Drug Metabolism
advertisement

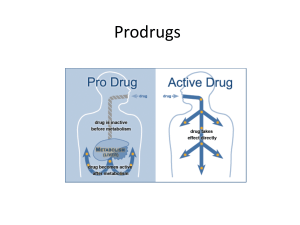
Tam Nguyen November 25, 2014 CHEM4201 Introduction What is prodrug? Why use prodrugs? Classification of prodrugs Applications of prodrugs Esters Enalapril Conclusion References Metabolism is an essential pharmacokinetic process, which renders lipid soluble and nonpolar compounds to water soluble and polar compounds so that they are excreted by various processes. Drugs are considered xenobiotics and most are extensively metabolized in humans. Not all drugs are bioavailable, in which this led to the development of prodrugs. Prodrug is a pharmacological substance administered in an inactive form. Once administered, the prodrug is metabolized in vivo into an active drug within the body through metabolic process, such as hydrolysis of an ester form of the drug. http://s2.hubimg.com/u/7766331_f520.jpg Improve membrane permeability Improve absorption and distribution Improve solubility Alter metabolism Alter toxicity Alter elimination Carrier-linked prodrugs: Simple prodrug that contains an active drug linked with a carrier group that is removed enzymatically. The carrier group must be non-toxic and biologically inactive when detached from drug. Bioprecursors: A compound that is metabolized by molecular modification into a new compound that may itself be active or further metabolized to an active metabolite. Pharmaceutical applications Improvement of taste Improvement of odour Reduction of irritation Reduction of pain on injection Enhancement of drug solubility and dissolution rate Enhancement of chemical stability of drug Pharmacokinetic applications Enhancement of provability Prevention of pre-systemic metabolism Prolongation of duration of action Reduction of toxicity Site specific drug-delivery Esters are the most commonly employed prodrugs. Numerous catalytic esterases are present in vivo to hydrolyze simple esters. Prodrug Active Form of Drug The monoethyl ester of enalaprilat Enalaprilate was first discovered as an inhibitor of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) and used to treat hypertension. Due to its high polarity, note two COOH’s, it was not orally bioavailable, and thus needed to be administered by injection. https://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/rem/2012/images/c10-fig-10-25.png http://www.drug3k.com/img4/enalapril_14733_9_(big)_.jpeg http://www.benvenue.com/online_catalog/products/enalaprilat/ _jcr_content/par/text/image.123901685.image.png Prodrugs are inactive compounds which are converted to active drugs in the body by the process of drug metabolism. Prodrugs were design to improve pharmacokinetic and drug delivery properties. Esters are commonly used as prodrugs to make a drug less polar and allowing it to cross cell membranes more easily. The nature of the ester can be altered to vary the rate of hydrolysis. Brochure concept and application of prodrugs Alagarsamy, V. (2010). Textbook of medicinal chemistry (Vol. 1, pp. 7179). New Delhi: Reed/Elsevier. Testa, B., & Mayer, J. (2003). <i>Hydrolysis in drug and prodrug metabolism: Chemistry, biochemistry, and enzymology</i>. Zürich: VHCA. Drug Metabolism. (n.d.). Retrieved November 18, 2014, from http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/drugs/administration_and_kine tics_of_drugs/drug_metabolism.html Rautio, J., Kumpulainen, H., Heimbach, T., Oliyai, R., Oh, D., Järvinen, T., & Savolainen, J. (n.d.). Prodrugs: Design and clinical applications. <i>Nature Reviews Drug Discovery,</i> 255-270. Retrieved November 18, 2014, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18219308 Pharmacological Effects, Prodrugs (Definition, Examples) and Sources of Drug Information. (n.d.). Retrieved November 18, 2014, from http://epharmacology.hubpages.com/hub/Pharmacological-EffectsProdrugs-Definition-Examples-and-Sources-of-Drug-Information