File - Coach Nowell
advertisement

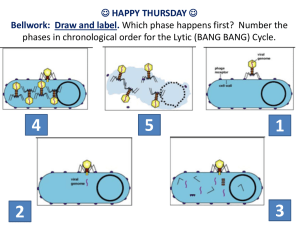
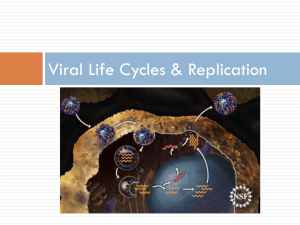
Viruses Something you don’t want to catch… Viruses 1. How do scientists classify things as living? 1. Made of cells 2. Has a metabolism to grow and reproduce 3. Information stored in DNA 2. Are viruses alive? NO! Living or Nonliving? NONLIVING LIVING Viruses 3. What do viruses and living organisms have in common? • Both use nucleic acids to store genetic information in the form of DNA or RNA • Both change over time (evolve) Viruses 4. If viruses do not have their own metabolism to grow and reproduce, how do they survive? • By hijacking living cells and using their metabolism to grow and reproduce. There are 2 types of viral infections • Lytic infection- a virus enters a cell, makes copies of itself, and causes cell to burst . • Lysogenic infection- a virus integrates its DNA into the DNA of the host cell, and the viral genetic information replicates along with the host cell’s DNA. Viral Reproduction – Lytic Cycle • Lytic Cycle • Attaches to host (1) • Injects genetic material into host(2) • Cellular machinery duplicates genetic material and creates viral proteins (capsids, tail fibers) (3) • New viruses are assembled (4) • New viruses exit the cell by bursting the cellular membrane (5) • End result – more viruses made, cell dies Viral Reproduction – Lytic Cycle Attachment Lytic Cycle Entry Release Assembly Replication Viral Reproduction – Lysogenic Cycle • Lysogenic Cycle • • • • • Attaches to host Injects genetic material into host Viral genetic material is inserted into host genome (6) Viral genetic material lies dormant (6) When cell reproduces, new copies have viral genetic information (7) • When virus is ready to exit dormant stage it will separate from cell’s DNA and enter Lytic cycle (8) • End result – more viral genome made, cell lives Viral Reproduction – Lysogenic Cycle Lysogenic Cycle Attachment Entry Separation Insertion Reproduction Viral Reproduction Lytic Cycle •New viruses made •Cellular host dies Lysogenic Cycle •Genome copies made •Cellular host lives Viruses can use both cycles 1.Infect many cells with lysogenic 2.Create many viruses at once with lytic Viral Reproduction Lytic & Lysogenic Cycles Virus Types • Bacteriophages = are viruses that attack bacteria • Retroviruses = viruses that use RNA to reverse transcribe DNA that integrates into the host genome. Example: HIV More Virus Types • What makes these viruses different from bacteria? THEY ARE NOT LIVING ! CHECK POINT • This graphic shows a virus’ _____ _______. A. Viral Reproduction B. Viral Transription How do you treat a virus? • Remember you cannot treat a viral infection but you can prevent one by getting a vaccine. Vaccine A vaccine improves immunity to a particular disease. How do vaccines work? • A vaccine contains a weakened strain of the microbe. •When injected into your body it stimulates your immune system to recognize it as foreign, destroy it, and remember it. • So if your body encounters the full strain later, it can easily recognize and destroy it!!!!! http://health.howstuffworks.com/adam-200097.htm SUMMARY Important facts about viruses • Viruses must be produced within living cells • Viruses destroy the living cells they grow in • Viruses gain entry by specific receptors on the host cell Viruses •How do you catch many viruses? Through body fluids. •What are your chances of catching a virus from someone in this classroom? Viral Diseases - AIDS • AIDS – acquired immune deficiency syndrome • Describes loss of immune system because of HIV • Caused by HIV - human immunodeficiency virus • makes helper T cells useless • Prevention • No vaccine • Limit transmission (use condoms) • Avoid transmission (use clean needles) Viral Diseases – AIDS – HIV Replication Viral Diseases - AIDS • Initial infection • Helper T cells rapidly decline • Viral genome rapidly increases • Clinical latency • Viral genomes lay mostly dormant in infected cells • AIDS • Rate of viral creation outweighs helper T cell creation • Death • Immune system too weak to fight common pathogens Viral Diseases - Influenza • Influenza (the flu) • Causes fever, fatigue, and respiratory infections • More severe than common cold, can be deadly • Caused by a variety of influenza viruses – Change often, new vaccines yearly – Can blend with bird and swine strains to produce new viruses • Prevention – Seasonal vaccine – Limit transmission (wash hands) Image by NIAD [Public Domain] Viral Diseases – Common Cold • The Common Cold • Causes fever, fatigue, and respiratory infections • Less severe than influenza • Caused by a variety rhinoviruses • Over 200 different virus strains • Prevention • No vaccine • Limit transmission (wash hands) Image by Robin S [GNU] Viral Diseases – Hepatitis A • Hepatitis A • Causes inflammation of liver, jaundice appearance • Rarely results in liver failure • Caused by a hepatitis A virus • Carried through infected food or water • Prevention • Vaccine • Limit transmission (wash hands, food) Image by The CDC [Public Domain]