Percentage of All Firms Offering Health Benefits, 1999-2013
advertisement

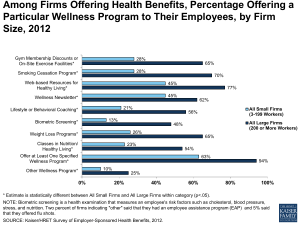
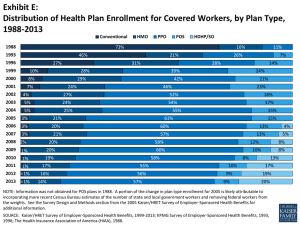
Employer Health Benefit Survey Release Slides Tuesday, August 20, 2013 Cumulative Increases in Health Insurance Premiums, Workers’ Contributions to Premiums, Inflation, and Workers’ Earnings, 1999-2013 250% Health Insurance Premiums Workers' Contribution to Premiums Workers' Earnings 200% 196% Overall Inflation 182% 150% 117% 119% 100% 56% 57% 50% 50% 34% 40% 14% 29% 11% 0% 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 1999-2013. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index, U.S. City Average of Annual Inflation (April to April), 1999-2013; Bureau of Labor Statistics, Seasonally Adjusted Data from the Current Employment Statistics Survey, 1999-2013 (April to April). 2013 Average Annual Premiums for Single and Family Coverage, 1999-2013 $2,196 1999 $5,791 $2,471* 2000 $2,689* 2001 Family Coverage $7,061* $3,083* 2002 Single Coverage $6,438* $8,003* $3,383* 2003 $9,068* $3,695* 2004 $9,950* $4,024* 2005 $10,880* $4,242* 2006 $11,480* $4,479* 2007 $12,106* 2008 $4,704* 2009 $4,824 $12,680* $13,375* $5,049* 2010 $13,770* $5,429* 2011 $15,073* $5,615* 2012 $15,745* $5,884* 2013 $0 $2,000 $4,000 $6,000 $16,351* $8,000 $10,000 * Estimate is statistically different from estimate for the previous year shown (p<.05). SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 1999-2013. $12,000 $14,000 $16,000 $18,000 Average Annual Worker Premium Contributions and Total Premiums for Covered Workers, Single and Family Coverage, by Firm Size, 2013 $18,000 $16,000 All Small Firms (3-199 Workers) All Large Firms (200 or More Workers) $16,715 $15,581 $14,000 $12,000 $10,000 $8,000 $6,000 $5,711 $5,967 $5,284 $4,226 $4,000 $2,000 $862 $1,065 $0 Premium Worker Contribution* Single Coverage * Estimates are statistically different between All Small Firms and All Large Firms (p<.05). SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013. Premium* Worker Contribution* Family Coverage Average Worker and Employer Premium Contributions For Covered Workers at Higher- and Lower-Wage Firms, 2013 $16,989 $18,000 $16,000 $7,000 $6,025* $15,225 $6,000 $5,450 * $14,000 $5,000 $12,000 $10,000 $9,407 * $12,959 * $8,000 $4,000 $3,000 $6,000 $4,216 * $5,071* $1,234 * $954 * Many Workers are LowerWage Many Workers are HigherWage $2,000 $4,000 $2,000 $5,818* $4,030 * $1,000 $0 $0 Many Workers are LowerWage Many Workers are HigherWage Family Coverage Employer Premium Contribution Single Coverage Worker Premium Contribution *Estimate for many workers are lower-wage is statistically different from estimate for many workers are higher-wage, within coverage type (p<.05). NOTE: Firms with many lower-wage workers are ones where 35% or more of employees earn $23,000 or less. Firms with many higher-wage workers are ones where 35% or more of employees earn $56,000 or more. Wage cutoffs are the inflation adjusted- 25th and 75th percentile of national wages according to Bureau of Labor Statistics using data from the Occupational Employment Statistics (OES) (2011). 1% of covered workers are in firms which are both high income and low income, excluding these firms does not change the estimates or significance testing. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013. National Compensation Survey: Occupational Earnings in the United States, 2010. http://www.bls.gov/ncs/ocs/sp/nctb1489.pdf. Percentage of All Firms Offering Health Benefits, 1999-2013 100% 90% 80% 70% 66% 68% 68% 66% 66% 69%* 63% 60% 61% 60% 50% 55% 57% 58% 58% 55% 63% 59% 60%* 59% 61% 57% 59%* 52% 47% 40% 50% 49% 45% 48%* 47% 50% 45% 30% All Firms 20% Firms with 3-9 Workers 10% 0% 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 *Estimate is statistically different from estimate for the previous year shown (p<.05). NOTE: Estimates presented in this exhibit are based on the sample of both firms that completed the entire survey and those that answered just one question about whether they offer health benefits. The percentage of firms offering health benefits is largely driven by small firms. The large increase in 2010 was primarily driven by a 12 percentage point increase in offering among firms with 3 to 9 workers. In 2011, 48% of firms with 3 to 9 employees offer health benefits, a level more consistent with levels from recent years other than 2010. The overall 2011 offer rate is consistent with the long term trend, indicating that the high 2010 offer rate may be an aberration. