Cell Biology: Unity of Life, Microscopes, and Cell Theory
advertisement
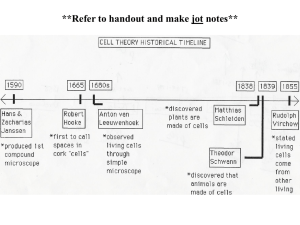
UNITY OF LIFE A STUDY OF CELLS Despite vast differences in appearance and ways of life, all living things have a unity of life. They are all composed of cells that are similar in structure and function. Some organisms such as Paramecuim and Euglena, are made of only one cell. In more complex, multicellular organisms, the cells may perform more specialized functions, but all have certain features in common. Before we begin our study of cells. It is necessary to discuss the instrument that allowed people to see cells in the first place! This discovery lead to our modern Cell Theory MICROSCOPES • 1590- The first microscope is built by Zacharias Janssen • 1670’s Anton von Leeuwenhoek built a simple microscope that could magnify objects 270X. Compound light microscope • The compound light microscope is widely used in science. The term light refers to the method by which light transmits the image to your eye. Compound deals with the microscope having more than one lens. Microscope is the combination of two words; "micro" meaning small and "scope" meaning view. Stereomicroscope • • • • Also called dissecting scope Has two eyepieces (binocular) Objects are seen in 3-D Does not have high power, use to observe relatively large objects such as insects or crystals Phase-contrast microscope • Allows observer to distinguish different structures within a cell, without staining, using light waves. Electron microscope • Uses a beam of electrons instead of light rays • Can provide magnifications of 200,000X • Tissues must be thinly sliced, dry and in a vacuum chamber, therefore electron microscopes cannot be used to view living specimens The surface of a strawberry Bacteria on the surface of the human tongue Head of zebra fish embryo Stem surface of a black walnut tree Lettuce leaf, showing stomate with E.coli bacteria inside Micro-dissection apparatus Centrifuge Cell Theory • 1665- Robert Hooke looked at cork with his compound light microscope and saw walled compartments, he called “CELLS” 1831- Robert Brown ( Scottish botanist) • Discovers the nucleus of the cell. • 1838- Matthias Schleiden ( German botanist) concluded “All plants are made of cells” • 1839- Theodor Schwann (German zoologist) said “All animals are composed of cells” • 1839- Johannes Purkinje- (Czech physiologist) discovered cytoplasm. • 1858- Rudolph Virchow (German biologist) said “Cells arise from other cells by cell reproduction” CELL THEORY • • • • 1. Cells are the basic unit of life ( How else could we express this idea?) 2. Cells come from pre-existing cells. (How else could this idea be expressed?) Exceptions to cell theory • Viruses • First cell? • Mitochondria and chloroplasts CELLS • There are two basic types of cells • Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic • Prokaryotic cells- (also called prokaryotes) belong to the kingdoms Eubacteria & Archaebacteria, are very small, 1-10 micrometers, have no nucleus and few organelles. They are primitive cells. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells (also called eukaryotes) • Larger than prokaryotes, 10100micrometers • Have nucleus • Have organelles • Complex cells • Protists, Fungi, Plants and Animals all have eukaryotic cells Cell Organelles • Tiny structures within a cell that perform various, specialized functions , such as transporting materials, building important biological substances, secreting products, releasing energy from food molecules, etc. Cell Organelles • Cell (plasma) membrane- separates the cell from its environment. • Consists of a double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins. • Called fluid-mosaic model • Selectively permeable membrane protein steroid glycoprotein Head of lipid Tail of lipid phospholipid protein Transport protein CYTOPLASM • Jelly-like fluid that fills the interior of the cell Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) • Network of tubes found throughout cytoplasm • Transports materials around the cell Ribosomes • Site of protein synthesis • Rough ER has ribosomes attached to its walls • Smooth ER has no ribosomes attached to its walls GOLGI COMPLEX • Look like flattened sacs • Function in the secretion of products produced in the cell. • Act like the “packaging and shipping department “ MITOCHONDRIA • Look like short rods or tiny spheres • Site of cellular respiration, (chemical reactions that release energy from food molecules) • “powerhouse of the cell” MICROTUBULES • Long, slender tubes that give the cell structure and support MICROFILAMENTS • Long thin threads attached to cell membranes • Aid in cell movement Lysosomes • • • • Small, oval organelles Contain digestive enzymes Digest food molecules Destroy old cells NUCLEUS • Contains chromosomes • Directs the activities of the cell • “Control center of the cell” NUCLEOLUS • Found inside the nucleus • Produces ribosomes • Produces nucleotides <> CENTRIOLES • Found in the cytoplasm of animal cells • Cylinder of tiny tubes • Important in cell division CILIA & FLAGELLA • Cilia are tiny hair-like structures on outside of cell • Flagella are long projections from cell membrane • Aid in movement of cell and in movement of