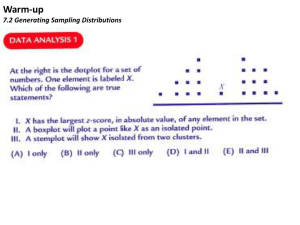
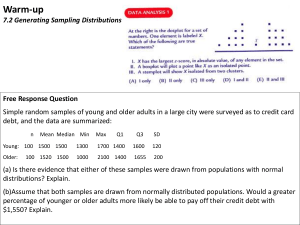
sample distribution
advertisement

SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS
DISTRIBUTIONS
Population Distribution
Sample Distribution
Sampling Distribution
2
Distributions
Definition
The population distribution is the
probability distribution of the population data.
The sample distribution is the
distribution for the sample/data collected.
{stem/leaf, dotplot, boxplot, …}
3
Sampling Distribution
Definition
The probability distribution of a statistic is called its
sampling distribution. It gives the various
values that the statistic can assume and the
probability of each value.
Web Applet ::
http://www.ruf.rice.edu/~lane/stat_sim/sampling_dist/index.html
4
SAMPLING AND
NONSAMPLING ERRORS
Definition
Sampling error is the difference between
the value of a sample statistic and the value
of the corresponding population parameter.
For Example :: In the case of the mean,
Sampling error = x
assuming that the sample is random and
no nonsampling error has been made.
5
SAMPLING AND
NONSAMPLING ERRORS
Definition
The errors that occur in the collection,
recording, and tabulation of data are called
nonsampling errors.
6
MEAN AND STANDARD
DEVIATION OF x
Definition
The mean and standard deviation of the
sampling distribution of x are called the
mean and standard deviation of x and
are denoted by x and x , respectively.
7
MEAN AND STANDARD
DEVIATION OF x
Mean of the Sampling Distribution of x
The mean of the sampling distribution
of x is always equal to the mean of the
population. Thus,
x
8
MEAN AND STANDARD
DEVIATION OF x cont.
Standard Deviation
of the Sampling Distribution of x
The standard deviation of the sampling
distribution of x is
x
n
where σ is the standard deviation of the
population and n is the sample size.
9
Two Important Observations
1. The spread of the sampling distribution
of x is smaller than the spread of the
corresponding population distribution,
i.e. x x
2. The standard deviation of the sampling
distribution of x decreases as the sample
size increases.
10
SHAPE OF THE SAMPLING
DISTRIBUTION OF x
Sampling from
a Normally Distributed Population
Sampling from a Population
That Is Not Normally Distributed
11
Sampling From a Normally
Distributed Population
If the population from which the samples
are drawn is normally distributed with mean
μ and standard deviation σ , then the
sampling distribution of the sample mean,
x ,will also be normally distributed with the
following mean and standard deviation,
irrespective of the sample size:
x and x
n
12
Sampling From a Population That
Is Not Normally Distributed
Central Limit Theorem
According to the central limit theorem,
for a large sample size, the sampling
distribution of x is approximately normal,
irrespective of the shape of the population
distribution. The mean and standard
deviation of the sampling distribution of
are
x and x
n
13
Examples …
14