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 1999-2013. 2013 Among Firms with 50 or More Workers, Percent of Firms Offering Health Benefits, 2013 Percent of Firms that Do Not Offer Health Benefits 7% Percent of Firms Offering Health Benefits 93% SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013. Percentage of Firms Offering Health Benefits, by Firm Characteristics, 2013 Less Than 35% Earn $23,000 a Year or Less * Low Wage Level 35% or More Earn $23,000 a Year or Less * 60% 23% Less Than 35% Earn $56,000 a Year or More * High Wage Level 49% 35% or More Earn $56,000 a Year or More * 69% Less Than 35% of Workers Are Age 26 or Younger * Younger Workers 35% or More Workers Are Age 26 or Younger * Less Than 35% of Workers Are Age 50 or Older Older Workers 35% or More Workers Are Age 50 or Older * Estimates are statistically different from each other within category (p<.05). SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013. 59% 23% 51% 58% Distribution of Health Plan Enrollment for Covered Workers, by Plan Type, 1988-2013 Conventional 1988 PPO POS HDHP/SO 73% 1993 16% 46% 1996 27% 1999 8% 2001 7% 21% 31% 10% 2000 2002 HMO 17% 5% 25% 2007 3% 55% 1% 20% 2010 1% 19% 2011 1% 2012 <1% 2013 <1% 17% 16% 14% 15% 60% 13% 57% 20% 2009 15% 61% 21% 2008 2% 23% 54% 2004 20% 46% 18% 24% 3% 21% 52% 5% 2006 24% 27% 2003 21% 14% 42% 24% 3% 7% 39% 29% 2005 26% 28% 28% 4% 11% 13% 58% 57% 8% 10% 58% 56% 5% 12% 60% 55% 4% 8% 8% 10% 9% 9% 13% 17% 19% 20% NOTE: Information was not obtained for POS plans in 1988. A portion of the change in plan type enrollment for 2005 is likely attributable to incorporating more recent Census Bureau estimates of the number of state and local government workers and removing federal workers from the weights. See the Survey Design and Methods section from the 2005 Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits for additional information. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 1999-2013; KPMG Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 1993, 1996; The Health Insurance Association of America (HIAA), 1988. Percent of Covered Workers Enrolled in a Plan That Includes a General Annual Deductible, 2006-2013 100% 90% 78%* 80% 74% 69%* 70% 72% 62% 60% 56% 57% 2007 2008 52% 50% 40% 30% 20% 2006 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 * Estimate is statistically different from estimate for the previous year shown (p<.05). NOTE: These estimates include workers enrolled in HDHP/SO and other plan types. Between 2012 and 2013 we did not collect information on the attributes of conventional plans, to be conservative, we assumed conventional plans did not have a deductible. Because of the low enrollment in conventional plans, the impact of this assumption is minimal. Average general annual health plan deductibles for PPOs, POS plans, and HDHP/SOs are for in-network services. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2006-2013. Average General Annual Deductible Among Covered Workers Enrolled in a Plan with a Deductible for Single Coverage, by Firm Size, 2006-2013 $2,000 All Small Firms All Large Firms $1,800 $1,715 All Firms $1,537 $1,600 $1,596 $1,391 $1,400 $1,254 $1,124* $1,200 $1,000 $800 $600 $400 $775 $584 $917* $852 $1,097* $1,135 $875* $884 2012 2013 $991 $826* $735* $616 $640* $496 $519 $553 2006 2007 2008 $686 $757 $200 $0 2009 * Estimate is statistically different from estimate for the previous year shown (p<.05). SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2006-2013. 2010 2011 Percentage of Covered Workers Enrolled in a Plan with a General Annual Deductible of $1,000 or More for Single Coverage, By Firm Size, 2006-2013 All Small Firms (3-199 Workers) 60% 58%* All Large Firms (200 or More Workers) 50% All Firms 50% 49% 46% 40% 40% 38% 35%* 34% 31% 27%* 30% 22%* 21%* 20% 18%* 16% 10% 28% 22%* 12%* 17% 10% 0% 26% 13%* 6% 2006 8% 9% 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 * Estimate is statistically different from estimate for the previous year shown (p<.05). NOTE: These estimates include workers enrolled in HDHP/SO and other plan types. Average general annual health plan deductibles for PPOs, POS plans, and HDHP/SOs are for in-network services. