Human Inheritance
Key Concepts
1. What are some patterns of
inheritance in humans?
2. What are the functions of the sex
chromosomes?
3. What is the relationship between
genes and the environment?
Key Terms
Multiple alleles
Sex chromosomes
Sex-linked genes
carrier
Patterns of Human Inheritance
Human traits are controlled by:
◦ single genes with two alleles
◦ others by single genes with multiple alleles.
◦ Still other traits are controlled by many genes
that act together
Single Gene with Two Alleles
Have 1 dominant and 1 recessive allele
Have 2 distinctly different phenotypes
Ex. Widow’s Peak
◦ Smile dimples – Draw a Punnett Square that
shows a cross between two heterozygotes for
smile dimples
Single Genes with Multiple Alleles
Some traits have more than 2 alleles
although a person can have only 2 of
those alleles because chromosomes exist
in pairs. Each chromosome in a pair
carries only 1 allele for each gene
Ex. Human blood type –
3 alleles A, B, O
A and B are codominant
O is recessive
Traits Controlled by Many Genes
Produce a large variety of phenotypes
Genes act together as a group to produce
a single trait
Ex. Height – at least 4 genes
◦ Skin color – at least 3 genes
Question: In our face trait lab most of the
children had dark colored
skin. What was the
assumption about the
parents that caused this
result?
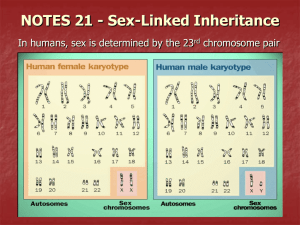
The Sex Chromosomes
One of the 23 pairs of chromosomes that
carries the genes that determine whether
a person is male or female
Also carries genes that determine other
traits
Girl or Boy?
The only chromosome
pair that does not always
match
Girl – two sex
chromosomes match
(X,X)
Boy –don’t match, one is
an X other is a Y
◦ The Y chromosome is
smaller than the X
Sex Chromosomes and Fertilization
Egg cells all carry an X chromosome
Sperm cells carry either an X or a Y
When a sperm cell with an X
chromosome fertilizes an egg cell, the egg
has 2 X’s = girl
When a sperm cell with a Y chromosome
fertilizes an egg cell, the egg has an X and
a Y = boy
Sex-linked Genes
Genes for some human traits are carried
on the sex chromosomes
Traits controlled by sex-linked genes are
called sex-linked traits
EX. Red-green colorblindness
Most of the genes on the X chromosome
are not on the Y chromosome
An allele on the X may not have a match on
the Y
Sex-Linked Genes
Sex-linked genes can have dominant and
recessive alleles
In females a dominant allele on one x will
mask a recessive on the other X
In males, there is no matching allele on
the Y to mask a recessive allele on the X
Any trait on the X chromosome in males
(even a recessive trait) will produce the
trait in a male who inherits it.
Inheritance of Colorblindness
Colorblindness is a trait controlled by a
recessive allele on the X chromosome
Many more males have colorblindness
than females
Females can be carriers. They have one
dominant trait for normal color vision and
one recessive trait for colorblindness.
They have normal color vision
Red-Green Colorblindness
Inheritance of Colorblindness
If the mother passes on the X
chromosome to a son, he will be
colorblind
If she passes it onto a daughter, she will
also have an X chromosome from her
father. If her father has normal color
vision, then she will inherit the dominant
allele for normal color vision from him
and she will have normal color vision
Test for Red Green Colorblindness
Inheritance of Colorblindness
Father XCY
XC
Y
XC
XCXC
XCY
XCXc
XcY
Mother
XCXc
Xc
The Effect of Environment
Many of a person’s characteristics are
determined by an interaction between
genes and the environment
Several genes work together to determine
height
Environment affects height – a poor diet
can prevent a person from reaching their
potential
Environmental factors can also affect
human skills – Ex. Playing a musical
instrument – need instruction to play well