Cellular Respiration
advertisement

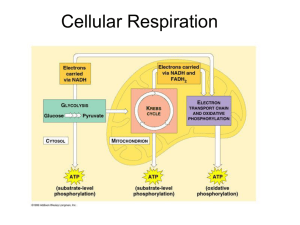
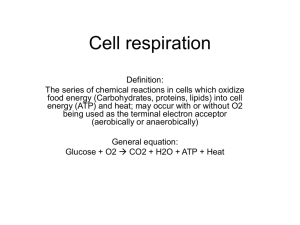
Cellular Respiration! CA State Standard CELL BIOLOGY 1.g. Students know the role of the mitochondria in making stored chemical-bond energy available to cells by completing the breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide. How do heterotrophs get energy? They eat it! When you eat food, how does it become the energy that makes your body function? Through a process called cellular respiration! As this figure skater breathes, she takes in oxygen. Why? The oxygen is used in the process of cellular respiration, which allows her cells to break down glucose and turn it into ATP. This enables her to have the energy to perform her feats on ice. What is Cellular Respiration? Cellular Respiration is the process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen. What is the equation for Cellular Respiration? Hint: It’s the opposite of Photosynthesis! What is the equation for Cellular Respiration? Oxygen What we breathe 6O2 + C6H12O6 6H2O + 6CO2 + Energy Carbon Dioxide Glucose Water What we exhale Cellular Respiration has 3 Stages 1. Glycolysis (occurs in the cytoplasm) 2. Krebs Cycle (occurs in the mitochondria) 3. Electron Transport Chain (occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria) Overview of Cellular Respiration Glycolysis: Breakdown of Glucose Pyruvic acid Cytoplasm Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain: Production of ATP Pyruvic Acid Alcohol & CO2 or Lactic Acid ATP! Glycolysis Glyco = sugar; lysis = breaking; so glycolysis is the breaking of glucose! It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. Glycolysis – the process in which one molecule of glucose is broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid, a 3-carbon compound. 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules are created. During Glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvic acid, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH. Cellular respiration occurs in three stages. Pyruvic Acid Glycolysis Step 1 1. Phosphate groups from 2 ATP are transferred to a glucose molecule Glycolysis Step 2: 2. Six-carbon compound broken down to two 3-carbon compounds, each with a phosphate group. Glycolysis Step 3: 3. Two NADH molecules are produced, one phosphate group is transferred to each 3-carbon compound. Glycolysis Step 4: 4. Two 3- carbon compounds converted to pyruvic acid and 4 molecules of ATP Glycolysis Glycolysis has a net gain of 2 ATP. (It uses 2 ATP but produces 4 ATP) What happens in the stages of glycolysis? 1. A molecule of glucose is split 2. 2 pyruvic acids are made 3. 2 ATP and 2 NADH are produced An important example of an electron acceptor that functions in glycolysis is… NAD+ NAD+ becomes NADH when it accepts an e- What happens after Glycolysis….? Only 2 ATP were made and pyruvic acid still has a lot of energy in its bonds… If there is O2 available AEROBIC RESPIRATION! If there is NO O2 available FERMENTATION (ANAEROBIC) Aerobic Respiration Pyruvic Acid Aerobic = requires O2 When oxygen is present, pyruvic acid and NADH are used to make a large amount of ATP in the Mitochondrion during the Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain. Fermentation (Anaerobic respiration) Pyruvic Acid When oxygen is not present, pyruvic acid is converted to either lactic acid or alcohol and carbon dioxide through fermentation. Two Types of Fermentation: Alcoholic Fermentation Lactic Acid Fermentation Two Types of Fermentation: Alcoholic Fermentation Pyruvic acid + NADH alcohol + CO2 + NAD+ WHO? Yeast and other microorganisms Example: This is how bread and alcohol are made! Two Types of Fermentation: Lactic Acid Fermentation Pyruvic acid + NADH lactic acid + NAD+ WHO? Animals, prokaryotes Examples: Lactic acid build-up creates sore muscles after intense exercise Cheese, yogurt, sour cream, pickles, kimchi are made this way Fermentation makes cheese! Fungi or bacteria are added to milk to carry out lactic acid fermentation on some of the sugar in the milk. This is how cheese is made! Lactic Acid Fermentation! If OXYGEN is available…. CELLULAR RESPIRATION TAKES PLACE! When oxygen is available, Pyruvic Acid goes into the mitochondrion and goes through the Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain to get ATP! Krebs Cycle occurs in area enclosed by inner membrane. Electron Transport Chain occurs within inner membrane itself. Cellular Respiration 1. Glycolysis (breakdown of glucose) 2. Krebs Cycle 3. Electron Transport Chain Production of ATP! 2. KREBS CYCLE Pyruvic acid from glycolysis enters the mitochondria and gets transformed into AcetylCoA and other carbon compounds. CO2 is produced. 