vHTS
advertisement

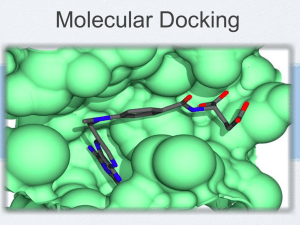
Tecniche vHTS per il Drug Design Drug Discovery is: interdisciplinary expensive time-consuming Drug Discovery is: Disease target identification Discovery and optimization of lead structures Clinical tests and approval Survey of about 50 companies 75% efforts lost due to failures! Single new drug: $880 million 15 years development In silico Drug Discovery Bioinformatics: biological target identification and validation Cheminformatics: search for and optimization of chemical lead structures Cost saving: $130 million Time saving: 0.8 years Outline: 1. Cheminformatics: vHTS 2. Bioinformatics: Systemic approaches Real vs. In Silico HTS Flexibility In Silico vHTS Cost-effectiveness Speed vHTS: modelling molecular recognition Highly sophisticated way to query databases Strongly simplified simulation of high-throughput screening essays vHTS Principle of similarity Principle of complementarity vHTS: principle of similarity (ligand based) If one or more active compounds are known Search databases for more potent molecules Three categories: Alignment / Superimposition Pharmacophore modeling Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) Ligand-based methods: Alignment Single 3D structure as a template Superpositioning and scoring of molecules from databases Scoring: steric and physicochemical properties Ligand-based methods: Pharmacofores A pharmacophore is the 3D arrangement of chemical groups that is required for the biological activity of a molecule 1. Generated from a series of known active compounds 2. Database-search for molecules that fulfill the specified geometrical constraints Metodi Ligand Based: QSAR QSAR methods are statistical approaches that correlate biological data with molecular descriptors to derive QSAR models. QSAR models are then used to predict the activity of novel compounds vHTS: modelling molecular recognition Highly sophisticated way to query databases Strongly simplified simulation of high-throughput screening essays vHTS Principle of similarity Principle of complementarity Drug Design and Structural Genomics 72717 structures (27 April 2011) vHTS: principle of complementarity (receptor based) Knowledge of the receptor 3D structure allows… …screening for molecules that fit the active site Receptor Based Methods: Docking Metodi Receptor Based: Docking 3D Structure Determination Site Representation Site Identification/Characterization Ligand Generation Docking De Novo Design Scoring DGbind = DGcomplex – (DGligand – DGreceptor) DGbind = -RT ln Keq = -RT ln Kd Metodi Receptor Based: Docking Problem 1: PES sampling Receptor flexibility: • Difficult to predict from X-ray data • Computationally unfeasible in HTS Ligand flexibility Problem 2: Scoring and rankings Computational time limits (vHTS) Empirical forcefield Consensus scoring Our job: Sampling the PES of molecules Energia di una molecola in funzione delle coordinate atomiche • minimi: conformazioni • punti sella: stati di transizione QM-based methods • QM methods are based on the following principles: • Nuclei and electrons are distinguished from each other. • Electron-electron (usually averaged) and electron-nuclear interactions are explicit. • Interactions are governed by nuclear and electron charges (i.e. potential energy) and electron motions. Interactions determine the spatial distribution of nuclei and electrons and their energies. MM-based methods MM methods are based on the following principles: Nuclei and electrons are lumped into atom-like particles. Atom-like particles are spherical and have a net charge. Interactions are based on springs and classical potentials. Interactions must be preassigned to specific sets of atoms. Interactions determine the spatial distribution of atom-like particles and their energies. ADMET Full power of in silico screening of large databases: Integration of virtual molecular recognition with… …filter algorithms for ADMET Adsorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion Toxicity Conclusions: what really is vHTS? It is not: the recipe to discover a new drug a single method a stand-alone approach It is: a tool to drive rational screening the integration of several methods a key actor in drug discovery

![Shark Electrosense: physiology and circuit model []](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005306781_1-34d5e86294a52e9275a69716495e2e51-300x300.png)