PowerPoint
advertisement
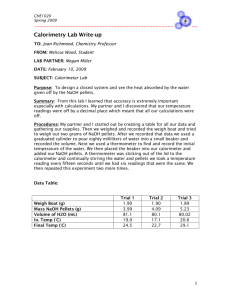
Calorimetry 6.03 Honors 6.03 Calorimetry honors In this experiment, you will determine the quantity of heat involved in two different chemical processes. The heat given off or absorbed will be measured using an insulated calorimeter. Be sure to record all measurements carefully, as you will use the data to calculate the enthalpy change of each process. Procedure Part I: The Dissolving of Solid Sodium Hydroxide in Water 1. Measure out approximately 200 mL of distilled water and pour it into the calorimeter. Stir carefully with a thermometer until a constant temperature is reached. Record the volume of water and the constant initial temperature of the water on your data table. 2. Place a plastic measuring trough on top of the digital balance, and then zero the balance (press the tare button) so that the mass of the trough will be “ignored” and will not be added to the total mass measured by the balance. 3. Measure out approximately three to five scoops of solid sodium hydroxide and record the mass to your data table. 4. Place the solid sodium hydroxide into the water in the calorimeter and replace the lid immediately. Stir gently until the solid is completely dissolved and record the highest temperature reached. Procedure cont. Part II: The Reaction of Sodium Hydroxide Solution with Hydrochloric Acid 1. Measure out approximately 100 mL of 0.50 M HCl solution and 100 mL of 0.50 M NaOH solution. Record both volumes on your data table. 2. Pour the hydrochloric acid solution into the calorimeter. Measure and record the initial temperature of each solution and record on your data table. 3. Add the sodium hydroxide solution to the acid solution in the calorimeter and immediately replace the lid of the calorimeter. Stir the mixture and record the highest temperature reached. Data and Observations – Part I Data and Observations – Part II Recipe for success Part I: The Dissolving of Solid Sodium Hydroxide in Water 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Calculate mol of NaOH, n = grams/molar mass q = m × c × Δt m reactants = mass water + mass NaOH Convert q from joules to kilojoules Divide kJ by moles of NaOH to solve for ΔH (KJ/mol) ΔH = q/n 6. Then ΔH surroundings = - ΔH system Recipe for Success Part II: The Reaction of Sodium Hydroxide Solution with Hydrochloric Acid • Calculate mol of NaOH, n = M x V, M = 0.5 M and V = 100 mL (convert to L) • q = m × c × Δt m reactants = mass NaOH solution + mass HCl solution • Convert q from Joule to kiloJoule • Divide kJ by moles of NaOH to solve for ΔH (KJ/mol) ΔH = q/n • Then ΔH surroundings = - ΔH system Conclusion 1. Use calculated values in Hess’s law to solve for the enthalpy change of the given reaction. ΔH [1] + ΔH [2] = ΔH [3] NaOH (s) + H2O (l) → NaOH (aq) [1] NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) [2] NaOH (s) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) [3] Conclusion 2. If the accepted enthalpy change value for the dissolving of sodium hydroxide in water is −44.2 kilojoules per mole, determine the percent error of the experimental value that you calculated in Part I. Show your work.(2 points) ΔH [1] % error = accepted enthalpy change value – experimental enthalpy change value × 100 = accepted enthalpy change value Conclusion 3. Give a detailed explanation, using what you know about bonds and forces of attraction, for the enthalpy changes you observed in parts I and II of this lab. http://www.docbrown.info/page03/3_51energy.htm Conclusion 4. If the hole for the thermometer in a calorimeter is wider than the diameter of the thermometer, leaving a gap between the lid and the thermometer itself, how do you think this would this affect the temperature change observed in the experiment? How would this affect the calculated enthalpy change?