Protista II

PROTISTA II
Mostly SINGLE CELLED
PHOTOSYNTHETIC AUTOTROPHIC
Eukaryotes - Algae
Secondary Endosymbiosis
Green Algae
Fig. 28.3
Cryptomonad
–Cryptomonad algae chloroplast still
–contain a vestigial nucleus called a nucleomorph
.
Tertiary Endosymbiosis ?!! Fig. 28.25
Origins of plastids,
Not phylogeny of
Cell (cytoplasm) itself.
Dinoflagellate
Dinoflagellata
• Cellulose cell walls
• Phytoplankton- base of food chain
• 2 flagella
– One in transverse grove
– One propels them along
– Spiral in water as they swim
– Cause red tides – toxic
– Bioluminescence
– zooxanthellae
Stramenophiles
Water “Molds” & Diatoms
Brown Algae
Oomycota
• Water “molds”
• Hyphae
• Diploid dominant
• Swimming zoospores
• Cellulose cell walls
• Saprobic & disease causing
– Potato blight
– Sudden Oak Death
• Attacks goldfish
Saprolegnia
Bacillariophyta
• Diatoms
• Plates of SiO
2
• Ripple membrane along plate to move ???
• Golden brown color- pigments
• Diatomaceous earth – microfossils
• Major autotroph in cold water
BACILLARIOPHYTA (DIATOMS)
• Cell wall of silica
• Cell wall consists of two valves
• Buoyancy
• Pigments
– Chlorophyll a and d
– Fucoxyanthin
– Xanthophyll, -accessory
Diatoms
Synedra sp.
Phaeophyta
• Brown Algae- the Kelps
• Can grow large !!! Fast !!
• Use Chlorophyll a & Fucoxyanthin as pigments
– Holdfast
– Stipe
– Blade
• We’ll see them at M Bay Aquarium, or
Bodega Bay
PHAEOPHYTA
• Mostly marine
• Largest Algae
• Kelp
• Pigments
– Chlorophyll a and fucoxanthin
• Blade
• Stipe
• Holdfast
Nereocystis
Fucus
Gas Bladder
Male Plant with Antheridia conceptacle
Female Plant with Oogonia conceptacle
RHODOPHYTA
• Mostly marine
• Pigments
– Chlorophyll a
– Phycobilins – phycocyanin & phycoerythrin
Rhodophyta
• Red Algae
• Carageenan
• Agar
• Use chlorophyll a & Phycoerithrin , phycocyanin as pigments
Polisiphonia n= female plant
Makes n carpospres that become 2n zygotes
2n –plant
Makes
N tetraspores n= male plant
Makes n spermatia
2n –plant Makes (n) tetraspores
female plant (n)
Makes carpospores that become 2n zygotes male plant (n) makes spermatia
Multicellularity
• Arose independently several times in
Eukarya
• Caused another new wave in evolution
• Origins in simpler colonial forms –
Volvox
• Cellular specialization and Division of labor
• Escape cell size limitations
– Membrane area to cytoplasm volume ratio
• Multicellularity solves ratio limits Fig 7.5
Viridiplantae??
Red Algae
Green Algae
Plants
Tentative
Phylogeny
Fig 28.8
CHLOROPHYTA
• Most fresh water, some marine, symbiotic with fungi in lichens.
• Chlorophyll a and b, carotenoids
• Cellulose cell walls
Chlamydomonas
Pandorina
Pandorina
Desmids
Spyrogyra
Spirogyra conjugation
Volvox
Volvox sp.
Volvox zygotes
Oedogonium sp.
Oedogonium
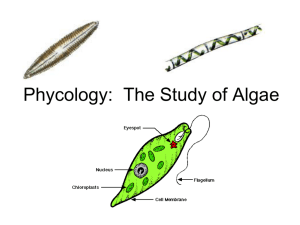
Euglena – example of cellular complexity in Protists
Ulva sp.
Dinoflagellates
• Two flagella one wrapped inside grove.
• Cell walls of cellulose
• Can cause red-tides – and disease for some organisms
• Similar pigments to red algae
KINGDOM PARABASALA
Phylum Euglenophyta
Euglena – example of cellular complexity in Protists
Physarum
Physarum (Life Cycle)