Food Group Pwr Pt Nov 6 2010
advertisement

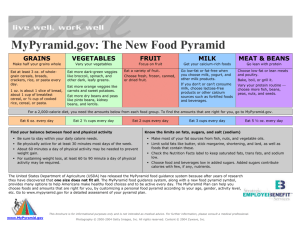
the FOOD Pyramid Steps to a healthier you EQ: What is the proper way to eat healthy? Eating Right Every Day Achieving a Balanced Diet Use the Food Guide Pyramid as you select foods. Remember these guidelines: • Eat at least the minimum number of servings from 5 food groups • Choose low-fat and lean options • Have a colorful plate • Know what a single serving is • Limit intake of fats, oils, and sweets • Average 2,000 calorie diet The Old Food Pyramid The Food Pyramid Steps to a healthier you Grains Vegetables Fruit Milk Meat and Beans What’s on the pyramid 5 food groups • Grains, Fruits, Vegetables, Milk and Meat/beans Oils, fats, and sweets should be used sparingly Physical activity impacts how much your calorie intake needs to be. New Pyramid One size doesn't fit all. •MyPyramid offers personalized eating plans, interactive tools to help you plan and assess your food choices, and advice to help you. •Now personalized to YOU based upon Age Gender Weight Height Physical activity Examples A 15 year old male, 5 feet 9 inches tall, 150 pounds, physically active less than 30 minutes a day.) Grains - 9 ounces Vegetables - 3.5 cups Fruits 2 cups Milk - 3 cups Meat/Beans - 6.5 ounces A 15 year old female, 5 feet 4 inches tall, 120 pounds, physically active less than 30 minutes a day. Grains - 6 ounces Vegetables - 2.5 cups Fruits – 1.5 cups Milk - 3 cups Meat/Beans - 5 ounces http://www.mypyramid.gov/mypyramid/index.aspx *** Complete a personalized plan for yourself, print and turn in for extra credit on quiz! Grains Make half of your grains whole Any food made from wheat, rice, oats, cornmeal, barley or another cereal grain is a grain product. Bread, pasta, oatmeal, breakfast cereals, tortillas, and grits are examples of grain products. Grains are divided into 2 subgroups: Whole grains • Whole grain bread • oatmeal • brown rice Refined grains • Are milled, a process that removes the bran and germ. • Done to give grains a finer texture and improve shelf life • But it also removes dietary fiber, iron, and many B vitamins. • Ex: white bread, white rice • Most refined grains are enriched. This means certain B vitamins and iron are added back. • Fiber is not added back in http://www.mypyramid.gov/pyramid/grains.html Vegetables Vary your veggies Any vegetable or 100% vegetable juice. Raw or cooked; fresh, frozen, canned, or dried/dehydrated Vegetables are organized into 5 subgroups, based on their nutrient content. Dark green vegetables: spinach, broccoli, dark green leafy lettuce Orange vegetables: carrots, pumpkin, sweet potatoes Dry beans and peas: black beans, black-eyed peas, kidney beans, soy beans Starchy vegetables: corn, green peas, lima beans, potatoes Other vegetables: beets, brussels sprouts, cabbage, celery, cucumbers http://www.mypyramid.gov/pyramid/vegetables.html# Fruits Focus on fruits Any fruit or 100% fruit juice Fresh, canned, frozen, or dried Some commonly eaten fruits are: • Oranges, apples, bananas, berries, grapes http://www.mypyramid.gov/pyramid/fruits.html Oils Know your fats Oils - Fats that are liquid at room temperature, like the vegetable oils used in cooking, come from many different plants and from fish. • Ex: canola oil, olive oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil Solid fats are fats that are solid at room temperature and come from many animal foods. • They also are the worst because they contain more saturated fats and/or trans fat. • Ex: butter, chicken fat, pork fat (lard), stick margarine A number of foods are naturally high in oils, like: nuts, olives, and some fish • Most Americans consume enough oil in the foods they eat. Limit the intake of oils/fat as much as possible Milk Get your calcium rich foods All fluid milk products Foods made from milk that retain their calcium content are part of the group, • If they have little to no calcium, such as cream cheese, cream, and butter, they are not. Most milk group choices should be fat-free or low-fat. Examples • All fluid milk, puddings made with milk, yogurt, ice cream, hard natural cheeses, cheddar, mozzarella, swiss frozen http://www.mypyramid.gov/pyramid/milk.html Meat and Bean Go lean on protein Meat, poultry, fish, and dry beans or peas, eggs, nuts, and seeds Dry beans and peas are part of this group as well as the vegetable group. Most meat and poultry choices should be lean or low-fat. Fish, nuts, and seeds contain healthy oils http://www.mypyramid.gov/pyramid/meat.html Influence on Diet Diet influenced by: • cultural background • socioeconomic status • time Usually make choices from familiar foods served at home American Diet Fatty foods – hamburgers and french fries Sugars – sweets, milkshakes, soft drinks Sodium – potato chips Avoid: Fast Food and “Junk food” • Junk food - A high-calorie food that is low in nutritional value. Moderation is the key when dealing with unhealthy things • Within reasonable limits One serving size is usually smaller than what you think 1 gram of fat = about 9 calories Snacking – good or bad? Not all snacking is bad Some eat small amounts of food through the day, instead of big meals Needs to be healthy snacking Dangers with snacking • Adds extra calories to diet • Non-nutritious foods • Late at night http://www.mypyramid.gov/pyramid/discretionary_calories.html Food Additives Substances intentionally added to food either directly or indirectly • Maintain or improve nutritional quality • Maintain quality and freshness • Aid in the processing or preparation of food • To make food more appealing and tasteful The Nutrition Food Label Serving Sizes Calories from Fat % Daily Value, 2,000 calorie diet Fat Cholesterol Sodium Carbohydrates Protein Vitamins and Minerals http://www.fda.gov/Food/Lab elingNutrition/ConsumerInform ation/ucm078889.htm#twopart s What counts as a one serving? 1 slice of bread ½ cup cooked cereal, rice, pasta 1 medium whole fruit ¾ cup of juice ½ cup of cooked vegetables 3 ounces cooked meat (size of a deck of cards) Find your balance between food and physical activity (Left off notes, need to add into yours please!) ● Be sure to stay within your daily calorie needs. ● Be physically active for at least 30 minutes most days of the week. ● About 60 minutes a day may be needed to prevent weight gain. ● For sustaining weight loss, at least 60 to 90 minutes a day may be required. ● Children and teenagers should be physically active for 60 minutes every day, or most days. http://www.mypyramid.gov/pyramid/calories_used.html# Determining your Calorie Needs Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) The rate at which your body burns food and nutrients to perform normal, minimal bodily functions at rest. Females = 1,200 calories per day Males = 1,500 calories per day Sedentary Person - very little activity - add 200-300 calories per day Average Person - moderate activity - add about 1,000 calories per day Extremely active person - add from 1,800 to 3,800 calories per day Nutrition Fallacies Consuming extra protein will lead to greater or faster strength development. • Excess protein in diet is stored in the form of fat . Taking vitamin supplements will give you more energy. • Vitamins assist body in using nutrients to provide you with energy, excess does nothing Take salt tablets if you perspire a lot. • Your normal diet supplies you with enough, and the body learns to conserve salt so you do not lose to much in your sweat. Drink a sports drink after exercise. • Only small amounts of minerals are loss in sweat and can be replaced with food. • meant for endurance sports Drink caffeine to improve athletic performance. • Does stimulate central nervous system and tends to increase alertness