grasshopper PowerPoint Presentation
advertisement

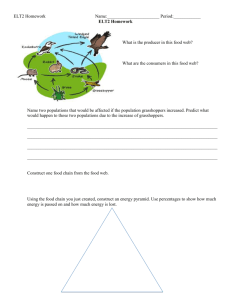
International Conference on Food Technology : Impact on Nutrition and Health ( ICFIN-2013) Grasshoppers: Food Security & Nutrition Aman Paul1, Sabine Danthine1, Michel Frederich2, Roel Uyttenbroeck1 & Frederic Francis1 1Gembloux Agro-Bio Tech (Belgium) 2Department of Pharmacy, University of Liege (Belgium) Contents • • • • • • • Concept- Entomophagy Eating Grasshoppers Multifarious Aspects Edible Species of Grasshoppers in Belgium Lab Rearing of Grasshoppers Protein & Fat Content of Lab Reared Species Conclusion Entomophagy Consumption of insects as human food Over 1900 insect species are popularly eaten in many parts of the world Important source of proteins, lipids and some minor components High social value to people who believe they have good nutritive and pharmaceutical properties Heavily influenced by local cultural and religious practices Eating Grasshoppers • About 80 species of grasshoppers are edible and consumed worldwide • They have lots of qualities: most important being primary consumers, univoltines, constitute enormous biomass, etc. • They not only serve as an important source of proteins and lipids but also some minor components like vitamins and minerals • Average nutrient composition of grasshoppers is shown below: Protein (N=40) Fat (N=38) Fibre (N=38) NFE (N=36) Ash (N=38) Nutrient Composition Eating Grasshoppers (Continued…) Proteins • Average protein content is 63.93% • They are also an important source of essential amino acids Fats Vitamins & Minerals • Average fat content is 11.38% (R. differens: 48% being highest) • They are a rich source of PUFA • They are source of magnesium and zinc • R. differens is a good source of αtocopherol, riboflavin and folic acid Multifarious Aspects Nutrition Environment Zoonotic Infection Green House Gas Production Water Requirement Feed Conversion Ratio % Edibility Crickets (1.7) Crickets Poultry Beef Poultry (2.5) 80% 55% 40% Beef (10) Edible Species of Grasshoppers in Belgium Conocephalus discolor Chorthippus parallelus Chorthippus biguttulus Chorthippus brunneus Tettigonia viridissima Lab Rearing of Grasshoppers Parameters Light: 12L-12D light hours (100 W bulb) Temperature: 28°C Humidity: 65% Collection of Egg For Laying Eggs Sieving Storage of eggs The eggs are stored in two phases: 1. Four weeks at 30°C 2. 16 weeks at 5°C Then the eggs are again brought at room temperature for hatching Protein & Fat Content of Lab Reared Species Lipid Content Protein Content (Dumas Method) Chorthippus parallelus 7.00% (Dry Weight) 77.80% (Dry Weight) Conocephalus discolor 13.07% (Dry Weight) 78.41% (Dry Weight) Product Protein % Whole Milk 3.15 Whole Egg 12.56 Beef 23.07 Cooked Salmon 25.44 Chicken 28.04 Source USFDA Method: Lipid extraction was done by a cold extraction technique using 2:1 chloroform/methanol as solvent Conclusion About 80 species of grasshoppers are consumed worldwide, which not only serve as an important source of proteins & fats but also minor components such as vitamins and minerals. Apart from being nutritionally superior to most conventional meats their production results in -lower emission ammonia, of greenhouse gases & -risk of zoonotic infections in humans is much lower, -water requirement for production is much less and -have higher feed conversion ratio. Lab rearing of grasshopper can be done to produce considerable amount of biomass enough for human consumption. The two edible grasshopper species Conocephalus discolour and Chorthippus parallelus have -13.0% & 7.0% fat content and -78.4 % & 77.8% proteins content respectively (on dry weight)