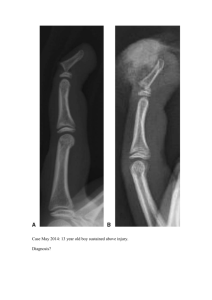
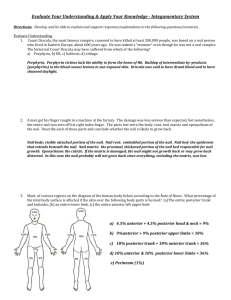
Section 10. - Zamorascience
advertisement

Holt Physics, Chapter 10 Section 2 DEFINING HEAT Heat and Energy Heat – energy transferred between objects because of a difference in their temperatures. It is helpful to shift attention to the behavior of atoms and molecules. Mechanics can be used to explain much of what is happening at the molecular, or microscopic, level. This in turn accounts for what you observe at the macroscopic level. Energy is transferred between substances as heat. Macroscopic viewpoint: always from higher to lower temperature. The direction of heat travel can be explained at the atomic level. Higher temperature juice has higher avg. KE than the water. Collision of particles transfers energy from high to low. Net transfer continues until avg. KE is the same between the juice and the water. With same avg. KE, juice and water at thermal equilibrium (i.e., at the same temperature). The transfer of energy as heat alters and object’s temperature. When two object are in thermal contact, there is no net gain or loss of energy, even though energy is transferred. Difference between heat and temperature. The amount of heat transferred depends on the temperature difference between the two objects. Greater the difference, greater the amount of energy transferred as heat. Concepts of heat and temperature can help explain hot and cold sensation. Because heat, like work, is energy in transit, all heat units can be converted to joules (J) Heat is symbolized with the letter Q. Heat and Work Hammer nail into wood, then pry out. Nail feels hot. Work done on nail was resisted by friction. Friction increases internal energy of nail temp. increases. Temperature difference between hand and nail results in transfer of heat. Deforming solids can increase internal energy. Total energy is conserved Not all work done to overcome fiction is converted to mechanical energy. If changes in internal energy are taken into account, along with changes in mechanical energy, energy in a closed system is a conserved property