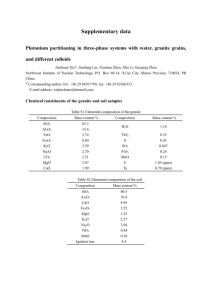
Was sind Kolloide ? - Universität Potsdam

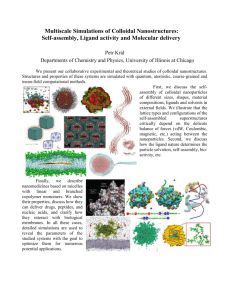
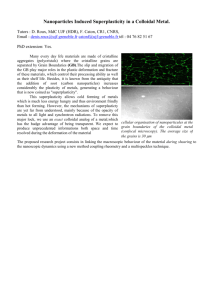
Introduction to Colloidal systems
Joachim Koetz, Universität Potsdam
Alchemist
• Elexier of life ?
• potable gold-solution (aurum potabile)
Definition ( Graham )
•
Colloids are glue-like substances, diffuse very slowly, and do not dialyse
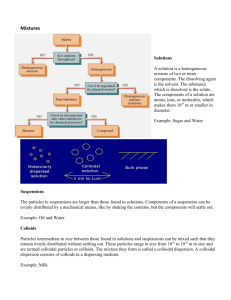
Types of disperse systems
( W. Ostwald )
Disperse systems suspensions
> 1000 nm colloidal dispersions
1 bis 1000 nm solutions
< 1 nm
Definition
Any particle that has some linear dimension between 1 nm and
1 μm is considered a colloid!
However, the limits are rather arbitrary.
Definition:
•
A state of subdivision in which the particles, droplets, or bubbles dispersed in another phase have at least one dimension between
1 – 1000 nm
• All combinations are possible between gas, liquid, and solid
W. Ostwald
History of Colloid Chemistry
•
1927 Burry, Ekwall: Associating Colloids
•
1929 Staudinger: Macromolecules
Associating Colloids
•
Amphiphilic self-organizing systems
•
Colloids are associated physically, not chemically
•
Size and shape of the associates can change
Macromolecules as colloidal systems
•
Any macromolecule consisting of
10 3 up to 10 9 atoms
•
Any dispersed macromolecular coil having colloidal dimensions
History of Colloid Chemistry
•
1923 Svedberg: Ultracentrifugation
•
1932 Ruska: Electron Microscopy
The Colloidal Domain
•
One dimension between 1 and 1000 nm
•
All combinations of dispersed matter
•
Classification: - colloidal dispersions
- associating colloids
- macromolecules
Biomineralization
Inorganic component
Organic component
SiO
2
* x H
2
O composite of hydrocarbon and protein
Aragonite,
CaCO
3
Hydroxyapatit,
Ca
10
(PO
4
)
6
(OH)
2 composite of hydrocarbon and protein composite of collagenfilament and protein
Organism
Diatomeen
Perl oyster
Bone and teeth
Nanoparticles as Quantendots
• Color effects in glases
(e.g. CdS or gold)
• Non linear optical effects
(fast optoelectronical switches)
• High storage capacity
(optical storage)
Formation of Nanoparticles
(Nanotechnology)
• Particle formation from gas phases
• Particle formation from droplets
• Particle formation from Sol-Gel-Processes
Nanoparticles produced by nucleation processes
• Colloidal Sulfur
•
Colloidal Gold
• Latex Particles
• Nanocrystallites
Conditions for the production of monodisperse nanoparticles
- Heterogeneous nucleation
- La Mer diagram
Disciplines and Topics for which Colloids and colloidal phenomena are important
•
Analytical chemistry
• Physical chemistry
• Biochemistry
• Material Science
• Petroleum Science
•
Household products
•
Imaging technology
• Adsorption phenomena, chromatography
•
Nucleation, supersaturation, liquid crystals
• Electrophoresis, osmosis, ultrafiltration
•
Ceramics, fibres, powder metallurgy
• Oil recovery,
•
Milk, beer, cosmetics
• Emulsions, printing inks, paper coating