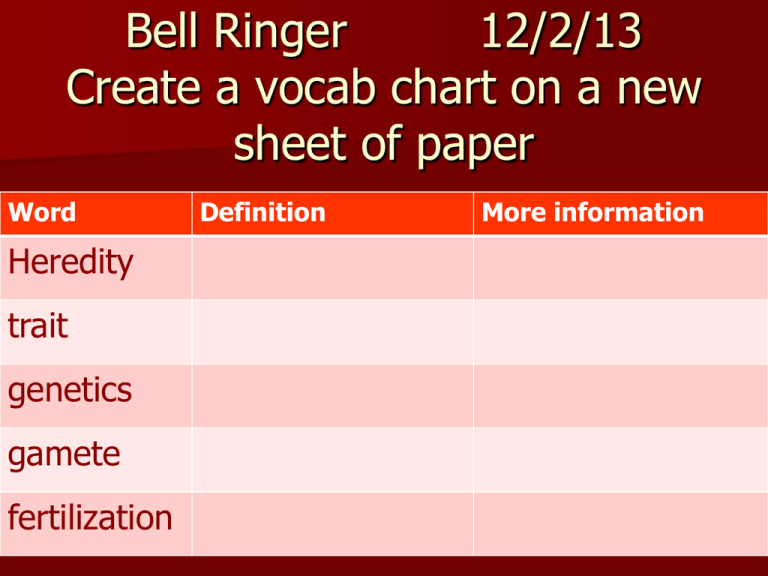
Bell Ringer
12/2/13
Create a vocab chart on a new
sheet of paper
Word
Heredity
trait
genetics
gamete
fertilization
Definition
More information
Genetics
http://www.youtube.com/w
atch?v=B_PQ8qYtUL0
Genetics Using
Punnett Squares
Early Genetics
• The study of genetics
began with observations
made by Gregor Mendel.
• After noticing that the
flowers his pea plants
were either violet or
white, Mendel began to
study the segregation of
heritable traits.
Between 1856 and 1863
he cultivated and tested
at least 28,000 pea
plants.
Remember that Mendel worked almost 150 years ago when nobody
knew about genes or even the structures (chromosomes) that carry
genes.
Here are some traits
observed by Mendel:
Mendel’s Conclusions
1.
Law of segregation –
– every individual has 2 forms (alleles) of a
gene and when sex cells (gametes) are
produced each gamete produced receives
one of these alleles
2.
Law of Independent Assortment
– Genes of individual traits are inherited
independently of each other
– Ex: gene for eye color is independent of hair
color gene
Lets consider a single gene…
• A gene carries
information that
determines your traits.
Traits are
characteristics you
inherit from your
parents.
• Genes are located in
chromosomes.
• Chromosomes come in
pairs and there are
thousands, of genes in
one chromosome.
Continued…
• In humans, a cell’s nucleus
contains 46 individual
chromosomes or 23 pairs of
chromosomes.
• Half of the chromosomes
come from one parent and
half come from the other
parent.
Here is the detailed
structure of a
chromosome
This is a human
karyotype
representing the 23
pairs of
chromosomes in a
male
Definitions
• Allele- discrete version of the same gene
• Genotype- the genes of an organism for one
specific trait
• Phenotype- the physical appearance of a trait in
an organism
Definitions
• Dominant trait refers to a genetic feature
that “hides” the recessive trait in the
phenotype of an individual.
• The term "recessive” describes a trait that
is covered over (or dominated) by another
form of that trait and seems to disappear.
• Homozygous= two alleles that are the same
for a trait (Pure)
• Heterozygous= two different alleles for a
trait (Hybrid)
Practice
• We use two letters to represent the genotype.
A capital letter represents the dominant form
of a gene (allele) and a lowercase letter is the
abbreviation for the recessive form of the
gene (allele).
• Example below: P=dominant purple and p=
recessive white
The phenotype for this
flower is violet while
its genotype (if
homozygous) is PP.
The phenotype for this
flower is white while
its genotype is pp (to
be white the flower
must have two of the
recessive copies of the
allele).
Punnett Squares
The Punnett square is
the standard way of
working out what the
possible offspring of
two parents will be.
– It is a helpful tool to
show allelic
combinations and
predict offspring ratios.
Before we go further lets review how to set
up a Punnett Square…
We begin by constructing a grid of two
perpendicular lines.
Next, put the genotype of one parent across
the top and the other along the left side.
For this example lets consider a genotype of BB crossed with bb.