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2006-2013. 2013 Among All Large Firms (200 or More Workers) Offering Health Benefits to Active Workers, Percentage of Firms Offering Retiree Health Benefits, 1988-2013 100% 90% 80% 70% 66% 60% 50% 40% 30% 46% 40% 40% 40% 36% 34% 37% 35% 36% 35% 32% 34% 32% 29% 28% 26% 26% 25% 28% 20% 10% 0% 1988 1991 1993 1995 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 NOTE: Tests found no statistical difference from estimate for the previous year shown (p<.05). No statistical tests are conducted for years prior to 1999. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 1999-2013; KPMG Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 1991, 1993, 1995, 1998; The Health Insurance Association of America (HIAA), 1988. Percentage of Covered Workers in Partially or Completely Self-Funded Plans, by Firm Size, 1999-2013 100% All Small Firms (3-199 Workers) All Large Firms (200 or more) 90% 83%* 80% 72% 67%* 70% 60% 66% 73% 75% 78% 77% 77% 82% 81% 83% 77% 66% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 13% 15% 17% 13% 10% 10% 10% 13% 13% 12% 12% 15% 16% 13% 15% 16% 0% 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 * Estimate is statistically different from estimate for the previous year shown (p<.05). NOTE: Sixty-one percent of covered workers are in a partially or completely self-funded plan in 2013. Due to a change in the survey questionnaire, funding status was not asked of firms with conventional plans in 2006. Therefore, conventional plan funding status is not included in the averages in this exhibit for 2006. For definitions of Self-Funded and Fully Insured plans, see the introduction to Section 10. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 1999-2013. 2013 Grandfathering Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), by Firm Size, 2011-2013 Percentage of Covered Workers in a Grandfathered Health Plan 2011 2012 2013 All Small Firms (3-199 Workers) 63% 54%* 49% All Large Firms (200 or More Workers) 53% 46% 30%* 56% 48%* 36%* 2011 2012 2013 All Small Firms (3-199 Workers) 72% 58%* 54% All Large Firms (200 or More Workers) 61% 57% 43%* 72% 58%* 54% ALL FIRMS Percentage of Firms with At Least One Grandfathered Plan ALL FIRMS * Estimate is statistically different from estimate for the previous year shown (p<.05). Note: For definitions of Grandfathered health plans, see the introduction to Section 13. Source: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2011-2013. Among Firms Offering Health Benefits, Distribution of Firms’ Opinions on the Effectiveness of the Following Strategies to Contain Health Insurance Costs, 2013 Don’t Know Not At All Effective Not Too Effective Somewhat Effective 100% 20% 80% 22% 17% Very Effective 8% 35% 37% 60% 32% 41% 33% 32% 40% 26% 29% 21% 20% 0% 27% 24% 9% 1% Wellness Programs 14% 15% 4% 2% Disease Management Programs Consumer-Driven Health Plans (Ex: High-Deductible Plan Combined with a Health Savings Account) SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013. 20% 24% 4% 4% Higher Employee Cost Tighter Managed Care Sharing Restrictions Among Firms Offering Health Benefits, Percentage Offering a Particular Wellness Program to Their Employees, by Firm Size, 2013 Other Wellness Program* 26% 10% Offer at Least One Specified Wellness Program* 99% 76% Class in Nutrition/Healthy Living* 50% 20% Flu Shot or Vaccinations* 87% 53% Employee Assistance Program (EAP)* 79% 22% Weight Loss Programs* Biometric Screening* 55% 26% Lifestyle or Behavioral Coaching* Wellness Newsletter* 47% Web-based Resources for Healthy Living* 47% 60% 78% 71% 39% Gym Membership Discounts or On-Site Exercise Facilities* 69% 21% 0% 20% 40% 60% * Estimate is statistically different between All Small Firms and All Large Firms within category (p<.05). NOTE: Biometric screening is a health examination that measures an employee's risk factors SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013. All Small Firms (3-199 Workers) 57% 33% Smoking Cessation Program* All Large Firms (200 or More Workers) 58% 31% 80% 100% Among Firms Offering Health Benefits, The Use of