Cellular Respiration Notes - Ponderosa High School Agriculture
advertisement

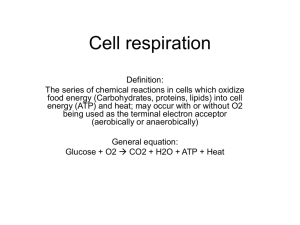
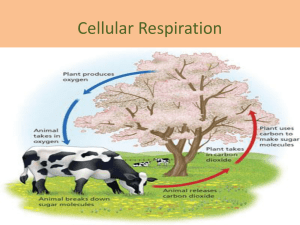
Cellular Respiration Chapter 9 Ag Biology Ms. Prescott 9-1 Overview Lactic Acid Electron Trans. 9-2 Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Flowchart 9-1 Chemical Pathways 9-1 Overview Lactic Acid Electron Trans. 9-2 Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Flowchart Feel The Burn Do you like to run, bike, or swim? These all are good ways to exercise. When you exercise, your body uses oxygen to get energy from glucose, a six-carbon sugar. 1. How does your body feel at the start of exercise, such as a long, slow run? How do you feel 1 minute into the run; 10 minutes into the run? 2. What do you think is happening in your cells to cause the changes in how you feel? 3. Think about running as fast as you can for 100 meters. Could you keep up this pace for a much longer distance? Explain your answer. 9-1 Chemical Pathways Vocabulary Calorie Glycolysis term used by scientists to measure the energy stored in food first step in releasing the energy of glucose, in Glucose which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid. PA PA Cellular respiration process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules in the presence of oxygen; made up of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Krebs Cycle ETC 9-1 Chemical Pathways Vocabulary NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) – electron carrier involved in glycolysis Fermentation Energy O2 process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen Anaerobic Electron process that does not require oxygen. O2 9-1 Chemical Pathways 1. Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules (protein, fat, carbohydrates: glucose) in the presence of oxygen within the mitochondria of the cell 2. The equation is the opposite of photosynthesis: a. 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O+ Energy b. oxygen+ glucose carbon dioxide+ water+ Energy 9-1 Chemical Pathways 3. If energy was released quickly in one stage, the energy would be lost as heat and light 4. Most of the energy is converted into ATP, that powers the cell’s activities 5. The cellular respiration cycle includes three processes: a. Glycolysis b. Kreb’s Cycle c. Electron Transport Section 9-1 Chemical Pathways Glucose Glycolysis Krebs cycle Fermentation (without oxygen) Go to Section: Electron transport Alcohol or lactic acid 9-1 Chemical Pathways 6. Glycolysis a. During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is broken in half, making two carbon compound molecules b. Glycolysis requires a small amount of energy to get it going Figure 9–3 Glycolysis Section 9-1 Glucose 2 Pyruvic acid To the electron transport chain Go to Section: Figure 9–3 Glycolysis Section 9-1 Glucose 2 Pyruvic acid To the electron transport chain Go to Section: Figure 9–3 Glycolysis Section 9-1 Glucose 2 Pyruvic acid To the electron transport chain Go to Section: 9-1 Chemical Pathways c. After glycolysis there are two possible paths: i. Fermentation- ends cellular respiration 1.Releases energy from food molecules in the ABSENCE of oxygen so it is called anaerobic 2.Alcoholic Fermentation: Alcohols and carbon dioxide are produced (Example = Rootbeer) 3.Lactic Acid Fermentation: Lactic acid is produced (Example = yogurt & muscle cramps) ii. Kreb’s Cycle- continues cellular respiration Section 9-1 Glucose Go to Section: Figure 9–4 Lactic Acid Fermentation Pyruvic acid Lactic acid Section 9-1 Glucose Go to Section: Figure 9–4 Lactic Acid Fermentation Pyruvic acid Lactic acid Section 9-1 Glucose Go to Section: Figure 9–4 Lactic Acid Fermentation Pyruvic acid Lactic acid 9-2 The Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport 9-1 Overview Lactic Acid Electron Trans. 9-2 Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Flowchart Rolling and Folding Some of the steps in cellular respiration take place in the membrane inside the cell structure called the mitochondrion, which has a folded inner membrane. What purpose do these folds serve? To find out the answer to this question, perform this activity. 1. Obtain two sheets of paper and a metric ruler. What is the surface area of the paper? 2. Roll one sheet of paper into a tube lengthwise. What is the surface area of the rolled paper? 3. Fold the second sheet of paper into a fan. Then, roll the first sheet of paper around the folded paper so it is inside the rolled paper. What has happened to the surface area of the inside of the rolled paper? 4. What would be the value of increasing the surface area of the membrane inside a mitochondrion? 9-2 Vocabulary Warning O2 AerobicRequired process that requires oxygen Krebs CycleEnerg second stage of cellular respiration, in which y pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting Pyruvic Acid reactions. CO2 Electron transport chainCO2 a series of proteins in which the high-energy electrons from the Krebs Cycle are used to convert ADP into ATP. ADP Before ATP After 9-2 Krebs Cycle 1. Krebs Cycle a. Krebs Cycle happens in the mitochondrial matrix b. It occurs in the PRESENCE of oxygen and is aerobic c. Carbon compounds from glycolysis break down and release CO2 Figure 9–6 The Krebs Cycle Section 9-2 Citric Acid Production Go to Section: Mitochondrion Figure 9–6 The Krebs Cycle Section 9-2 Citric Acid Production Mitochondrion Go to Section: 9-2 Electron Transport 2. Electron Transport a. The electron transport chain is located in the cristae (membrane of the mitochondria) b. There are 4 main steps i. Electrons are passed through the electron transport chain ii. Energy is built up iii. The energy is used to transport hydrogen ions across the membrane iv. As this happens, ATP is produced Section 9-2 Figure 9– 7 Electron Transport Chain Electron Transport Hydrogen Ion Movement Channel Mitochondrion Intermembrane Space ATP synthase Inner Membrane Matrix ATP Production Go to Section: 9-2 Krebs Cycle & Electron Transport 3. Energy Totals a.Glycolysis Fermentation = 2 ATP (without oxygen) b.Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport = (with oxygen) ------------------- + 34 ATP 36 ATP Total!! Which process is better at providing energy for the cell? Is this process anaerobic or aerobic? Section 9-1 Figure 9– 2 Respiration: An Overview Mitochondrion Electrons carried in NADH Pyruvic acid Glucose Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electrons carried in NADH and FADH2 Electron Transport Chain Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Go to Section: Section 9-2 Flowchart Cellular Respiration Glucose (C6H1206) + Oxygen (02) Go to Section: Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Carbon Dioxide (CO2) + Water (H2O)