THE INSULATION OF FLAT ROOFS
advertisement

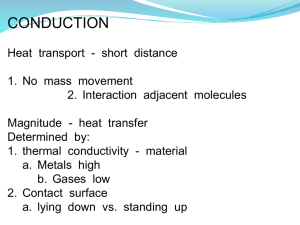
THERMAL INSULATION IN THE NEW ERA INSULATION THICKNESS IN EUROPE ROOFS INSULATION THICKNESS IN EUROPE WALLS ENERGY LOSSES IN EUROPE ROOFS ENERGY LOSSES IN EUROPE WALLS THE NEW REALITY • CO2 emissions increase due to increased energy consumption. • Result is climate change. • Result is even higher energy consumption. • Closed loop effect. • On top of that oil prices increased by 80%. THE ONLY RELIABLE SOLUTION IS PROPER THERMAL INSULATION • Increased energy consumption in industry due to growth is inevitable. • Decrease energy consumption in housing by efficient thermal insulation. CALCULATION OF OPTIMUM INSULATION THICKNESS BUILDING ENERGY LOSSES 10% THERMAL TRANSPORT MECHANISMS • Conduction through material mass. • Convention via gas phase movement. • Radiation. CONDUCTION THERMAL TRANSPORT HOT (lots of vibration) COLD (not much vibration) Heat travels along the rod CONVENTION THERMAL TRANSPORT BY GAS PHASE CONVENTION THERMAL TRANSPORT – HOME RADIATOR THERMAL TRANSPORT VIA RADIATION Increased temperature THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY λ MATERIAL ? Kcal/m h C COPPER MARMOR / GRANITE BETON PLASTER BRICK WOOD OAK WOOD PINE 330 3 1.8 0.8 0.5 0.2 0.1 POLYURETHANE (Solid) POLYSTYRENE (Solid) 0.2 0.1 WATER 0.5 AIR (dry ( / still) HFC 152a/134a CO2 0,023 * 0.013 0.014 IS AIR A THERMOINSULATING AGENT? λ (dry / still) = 0.023 kcal / m h C Vertical Air Mass Thickness d (mm) λ A I R 10 50 100 0.0652 0.23 0.5 d Vertical Air Mass AIR d Thickness d (mm) λ 10 0.0625 20 0.12 50 0.26 THEORY OF THERMAL INSULATING MATERIALS Factors Affecting λ Value Of Cellular Plastic Materials 1. Gas λ value (Humidity content ) 2. Solid λ value 3. Cell structure 4. Percentage of closed cells 5. Diffusion of gases Chemical nature /permeability Cell size ( Small cells better than big cells) Skin Layer Geometry (Thicker = better) Conditions ( T and RH ) Types of Thermal Insulation Cork Glass Wool EPS XPS Types of Thermal Insulation HUMIDITY - THE WORST ENEMY OF THERMAL INSULATION EFFECT OF HUMIDITY ON THE THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF CELLULAR FOAMS AT START 28 days in water 28 days in humidity Product λ Water (Kcal/hm°C) EPS 12 Kg/m3 λ (Kcal/hm°C) Absorption Water λ (Kcal/hm°C) Absorption Water 0.035 0% 0.048 12% 0.068 41% EPS 25 Kg/m3 pressed 0.032 o% 0.041 6% 0.051 21% AplaXFoam XPS 32Kg/m3 0.025 0% 0.0255 0.40% 0.0272 2.26% BASIC INSULATING MATERIALS BASIC INSULATING MATERIALS Dry condition / 100mm thick 4 3.5 2.5 2 R-Value (m KW) 3 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 AplaXFoam 32kg/m3 EPS 20kg/m3 Perlite Cement Board 200kg/m3 BASIC INSULATING MATERIALS 350 AplaXFoam Products and EPS Strenght - kPa 300 AplaXFoam 100 AplaXFoam SL EPS 20kg/m3 BASIC INSULATING MATERIALS The retained thermal resistance after 18 months on the exterior foundation wall. Retained Thermal Resistance 97% 71% 58% AplaXFoam EPS Polyurethane BASIC INSULATING MATERIALS How the insulation acts when exposed to moisture. Retained Thermal Resistance 98% 77% AplaXFoam EPS 85% Polyurethane BASIC INSULATING MATERIALS How insulations acts when exposed to moisture vapors. Retained Thermal Resistance 93% 35% 18% AplaXFoam EPS Polyurethane BASIC INSULATING MATERIALS How the insulation acts when exposed to freeze - thaw cycling. Retained Thermal Resistance 98.5% 30% 5.5% AplaXFoam EPS Polyurethane BASIC INSULATING MATERIALS • EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE • FIBERS (GLASS - ROCK ) • EXTRUDED POLYSTYRENE XPS – Extruded Polystyrene • • • • • • • • • • • • • Implementation of up to date technology. Excellent thermal insulation. Low retention of water and humidity. High mechanic resistance. High compression resistance. Dimensional stability. Homogeneous density to mass. Resistance to the action of acids and bases. Insensitive to temperature variations. Compatibility to materials used in constructions (cement, gypsum). Easy to transport, cut and applied. Self extinguishing properties. Clean, odorless, non irritating to skin. PROPERTIES STABLE THROUGH TIME SELECTION OF INSULATION SYSTEM AND MATERIAL • Study and analysis of the total problem. • Selection of the best solution. • Assurance of properties for long time. • Incorporation of all cost affecting parameters. THE INSULATION OF FLAT ROOFS –INVERSED ROOF • Insulation of flat roof with the traditional method the insulation is under the waterproofing (EPS-STONEWOOL) • Insulation of flat roofs with the inversed roof principal the insulation is above the waterproofing material (XPS) THE INSULATION OF FLAT ROOFS –TRADITIONAL ROOF THE INSULATION OF FLAT ROOFS –INVERSED ROOF DAY NIGHT TEMP VARIATION FOR MEMBRANE Temperature Variation Day Night 80 Temperature 60 40 20 0 -20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Month DAY NIGHT 10 11 12 FAQ • • • • • • • FAQ FAQ FAQ FAQ FAQ FAQ For a facade what should I use: XPS or EPS or stone wool ? Is polyurethane a bad insulating material ? Is cellular cement a good insulating material ? Is stone wool better than XPS as a thermal insulating material? Is XPS a sound insulating material? Is stone wool a good sound insulating material? For a flat roof what thermal insulation should I use ? Thank you!