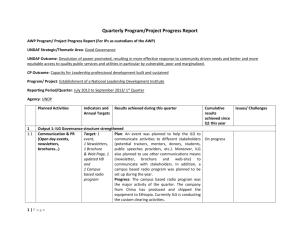
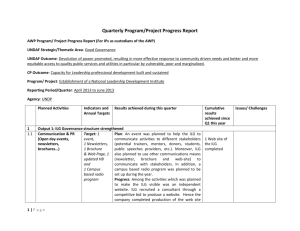
Constructing and Conducting a Comp Analysis
advertisement

Constructing and Conducting a Compensation Analysis 2012 ILG National Conference Waikoloa, Hawaii August 28, 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 1501 M Street, N.W. | Suite 400 Washington, D.C. 20005 Presented by: Chris Gokturk Jeff Norris The Equal Employment Advisory Council (EEAC) is a nonprofit association of private sector employers dedicated exclusively to the elimination of workplace discrimination through advancement of practical and effective equal employment opportunity, affirmative action, and diversity programs. The materials developed for this program and the discussions based upon them are designed to provide accurate and authoritative information regarding the subject matter covered. They are provided with the understanding that EEAC is not engaged in rendering legal, accounting, or other professional services. For legal advice or other expert assistance, the services of a competent attorney or other professional should be sought. © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 2 Seminar Overview • Establishing a Compensation Analysis Process – Preliminary Considerations • Understanding Your Current Compensation Structure • Data Preparation and Review • Conducting the Statistical Analyses – Understanding Statistical Procedures – Analyzing Compensation Practices – What Compensation Should Be Analyzed? – Analyzing Compensation Beyond Base Pay and Performance • Considerations in Making Pay Adjustments © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 3 Establishing a Compensation Analysis Process © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 4 Preliminary Considerations © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 5 Purpose of Analysis Narrow Scope Reactive OFCCP Review CSAL List Proactive © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council Expanded Scope Litigation/ EEOC Charge Proactive Analysis “in anticipation of litigation” 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 6 OFCCP Review • Evolving landscape • Focus on current compensation • Initial scope still USUALLY limited to base pay – Follow up request includes beyond base pay dollars © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 7 Contractor Selection Advance Notice Letter (CSAL) • Still responding to a potential review • May have additional time to analyze data or expand scope as warranted • Ability to address issues PRIOR TO receipt of scheduling letter © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 8 Litigation or EEOC Charge • Must stem from or be reasonably related to charge • Focus on defending the data and practices in effect during the alleged time period • Questions: – What is the alleged time period? – What practices are being challenged? • These may alter the scope of your analysis © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 9 Proactive Analysis • More options available, so determining scope becomes trickier • Scope of analysis can be defined more broadly • Limitations usually data-related • Counsel’s involvement is critical © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 10 Purpose of Analysis • The company’s motivation to conduct the analysis impacts – Which types of pay practices to include – Time period of analysis – Whom to include in the analysis – Roles and responsibilities … more on these later… © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 11 Getting Started… • Where to start – Your Compensation Department • What analyses are currently being performed • Evaluate appropriateness for THIS purpose – Base or total compensation – Employee groupings – Do you have a compensation structure in place? What is it? – How is pay determined? – What influences what each employee gets paid? © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 12 Understanding Your Current Compensation Structure © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 13 Understanding Your Current Compensation Structure • What do you say that you do – Compensation philosophy – Compensation structure • Grades, bands, other – Company policies and procedures • Both formal and informal • How does it work in practice © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 14 Understanding Your Current Compensation Structure • Four keys to minimizing risk – Alignment of policy and practice – Data integrity – Transparency – Monitoring and analysis © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 15 Data Preparation and Review © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 16 The Key…Employment Data • Preparing data for analysis – Annualizing compensation for your parttimers – Does everyone have a race/gender code – Does everyone have data in the fields that matter – Review for any “garbage” in data fields • Any field important enough to determine or influence pay is important enough to check for accuracy © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 17 The Key…Employment Data • What data do you need – Groupings and factors that influence pay – Fields that define THE JOB – Fields that define “where the person sits” organizationally – Fields that differentiate an individual from others in the same type of job © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 18 The Key…Employment Data • What do you have in your system – How reliable are the data in the fields – Common data integrity issues: • System conversion issues – Example: Everyone has same “time in grade” date • Fields that are not kept up to date – Example: Education data • Fields that are important but not tracked – Example: Prior experience © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 19 Dates • Check for accuracy and incomplete values • Legacy System Problems: – Senior employees: hire date is not actual — mark or change date – Errors in updating • Decision date vs. Effective dates • Rehires — how handled • Missing parts of dates (e.g., no day) © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 20 Unexpected Data Values • Inconsistent or misspelled text entries • Missing values: – Identify the cause • Have you merged the data correctly – Don’t mix with “zero” values or “No” entries – Beware of conducting analysis only on the employees with available data • Outliers or misclassified employees: – Unidentified demotions – Erroneous entries • Wide ranges in pay or grade values for given job title © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 21 © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 22 Using the Right Data • General pay factor coding schemes: – Yes/No – Convert to Dummy/Indicator Factor (0=No, 1=Yes) – Multiple Category Factors: Use as scale or separate factors • Ex: Education level (<HS, HS, BA/BS, MS+Phd) = > 3 factors • Determine reference group and code dummies for others – Continuous Factors (e.g., experience) — plot it by salary and structure factor appropriately – Correlated Factors — try to identify distinct components • E.g., time in company and time in job => time in job and time in company beyond the current job © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 23 Conducting the Statistical Analyses © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 24 Understanding Statistical Procedures © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 25 Topics • Statistical test – Mean/Median Analysis – t-Test – Regressions • Examples of regression plots and results • Using the right statistical tool • Using the right data © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 26 Mean & Median Mean Analysis • What is it? − • The