8 ATP, FADH2 and NADH are created. Occurs in the mitochondria KREBS CYCLE 1. When oxygen is present, pyruvic acid enters the mitochondrion and is converted to a compound called Acetyl-CoA. 2. CO2 is released. Pyruvic Acid Citric Acid Krebs Cycle Acetyl-CoA 3. Acetyl-CoA is converted into Citric Acid, releasing more CO2. Citric Acid 4. More CO2 is released from the 6-carbon compound, forming a 5-carbon compound. 5. Electrons are transferred to NAD+ making NADH. 6. More CO2 is released when Citric Acid is converted into a 5-carbon compound. 7. ATP and NADH are made. 8. Electrons are transferred to FAD making FADH2 9. The 4-carbon compound is converted back into citric acid and the cycle starts all over! NADH and FADH2 go into the Electron Transport Chain, providing high-energy electrons, leading to the production of ATP! Electron Transport Chain The Electron Transport Chain occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Inner membrane of mitochondria 1. High-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along proteins in the membrane. Inner membrane of mitochondria 2. At the end of the electron transport chain, OXYGEN is the final electron acceptor of the electrons. The electrons combine with hydrogen ions and form WATER! The final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is Oxygen! The final end product in the electron transport chain is water 3. As the highenergy electrons are passed along, their energy is used to pump hydrogen ions, H+, across the membrane. This creates a concentration gradient. Inner membrane of mitochondria 4. ATP is created as H+ ions diffuse through ATP Synthase, a channel protein in the membrane. ATP Synthase The complete breakdown of glucose through glycolysis and respiration results in the production of chemical energy in the form of 36 total molecules of ATP. Cellular Respiration Quiz 1. What is cellular respiration? 2. What is the balanced equation for cellular respiration? 3. Glycolysis occurs in the mitochondrion/cytoplasm of the cell. (circle the correct response) 4. Glucose is broken down in glycolysis/Krebs Cycle/ electron transport chain. (circle the correct response) 5. CO2 is produced in glycolysis/Krebs Cycle/ electron transport chain. (circle the correct response) 6. The Krebs Cycle occurs in the mitochondrion/cytoplasm of the cell. (circle the correct response) 7. Why do we need to breathe oxygen? 8. After glycolysis, if there is no oxygen present, what process occurs instead of the Krebs Cycle and electron transport chain? Cellular Respiration Review! Standardized Test Prep When oxygen is present, most of the ATP made in cellular respiration is produced by A aerobic respiration. B glycolysis. C alcoholic fermentation. D lactic acid fermentation. What is the equation for cellular respiration? What is the equation for Cellular Respiration? Oxygen What we breathe 6O2 + C6H12O6 6H2O + 6CO2 + 36 ATP (Energy) Carbon Dioxide Glucose Water What we exhale What are the three stages of Cellular Respiration? Cellular Respiration has 3 Stages 1. Glycolysis (occurs in the cytoplasm) 2. Krebs Cycle (occurs in the mitochondria) 3. Electron Transport Chain (occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria) What does glycolysis do? Breaks down glucose into 2 pyruvic acid molecules, 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules. Where does glycolysis take place? The cytoplasm What happens if there is no O2 available? Fermentation Alcohol or Lactic Acid What happens if O2 is available? Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain What goes into the Krebs Cycle? Pyruvic Acid! What comes out of the Krebs Cycle? CO2 that we breathe out NADH and FADH2 ATP Where does the Electron Transport Chain occur? In the inner membrane of the mitochondria! What goes into the Electron Transport Chain? ELECTRONS! DUH! Seriously though, the electrons come from NADH and FADH2 What is the main purpose of the Electron Transport Chain? To make ATP! What molecule is the final electron acceptor for electrons in the Electron Transport Chain? HINT: YOU BREATHE IT IN. OXYGEN GAS! (02) What molecule results when O2 accepts electrons at the end of the Electron Transport Chain? WATER! (H20) How many net ATP molecules are created from cellular respiration? 