materials VACUOLE • Storage sacs in the cell • May store many different materials. Ex: Food, water ,wastes CHLOROPLAST • Found in photosynthetic organisms- plants, algae, some bacteria • Site of photosynthesis • Contain chlorophyll CELL WALL • Found in plant cells, fungi and bacterial cells • Surrounds and protects the cell • Composed of cellulose • Supports the cell DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS • • • • Plant cell Cell wall Chloroplasts Large vacuole • Animal cell • Centrioles • Small vacuoles WHERE DO CELLS COME FROM?????????? ABIOGENESIS • Spontaneous generation • Living organisms can come from non living things Spontaneous Generation •The idea that organisms originate directly from nonliving matter. •"life from nonlife" •abiogenesis - (a-not bio-life genesis-origin) These Scientist ran experiments to prove or disprove the theory of spontaneous generation. Review their experiments and attempt to answer the questions on the end. Listen to this story Fancesco Redi One of the first to disprove spontaneous generation. An Italian doctor who proved maggots came from flies. (Italian 1668) Lazzaro Spallanzani - One of the first to disprove spontaneous generation. An Italian scientist who proved microorganisms could be killed by boiling. (Italian 1767) Louis Pasteur - One of the first to disprove spontaneous generation. A French scientist who proved that micro organisms were carried by dust not air. (French 1864) Redi's Problem Where do maggots come from? Hypothesis: Maggots come from flies. Redi put meat into three separate jars. Jar 1 was left open Jar 2 was covered with netting Jar 3 was sealed from the outside Redi's Experiment Step 1 Jar-1 Left open Maggots developed Flies were observed laying eggs on the meat in the open jar Redi's Experiment Step 2 Jar-2 Covered with netting Maggots appeared on the netting Flies were observed laying eggs on the netting Redi's Experiment Step 3 Jar-3 Sealed No maggots developed Spallanzani's Problem What causes microbes to form in decaying broth? Hypothesis: Microbes come from the air. Boiling will kill microorganisms. Spallanzani put broth into four flasks Flask 1 was left open Flask 2 was sealed Flask 3 was boiled and then left open Flask 4 was boiled and then sealed Spallanzani's Experiment Step 1 Flask-1 Left Open Turned cloudy Microbes were found Spallanzani's Experiment Step 2 Flask-2 Sealed Turned cloudy Microbes were found Spallanzani's Experiment Step 3 Flask-3 Boiled and left open Turned cloudy Microbes were found Spallanzani's Experiment Step 4 Flask-4 Boiled and sealed Did not turn cloudy Microbes not found What did Spallanzani's experiment show? Was his hypothesis correct or incorrect? Pasteur's Problem Where do the microbes come from to cause broth to decay. Hypothesis: Microbes come from cells of organisms on dust particles in the air; not the air itself. Pasteur put broth into several special S-shaped flasks Each flask was boiled and placed at various locations Pasteur's Experiment Step 1 S-shaped Flask Filled with broth The special shaped was intended to trap any dust particles coming in. Pasteur's Experiment Step 2 Flasks boiled Micropes Killed Pasteur's Experiment Step 3 Flask left at various locations Did not turn cloudy Microbes not found Pasteur's Experiment Step 3 Flask Left Out Notice the dust that collected in the neck of the flask Pasteur's Experiment Results What did Pasteur's experiment show? Was his hypothesis correct or incorrect? • The theory of abiogenesis or spontaneous generation was disproved!!! BIOGENESIS • LIFE COMES FROM LIFE Questions: If you can answer the following questions you indicate a good understanding of this material. Why did early people believe in spontaneous generation? In Redi's experiment why did the flies lay their eggs on the netting? What important process in canning did Spallanzani teach us? How has the information from these scientists been used to protect our food from going bad? (application of information-technology) What process was named after Pasteur? Approximately how many years apart were the experiments of these three famous scientists? What does the phrase "Life From Life" Mean? Is the theory of spontaneous generation considered to be correct or incorrect? Why? CELL DIVISION • For life to continue, cells must replicate (make copies) of themselves. • New cells must have the exact same genetic info as the parent (original) cell • The number and types of chromosomes must be exactly the same. Stages of the Cell Cycle • Interphase- the cell spends most of its life in this phases • Mitosis- The period in a cell’s life when the cell divides to form two new cells. This includes the division of genetic information. INTERPHASE • the period in a cell’s life when the cell performs its function and grows • At the end of interphase , the cell replicates (makes a copy) of its chromosomes. Stages of MITOSIS • • • • Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase PROPHASE • Nuclear membrane disappears • Replicated chromosomes become visible METAPHASE • Chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell ANAPHASE • Replicated chromosomes separate and moved toward opposite poles of the cell. TELOPHASE • Nuclear membrane forms • Cytoplasm division occurs