average or mean is another way of describing the mid point of a group of salaries being analyzed. The average is computed by adding the salaries in a grouping and then dividing their sum by the number of salaries The OFCCP is using means for the preliminary review and in comparing groups that are too small to run a regression analysis on Median Analysis • What is it? − The median is one way to describe the mid point of the group of salaries being analyzed • Useful because it is not affected by very high or very low salaries • In the past has been heavily used by the OFCCP © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 27 © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 28 t-Test • What is it? – The t-test assesses whether the means of two groups are statistically different from each other – Does not consider other factors • When should it be used? – The t-test report in CompAuditor® II gives you a listing of each grouping regardless of size. This allows you to quickly see differences in the means. © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 29 © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 30 Regressions • Regression is a statistical tool used to understand the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more explanatory variables – simply a mathematical model of your pay system • Like prior comparisons, measures disparities in light of (“controlling for”) other factors • Simple Regression – one explanatory variable • Multiple Regression – multiple explanatory variables © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 31 Regression Analysis Armed with the right tools … and the right data … now we can develop the regression model • In order to develop a regression model, we need to determine three things: – Dependent variable – Grouping – Factors that influence the dependent variable within the grouping © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 32 Regression Analysis Dependent variable • This refers to the data we are trying to explain – Base pay – Total cash – Starting pay – Whether or not someone received a bonus © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 33 Regression Analysis Grouping • Balance “similarly situated” with group size • Typical groupings include: – Job title – Grade – AAP job group © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 34 Regression Analysis Pay factors • Virtually anything can be coded as a factor – Some best practice companies check each factor independently to determine its influence in the absence of other factors • Typical factors include: – Time factors (seniority, time in job, experience, etc.) – Market factors – Education factors to the extent they are different within the selected grouping © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 35 © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 36 Percentage of the variation in salaries that is statistically explained by the independent variables in the regression model, adjusted for the number of variables and sample sizes. Both measure the “significance” of each variable. Look for t-stats > |1.96| and p-values < .05 to be significant. Consider dropping variables that don’t contribute to the model © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 37 Analyzing Compensation Practices © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 38 What Compensation Should Be Analyzed? © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 39 What Compensation Should Be Analyzed? • Base salary – Historically what companies have focused on, both proactively and for OFCCP audits • Total compensation © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 40 What Compensation Should Be Analyzed? • Base salary is only one of the many elements of total compensation – Base salary – Short-term incentives • Cash bonuses • Annual bonus • Sign-on bonus • Referral bonus • Retention bonus • Holiday bonus • “Other cash” © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 41 What Compensation Should Be Analyzed? – Long-term incentives • Stock options – Employee benefits – Perquisites (“perks”) • Varies from company to company • Individual packages – product of negotiations • Internal perks – Luxury offices – Executive dining rooms – Special parking and cars © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 42 What Compensation Should Be Analyzed? • Merit Increases – OFCCP is routinely requesting – Do you give $$’s or percents? – How does this tie into performance evaluations? © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 43 Analyzing Compensation Beyond Base Pay and Performance © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 44 Why Monitor Beyond Base Pay? • The OFCCP is going to ask for it • It’s where the real money lies • It’s “discretionary” • It’s an “in-house” function … generally not outsourced • It’s better to do so proactively today – rather than defensively tomorrow © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 45 Evaluating Compensation Beyond Base Pay • Analyzing beyond base pay is not always as simple as a regression model. Many factors to consider. – Is a regression model the best test? – Are the groupings you use for base salary analysis appropriate for this comparison? – What employees are eligible? © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 46 Evaluating Compensation Beyond Base Pay • Two phase process – Participation • Impact ratio analysis • Distribution and patterns – Extent of Participation • Regressions • Mean analysis • Distribution and patterns © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 47 Considerations in Making Pay Adjustments © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 48 Key Questions • Three key questions Who should receive a pay adjustment? How much of an adjustment should be made? When should the adjustments be made? • All are strategic decisions with legal implications © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 49 Who Should Receive Pay Adjustments Individuals whose compensation is so low that they skew the data and no legitimate explanations are identified should be considered for adjustment Consult with (as appropriate): • Human resources and compensation staff • Individual’s line management • General counsel (risk/benefit analysis) • Senior management Full story rarely resides in the database or employee files Should disadvantaged males and non-minorities be afforded adjustments © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 50 How Much of an Adjustment Should Be Made • Immediate elimination of entire disparity • Amount sufficient to reach bottom of range • Amount sufficient to eliminate statistical significance • Additional considerations: – Budget limitations – Will adjustments create new disparities for men/non-minorities © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 51 When Should Adjustments Be Made • During next scheduled compensation review cycle – Least likely to generate questions • Immediately, mid-cycle – What explanation do you provide employee • Prior to submitting compensation data to OFCCP or EEOC for analysis – Conduct risk/benefit analysis – What if OFCCP asks © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 52 Conclusion Prudent employers will conduct compensation analyses routinely as part of a proactive, ongoing monitoring process, and will make appropriate pay adjustments — regardless of the race or gender of the individuals affected © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 53 Wrap-Up and Questions jnorris@eeac.org cgokturk@easiconsultants.com © 2012 Equal Employment Advisory Council 2012 ILG National Conference | August 28, 2012 | Page 54