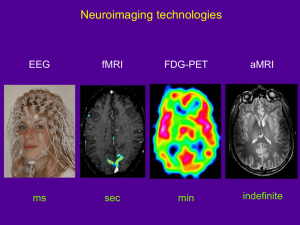
CT Scan vs MRI vs PET vs X-Ray vs Ultrasound: Differences
advertisement
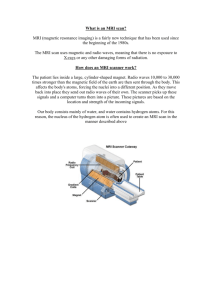
Medical Machinery What is the difference between a CT scan, MRI, PET, X-Ray and Ultrasound? CT SCAN or CAT SCAN Computed Tomography by using an x-ray beam passing through the body to produce an image. The CT scan x-ray beam spins on a ring in a round part of the scanner called the gantry. You lay on a table that moves in and out of the gantry while the table passes you through the spinning x-ray beam. CT USES A MAGNETIC IMAGERY similar to an x-ray. MODERATE to HIGH RADIATION EXPOSURE MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging • A powerful MAGNETIC field used to align nuclear magnets with water (hydrogen atoms) in the body. • Uses magnets and radio waves to create the image • Best used for soft tissues of the body • There are many types of MRIs • NO RADIATION EXPOSURE CAT versus MRI • MRI shows tendons and ligaments very well • Tendons and ligaments around the shoulder and knee are best seen in an MRI. • This is due to the density of the tissues that compose the tendons and ligaments. • Spinal cord is best seen by MRI for the same reason. The density of the spinal cord and the composition shows better on an MRI. CAT versus MRI • CT scan is the preferred modality for cancer, pneumonia, and abnormal chest x-rays. • Bleeding in the brain, especially from injury, is better seen on CT than MRI. • But a tumor in the brain is better seen on MRI. • If you've been in an accident, organs can get torn or damaged. • CT shows organ tear and organ injury quickly and efficiently. • Broken bones and vertebral bodies of the spine are better seen on CT but injury to the spinal cord itself is displayed on MRI far better than CT. • CT is far superior at visualizing the lungs and organs in the chest cavity between the lungs. • MRI is not a good tool for visualizing the chest or lungs at all. CT Scan Machine MRI Machine • First photo is a MRI of brain tumor you can see two tumors • Second photo is a CT of same brain showing only one tumor. (better in showing bleeding on the brain in trauma patients like bus/ car accidents) CT images of cervical spine (neck area) • CT for bone fractures (shown) shows the BONE of the cervical spine • MRI for spinal cord injury (area between bones) Pelvis CT Can you find the pelvis fracture? Pelvis CT Can you find the pelvis fracture? Abdomen CT • With CONTRAST…you would have to drink a chalky liquid in order to visualize particular areas OR get an IV for dye • Black spots show lesions, Cysts or tumors CONTRAST CONTENTS • Oral contrast is composed of a mineral called barium sulfate (BaSO4). • Barium is a metallic element that is chemically similar to calcium but more reactive. • The compound works due to barium's relatively high atomic number (Z = 56), since large nuclei absorb X-rays much better than smaller nuclei. Intravenous Contrast IV Content • Contains IODINE • Some people with shellfish allergies have an allergic reaction to this contrast • When administered, it brightens internal organs, arteries, veins and tissues as it courses through them. PET SCAN Positron Emission Tomography • an imaging test that can help reveal how your tissues and organs are functioning. • To show this chemical activity, a small amount of radioactive material must enter your body. • The radioactive material may be injected into a vein, inhaled or swallowed • Isotopes needed (C-11, N-13, Rb-82) PET SCAN More radioactive material accumulates in areas that have higher levels of chemical activity. This often corresponds to areas of disease and shows up as brighter spots on the PET scan. A PET scan is useful in evaluating a variety of conditions — including neurological problems, heart disease and cancer. PET with CAT The PET/CT is the most advanced medical imaging technique available today. It combines Positron Emmission Tomography (PET) with Computed Tomography (CT). A PET scan offers the ability to detect changes in cell function ULTRASOUND Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing SONOGRAM The most well known application of ultrasound is its use in sonography to produce pictures of fetuses in the human womb Sonogram It’s a Boy! Sonogram It’s a Girl! No boy parts… 3-D views TWINS! TRIPLETS X-Ray X-Radiation • X-radiation (composed of X-rays) is a form of electromagnetic radiation • They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays. • X-rays can penetrate solid objects, and their largest use is to take images of the inside of objects in diagnostic radiography and crystallography • X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation and exposure to them can be a health hazard. Electromagnetic Spectrum PLEASE NOTE • Sound waves (ultrasound) are not a part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum • X-Rays are a part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum • They travel at different speeds. Sound waves are slower. • SPEED OF LIGHT= 3.00 x 108 m/s (300,000,000 m/s) • SPEED OF SOUND= 340 m/s • Sound waves travel faster in water than in air. Cost of an MRI • MRI cost can range between $1000 to $3,500 depending upon which MRI procedure is performed • Average cost is over $1000 • (example: brain MRI vs. shoulder MRI) and where you have the MRI test performed Cost of a CT scan • Cost $300-700 per body part • Cost of a diagnostic scan (this is one that your doctor orders because of an injury or symptom) $600- 1500 • Full body CT scan with contrast- up to $6000 • Contrast is a dye injected or swallowed to show tissues…etc… Cost of Ultrasound • Cost of ultrasound is typically around $200 • Also depends on which area is being viewed. Cost of a X-Ray •Depends on the part and how many images are taken •$80-250 or higher •Example: a pelvic x-ray can cost $1,200 RADIOLOGY • Radiology is the branch or specialty of medicine that deals with the study and application of imaging technology like xray and radiation to diagnosing and treating disease. • A Radiologist is a Medical Doctor (M.D.) that reads MRIs and CT scans. • Radiologists know their chemistry! • Schooling – 4 years (Undergraduate degree…like Chemistry, Biology, Genetics, etc) – 4 years (Medical school) – 2-4 years (Residency-get paid here) Median salary is $290,000 per year According to salary.com • • • • • • • • • • • Radiation Physics Anatomy and Physiology Principles of Radiographic Exposure Radiobiology Radiographic Examination Radiographic Studies Fluoroscopic Studies Orthopedic Studies Special Imaging Studies Patient Care Patient Physical Assessment