Forensic Serology:
Color tests
By: Mike O'neill
Mazin Osman
Claudia Palma
Adam Ramirez
Color Tests
•
•
•
Determination of blood are made by
conducting color tests
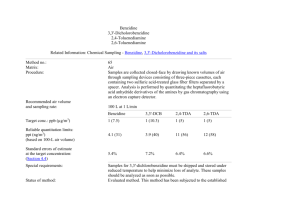
The Benzidine test was the most commonly
used for many years.
However it has been replaced by the KastleMeyer test because the benzidine has been
identified as a known carcinogen (Can cause
cancer)
Color Tests
•
•
•
The Benzidine and Kastle-Meyer color tests
are based on the observation that
hemoglobin possesses peroxidase-like
activity
Hemoglobin- A red blood cell protein that
transports oxygen in the bloodstream; it is
responsible for the red color of blood
Peroxidases are enzymes that accelerate the
oxidation of several classes of organic
compounds when combined with peroxides
Kastle-Meyer Test
•
•
The Kastle-Meyer test relies on the iron in
hemoglobin to promote the oxidation of
phenolphthalin to phenolphthalein.
Phenolphthalin is colorless, but in the
presence of blood and hydrogen peroxide, it
changes to phenolphthalein, which makes
the solution pink.
Sensitivity and Limitations
•
•
•
•
It is extremely sensitive
Capable of detect blood dilutions as low as
1x10^7
If the test result is negative, heme might be
absent in the sample
The test will give a false positive result in the
presence of any oxidizing agent like
cauliflower or broccoli
Performing The Kastle-Meyer
Test
1. Collect a sample of the blood using a cotton
swab (if the blood is dry, water could be used
to moisten the swab)
2. Add two drops of 70% ethanol to the swab
(Helps increase the sensitivity of the test)
3. Add a drop or two of the Kastle-Meyer
solution
4. Add two drops of hydrogen peroxide solution
Results
Pink Color Develops
Results
Interpretation
After Kastle-Meyer is applied
False Positive
The reaction did not occur as
the result of blood’s presence
After hydrogen peroxide is
applied
Positive
blood is indicated
Never
Negative
False Negative
Blood is not indicated (may not
be present)
Blood may be present, but
is too dilute to react
Benzidine Color Test
•
•
•
The benzidine color test was, for many years,
the most popular type of preliminary blood
test.
In 1988, however, benzidine was identified
as a carcinogen and since then its use has
mostly been discontinued.
Benzidine + Blood Stain + Hydrogen
Peroxide = Pink Color
Strengths of Benzidine
•
•
•
•
It was a common test for blood.
It is a presumptive test for identifying Blood
An enzyme in blood causes the benzidine to
be oxidized to a polymer
which is blue colored. This makes it very
easy to find the result
Weaknesses of Benzidine
•
•
•
This test is very unreliable. Although a test
may appear that it has been positive, the
substance that was found due to the color
presence may not be the actual substance
that was involved.
It is a carcinogen which has been used as
part of a test for cyanide and also in the
synthesis of dyes. It has been linked to
bladder cancer and pancreatic cancer.
It is highly sensitive.
Hemastix
•
•
•
•
Presumptive field test for blood
Designed as a dipstick test for blood
Involves moistening a strip in distilled water
and then placing it into contact with a
suspect blood stain
If the strip appears to turn green, it is
positive for blood
Strength and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Easy to use
Can be used on the field easily
•
•
Weaknesses:
Not as accurate as the Kastle-Meyer or
Benzidine tests
•
Susan May Case
•
On March 12, 1992, Susan May was visiting
her aunt Hilda Marchbank. She arrived at
the house at approximately 9:30 am and
discovered Hilda dead on her bed. She was
savagely beaten on her head and face and
was smothered with a pillow.
Susan May Case
•
•
•
•
Investigators found a number of stains that
appeared as blood on the walls of the scene.
The Kastle-Meyer tests was performed to
indicate whether it was blood or not
Some of the stains contained Susan May's
blood
Susan May was arrested on March 30, 1992
in connection with the murder of Hilda
Marchbank
Meredith Kercher Case
•
•
•
Meredith Kercher was found dead in the
bedroom of her apartment in Perugia, Italy.
She had several stab wounds in her throat.
The Kastle-Meyer test was performed on a
substance that appeared to be blood and
came back positive.
However, this could have been wrong
because the pink color could have been
caused by reagents used in fingerprint
analysis.
Review Questions
1. What are color tests used for?
2. What are the three tests mentioned in this
presentation?
3. What color does a positive Kastle-Meyer
tests turn?
4. What is one
5. What color does the Benzidine test turn?
6. Why was the Benzidine test discontinued?
7. What color does a hemastix strip turn if it is
positive for blood?
Sources
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Saferstein, R. (2011). Forensic Science - An Introduction (Second ed., p. 293). Upper Saddle
River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Bloodstains. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2, 2013, from
http://www.bcps.org/offices/science/secondary/forensic/Bloodstain.pdf
Benzidine (CASRN 92-87-5). (n.d.). In EPA Integrated Risk Information System. Retrieved
April 2, 2013, from http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0135.htm
http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fairprojects/project_ideas/BioChem_p037.shtml#background
http://chemistry.about.com/od/homeexperiments/a/Kastle-Meyer-Test-To-Detect-Blood.htm
http://lem.ch.unito.it/didattica/infochimica/2006_Luminolo/determinazionesangue.html
http://www.susanmay.co.uk/student-report2.htm
http://viewfromwilmington.blogspot.com/2011/07/forensic-tests-for-presence-of-blood.html