Caffext - Shaman Australis Ethnobotanicals
advertisement
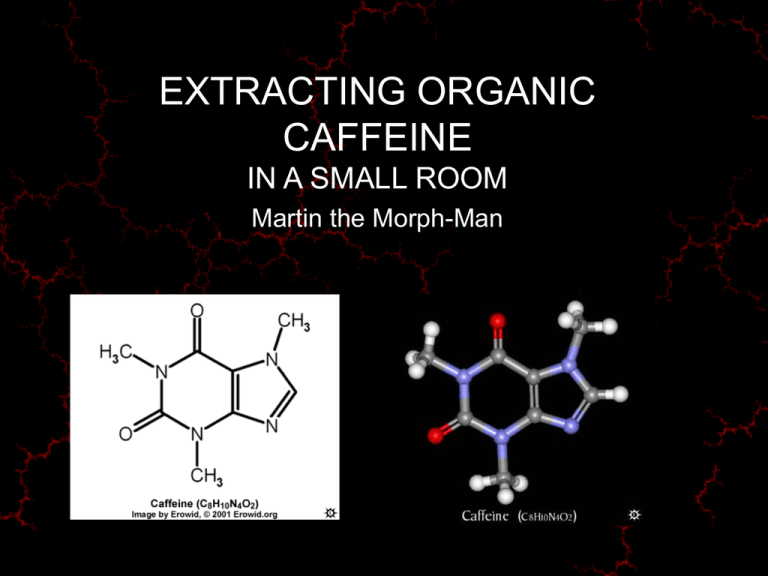
EXTRACTING ORGANIC CAFFEINE IN A SMALL ROOM Martin the Morph-Man Overview Caffeine may be isolated from coffee, tea and other aqueous solutions by a simple acid-base extraction procedure Disclaimer • It is legal to extract compounds (e.g. caffeine) from a wide range of natural sources • It is NOT legal to extract compounds from some other sources, nor to possess those compounds obtained by any means • This talk is for your general interest only • You are urged NOT to apply the following procedures to any natural products • You are encouraged to be aware of the legal implications of any extraction procedures performed without legal sanction Safety Toxic Flammable Corrosive Environment Dichloromethane Ethers Hydrochloric acid DCM Methanol Acetone Sodium hydroxide Chloroform Benzene Methanol Carbon tetrachloride Ethanol Benzene Toluene Toluene Theory: Caffeine and Alkaloid Chemistry • Alkaloids are heterocyclic organic compounds - ring containing carbon and nitrogen • May contain (non-ring) oxygen • N and O confer acid/base properties • Acid/base properties influence solubility in various solvents Theory: Acid-Base Extractions Generally: • N-atoms are charged positive in acid conditions and are neutral in basic (alkaline) conditions • O-atoms are neutral in acid conditions and are charged negative in basic conditions • Charged compounds are more soluble in polar solvents such as water & methanol • Neutral compounds are more soluble in non-polar solvents such as ether and toluene Target compound NAME : Caffeine CHEMICAL NAME : 3,7-Dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione ALTERNATE CHEMICAL NAMES : 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine; 1,3,7-trimethyl-2,6-dioxopurine; coffeine ALTERNATE NAMES : thein; guaranine; methyltheobromine; No-Doz CHEMICAL FORMULA: C8H10N4O2 MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 194.19 APPEARANCE: White hexagonal or needle-like crystals MELTING POINT: 238ºC SOLUBILITY: Water, Ethanol, Methanol, Acetone, Chloroform LD50 Dog: 140mg/kg oral LD50 Rat: 105mg/kg IV LD Low (Lethal Dose): Human deaths reported at less than 4 grams oral. Technique • • • • • • • • • • 1) Cook up 2) Clarify 3) Remove fatty impurities 4) Make solution alkaline 5) Extract alkaloids to organic solvent 6) Separate organic from aqueous phase 7) Repeat extraction to solvent (steps 5&6) 8) Dry organic solvent 9) Evaporate organic solvent 10) Purify compound by recrystallisation, often from another organic solvent Equipment • • • • • • Coffee/spice mill Pyrex or stainless steel pans Strainers, filter papers & funnels Separating funnel Drying dish & dryer Measuring cylinders, pipettes etc Reagents • Acid: Hydrochloric, citric, acetic • Alkali: Sodium hydroxide, ammonium hydroxide • Solvents: Dichloromethane, methanol, diethyl ether, petroleum ether (Vietti™ lighter fluid) Precautions • Ventilation – toxic volatiles • No flame – flammable volatiles • Protective clothing toxic or corrosive liquids • Be discreet – solvent smells attract attention - “loose lips sink ships” – Step 1: Cook-up Step 2: Filtration Step 3: Defatting Step 4: Raise pH Step 5: Organic solvent extraction Step 6: Separation of phases Step 7: Rinse organic phase Step 8: Dry organic phase Step 9: Evaporation & crystallisation Mission successful! Extraction of anything in a small room • Be careful • Be discreet • Be safe Happy extractions and happy travelling!