Financial Incentives for Participating in Various Health Programs, by Firm Size, 2013 100% 80% 99% 76% 77% Large Firms (200 or more Workers) Small Firms (3-199 Workers) All Firms 77% 57% 57% 60% 55% 55% 36% 40% 26% 27% 20% 0% 54% 8% 10% Percentage of Offering Firms Offers Incentive to Employees who Participate*^ Offers at least one Wellness Program~ 8% Percentage of Offering Firms 23% 24% 11% 2% 2% Offers Incentives to employees who participate* Offers at least one Disease Management Program Percentage of Offering Firms Offers reward or penalties for employees who meet biometric outcome* Biometric Screening`` Percentage of Offering Firms Opportunity for Health Risk Assessment‡ *Percent of firms offering incentives is among firms offering health benefits who also offer the specified health program or activity. ~ Includes the following wellness programs: weight loss programs, biometric screenings, gym membership discounts or on-site exercise facilities, smoking cessation program, lifestyle or behavioral coaching, classes in nutrition or healthy living, web-based resources for healthy living, flu shots or vaccinations, or employee assistance programs (EAP) or a wellness newsletter. ^Among Firms Offering Health and Wellness Benefits. Any financial incentive indicates firms that offer employees who participate in wellness programs one of the following incentives: smaller premium contributions, smaller deductibles, higher HRA or HSA contributions, or gift cards, travel, merchandise, or cash. ``Biometric screening is a health examination that measures an employee's risk factors such as cholesterol, blood pressure, stress, and nutrition. ‡A health risk assessment includes questions about medical history, health status, and lifestyle and is designed to identify the health risks of the person being assessed. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013. Offers Incentive to complete* Percentage of Firms whose Largest Plan Covers Care Received at Retail Clinics, and Percentage of Firms who Offer a Financial Incentive to do so, by Firm Size, 2013 100% Among Firms Offering Health Benefits: Among Firms whose Largest Plan Includes Coverage at a Retail Clinic: 80% 61% 60% 56% 56% 40% 17% 20% 13% 17% 0% Largest Plan Covers Care Received at a Retail Clinic All Small Firms (3-199 Workers) Offers Financial Incentives for Choosing a Retail Clinic Instead of a Traditional Physician's Office All Large Firms (200 or More Workers) ALL FIRMS NOTE: Tests found no statistical difference between All Small Firms and All Large Firms within category. A retail clinic is a health care clinic located in retail stores, supermarkets and pharmacies that treats minor illnesses and provide preventive health care services, such as flu shots. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013. Among Large Firms (200 or More Employees) Offering Health Benefits, the Percentage of Firms Considering Offering Benefits Through a Private Exchange, by Firm Size, 2013 100% 2% 2% 2% 2% 80% 69% 60% 91% 85% 89% 40% 20% 29% 0% 7% 200-999 Workers 13% 9% 1,000-4,999 Workers Yes No 5,000 or More Workers ALL LARGE FIRMS (200 or More Workers) Don't Know NOTE: A private exchange is created by a private company or consulting company where the employer offers a defined contribution for their employees and the employees choose among different health plan options from different health insurers selected by the exchange. The employees pays the difference between the defined contribution and the cost of the health insurance option that they choose. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013. Among Firms Offering Health Benefits, Percentage of Firms Whose Largest Plan Includes a High-Performance Provider Network, 2007, 2010, 2011, and 2013 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 15% 16% 2007 2010 20% 23% 0% 2011 2013 Note: The overall percentage of firms whose largest plan includes a high performance provider network is not significantly different between 2013 and previous years the question was included in the survey (2007, 2010, 2011) (p<.05). A high performance network is one that groups providers within the network based on quality, cost, and/or efficiency of care they deliver. SOURCE: Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits, 2013.