 26 39 52 13
Weeks
Jan
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec
Descriptive Analysis of Time
Smoothing Techniques
822
654
546
728
872
890
692
465
869
726
834
945
1000
500
3622/5=724,4
3690/5=738.0
3728/5=745.6
0
Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec
Effect of the Moving Average Window Size
Weekly Notifications of Salmonellosis, Georgia, 1993-1994
3 weeks
5 weeks
7 weeks
10 weeks
29
Steps in Surveillance Analysis
Prerequisite to Surveillance Analysis
– Knowledge of surveillance system (evaluation)
• Nature of surveillance data
• Data quality
– Choice of indicator & Denominator issue
Analysis
– Descriptive (PPT)
– Detection of unusual variations / test hypothesis
30
Methodological considerations when testing for time hypothesis
Surveillance data
– Does not result from sampling cases
– Can be viewed as a sample of time units
“ Ecological analysis ”
– Time units are not independent
“ Correlated over time ”
– Specific testing methods need to be applied
Testing for time hypothesis
Convert to rates (if needed)
Remove time dependency
– Trend and seasons
– By restriction or modelling
Test for detection of outbreaks
– More cases than expected?
Test for changes in trend
– Departure from historical trend?
Accounting for Time Dependency
400
300
200
100
700
600
500
Is the red dot consistent with the data?
0
1 10 19 28 37 46 55 64 73 82 91 100 109 118 127 136
Tests not accounting for time dependency
Mean + 1.96 Standard Deviations
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
-10
0
10 30
Yes
110 130
95% CI
Mean
150 50 70 90
Randomly ordered data
Tests accounting for time dependency
95% CI
0,0
-0,1
-0,2
-0,3
-0,4
0,3
0,2
0,1
400
300
200
100
700
600
500
0
1
1
10
12
19 28
23
37 46
No
Chronologically ordered data
55 64 73 82 91 100 109 118 127 136
34 45 56 67
Mois
78 89
Residuals, after removing trend and seasonality
100 111 122
95% CI
Mean
Statistical tests for time series
For time series with no trend and seasonality: random series
– Tests not accounting for time dependency (TD)
– Chi square, Poisson
For time series with seasonality and no trend
– Tests accounting for TD by restriction
– Similar historical period mean/median
For all time series
– Tests accounting for TD by modeling
Olympic Games Surveillance, Athens 2004
Septic Shocks, Syndromic Surveillance
Poisson test
– Count of cases/average previous 7 days ( l
)
P-value between 1-4% <1%
37
Restriction approach:
Historical mean
2009 X 0
2008 X 1
2007 X 4
X 2
X 5
2006 X 7 X 8
2005 X 10 X 11
2004 X 13 X 14
X
X
3
6
X 9
X 12
X 15
12-15 16-19 20-23
Mean and standard deviation
X = X i
/ 15
Std(X) = (X i
X)² / n
Test
X 0 >X + 1.96*Std(X)
Only applicable if data does not present a significant trend
Conclusion
Know the system / the data
– role of artefacts, errors, …
First step = graphic description
– PPT
More complex analysis
– Statistical testing
– Chance, bias, truth?
Data analysis by epidemiologist
– Added value +++
Hypothesis must be validated
– Specific investigation / study
Analysis of surveillance data
= Translating data into information
Provides the basis for public health action
Requires sound analysis and interpretation
Extracts meaningful, actionable findings
Requires clear presentation of complex issues
41
To know more about surveillance data analysis taking into account time dependency
…
EPIET TSA Module!
42