Gas Chromatography
advertisement

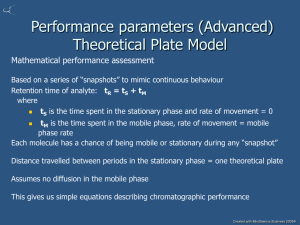
Effect of Packing Particle Size on Plate Height Resolution between 2 adjacent peaks The General Elution Problem Small k′ Large k′ The General Elution Problem 1. Poor separation of compounds with small capacity factors. 2. Excessive separation time and poor detectability of compounds with large capacity factors. Solutions to The General Elution Problem Alter k′ values during the separation: 1. Temperature Program (GC) 2. Gradient Elution (LC) 3. Coupled Columns (change the stationary phase) Temperature programming and gradient elution require “re-equilibration time” after the analysis of each sample. Temperature Programming: Separation of Normal Alkanes (C6 – C12) Ti = 100oC Tf = 200oC Tc = 130oC 0 25 0 12 Gradient Elution: Substituted Benzenes Organic Water GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY INSTRUMENTATION 1. 2. 3. 4. Mobile Phase Sample Injector Column (Stationary Phase) Detector GC MOBILE PHASES 1. 2. 3. 4. He H2 N2 CO2 GC On-Column Injector GC Glass-lined Injector for a Packed Column GC Injector for a Capillary Column GC “Split” Injector for a Capillary Column GC “Split-less” Injector for a Capillary Column GC Stationary Phases PDMS: PolyDiMethylSiloxane Organic stationary phases must have sufficient molecular weight to achieve low volatility GC Stationary Phases Increase Polarity by adding phenyl rings or CN groups… GC Stationary Phases Or by de-shielding the oxygen and forming a wax. (Carbowax) GC Stationary Phases Decrease Polarity by replacing methyl groups with longer chain alkanes. GC Stationary Phases Types Non-Bonded: Liquid phase is used to coat the inside walls of the column to a thickness of about 0.1 – 1.0 μm Bonded: Silanol groups on the column wall form a chemical bond with the stationary phase GC Stationary Phases Types Preparation of Bonded Phases: GC Stationary Phases Types Advantage of Bonded Phases: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. High Reproducibility Low Bleed Fast Equilibration Temperature Stability Easy to Back Flush Long Life GC Stationary Phases Types What about Packed GC Columns?? Open Tubular Column Packed Column GC Stationary Phases Types FSOT: Fused Silica Open Tubular WCOT: Wall Coated Open Tubular SCOT: Support Coated Open Tubular WCOT and SCOT are less flexible and more fragile (made of glass) FSOT with bonded phase is most common N ≈ 400,000 H ≈ 0.1 mm L ≈ 50 m GC Stationary Phases Types Packed Column: H = A + B/u + Cu C dp2 (particle diameter)2 Open Tubular: H = B/u + Cu C dc2 (column internal diameter)2 Open Tubular Packed Packed GC Columns Open Tubular Columns tr dc [η/(Po Dm)]1/2 where: η Po Dm dc mobile phase viscosity column outlet pressure Diffusion coefficient of analyte in gas Internal column diameter Dm MW-1/2 Open Tubular Columns So: tr [η MW1/2]1/2 Gas η MW1/2 Ar CO2 N2 He H2 1138 995 741 440 90 Open Tubular Columns with Different Gases