36 ATP Molecules! Review List the products of glycolysis. What is the role of each of these products in cellular respiration? Summarize the roles of the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain during aerobic respiration. Describe the role of fermentation in the second stage of cellular respiration. Critical Thinking Comparing Functions Explain why cellular respiration is more efficient when oxygen is present in cells. Critical Thinking Inferring Conclusions Excess glucose in your blood is stored in your liver as glycogen. How might your body sense when to convert glucose to glycogen and glycogen back to glucose? Leftover slides… Respiration, an aerobic process, takes place in the mitochondrion. The Krebs cycle takes place in the area enclosed by the inner mitochondrial membrane. Electron transport and ATP formation involve complex molecules embedded in the inner membrane. Acetic acid 6- carbon compound The Krebs Cycle Continuing series of reactions Pyruvic acid travels from cytoplasm to mitochondrion Acetic Acid • 1st step respiration: pyruvic acid broken down into carbon dioxide and acetic acid. Krebs cycle Acetic acid 6-carbon compound Acetic acid enters Krebs cycle reacts with 4-carbon compound to produce citric acid. Inner mitochondria membrane The high-energy electrons in the energy-storing compounds NADH and FADH2 are transferred to the molecules of the electron transport chain, which is located is the inner mitochondria membrane. At the end of the chain, the electrons react with hydrogen ions and oxygen to form water. Krebs cycle 2 carbon atoms added – from breakdown of pyruvic acid 2 carbon atoms removed (in 2 molecules of CO2) Krebs cycle 3 molecules of NAD+ converted to NADH 1 molecule of FAD converted to FADH2 1 molecule of GDP converted to GTP Acetic acid 6- carbon compound Electron Transport in the Mitochondrion High-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed to a series of electron transport enzymes in the inner membrane of mitochondrion At end of chain an enzyme combines electrons , hydrogen ions and O2 to form water. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor. Oxygen essential for obtaining energy from NADH and FADH2 ATP Formation Movement of hydrogen ions powers formation of ATP. The movement of a pair of electrons down ETC produces 3 ATP from ADP More hydrogen ions outside the inner membrane Hydrogen ions pumped across membrane Breathing and Respiration Oxygen is final acceptor for all electrons produced in respiration. Without oxygen ETC cannot operate, Krebs cycle stops and synthesis of ATP stops. Breathing gives us a constant supply of oxygen. Obtaining Energy from Food Complex carbohydrates broken down into simple sugars that are converted into glucose. Lipids & proteins can be broken down into molecules that can enter glycolysis at one of several places The cell can generate ATP from many sources. 4-5 ATP Synthesis The difference in electrical charges across the photosynthetic and mitochondrial membranes a source of energy. This energy could be used to attach a phosphate to ADP to make ATP. ATP is generated when hydrogen ions move from a high concentration to a low concentration. This is called chemiosmosis. 1. Define glycolysis. 2. Compare lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. 3. Critical Thinking-Inferring What would happen to wine if there was an air leak in the fermentation tank? 4. MIN) LAB Predict the effect that temperature has on the rate of fermentation. Energy in Balance Photosynthesis and respiration can be thought of as opposite processes. Photosynthesis is the storing of energy. Cellular respiration is using energy. The products of photosynthesis ar eht reactants of glucose breakdown The products of glucose breakdown are the reactans of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is to oxygen as cellular respiration is to what? • Carbon dioxide Cellular Respiration 1. Summarize how glucose is broken down in the first stage of cellular respiration. 2. Describe how ATP is made in the second stage of cellular respiration. 3. Identify the role of fermentation in the second stage of cellular respiration. 4. Evaluate the importance of oxygen in aerobic respiration.