B
b
b
B
• Notice only one
letter goes above
each box
• It does not matter
which parent’s
genotype goes on
either side.
Next, fill in the boxes by copying the column
and row head-letters down and across into
the empty spaces.
B
B
b
Bb
Bb
b
Bb
Bb
Punnett Squares
Now
that we have learned the
basics of genetics lets walk
through some examples using
Punnett Squares.
W
w
WWW Ww
w Ww ww
Usually write the
capital letter first
Lets say:
W- dominant white
w- recessive violet
Parents in this cross are heterozygous (Ww).
Note: Make sure I can tell your capital letters from
lowercase letters.
What percentage of the offspring will have violet
flowers?
ANSWER: 25% (homozygous recessive)
Red hair (R) is dominant over blond hair (r). Make a
cross between a heterozygous red head and a
blond.
R
r
r
r
Rr
rr
Rr
rr
What percentage of the offspring will have red hair? 50%
Let’s try some more…
In pea plants, tall pea plants (T) are dominant
over short pea plants (t). Construct a Punnett
Square for a heterozygous tall pea plant and a
short pea plant.
t
t
T
Tt
Tt
t
tt
tt
What are the
percentage of
phenotypes?
50% tall
50% short
Black eyes (R) is dominant over red eyes (r)
in rats. Make a cross between a homozygous rat
with black eyes and a rat with red eyes.
r
r
R
Rr
Rr
R
Rr
Rr
What is the possibility of
a red eye off springs?
0%
References
http://www.athro.com/evo/gen/punnett.html
http://www.kidshealth.org/kid/talk/qa/what_is_gene.html
http://brookings.k12.sd.us/biology/ch%2011%20genetics/punnettpr
actice.ppt#1
http://www.usoe.k12.ut.us/CURR/Science/sciber00/7th/genetics/sci
ber/punnett.htm
http://www.biotechnologyonline.gov.au/images/contentpages/karyo
type.jpg
Bell Ringer
12/3/13
Add these terms to your vocab chart:
Hybrid
Homozygous
Allele
Heterozygous
Dominant
Law
Recessive
Phenotype
genotype
of
segregation
Law of
Independent
Assortment
These terms will be checked on Thursday during the bell ringer
Heterochromia
Iridum
http://images.search.yahoo.com/s
earch/images?_adv_prop=image&
fr=ytff1yff24&va=heterochromia+iridum
Work with your group to complete
the
“punnett square practice”
worksheet
Bell Ringer 12/3/13
Complete your punnett square
practice handout pg 2-3
20 min
Self-grade your paper
For each of the genotypes (AA, Aa or aa)
below determine what the phenotype
would be.
Purple flowers are dominant to white
flowers.
PP - purple
Pp - purple
pp - white
AA – homoz dominant
GG – homoz dominant
TT – homoz dominant
Ff – heterozygous
Pp – heterozygous
Tt - hterozygous
Aa – heterozygous
Ii – heterozygous
aa – homoz recessive
gg – homoz recessive
tt – homoz recessive
Oo - heterozygous
Hairy knuckles are dominant to non-hairy
knuckles in humans.
HH - hairy
Hh - hairy
hh - non-hairy
Bobtails in cats are recessive. Normal
tails are dominant.
TT - bobtail
Tt - bobtail tt – normal tail
Round seeds are dominant to wrinkled
seeds in pea plants.
RR - round
Rr - round
rr – wrinkled
No-cleft chin is dominant. Cleft chin is
recessive.
CC – no cleft Cc – no cleft cc -cleft
2) For each of the following
write whether it is homozygous
dominant, heterozygous or
homozygous recessive.
Use the following information for
questions 3-5:
In dogs, the gene for fur color has two
alleles. The dominant allele (F) codes for
grey fur and the recessive allele (f) codes
for black fur.
3) The female dog is heterozygous. The
male dog is homozygous recessive. Figure
out the phenotypes and genotypes of their
possible puppies by using a Punnett
Square.
4. The female dog has black fur. The male
dog has black fur. Figure out the
phenotypes and genotypes of their
possible puppies by using a Punnett
Square.
5) The female dog is heterozygous. The
male dog is heterozygous. Figure out the
phenotypes and genotypes of their
possible puppies by using a Punnett
Square.
Use the following information for questions 6-8:
In fruit flies, red eyes are dominant (E). White
eyes are recessive (e).
6) If the female fly has white eyes and the
male fly has homozygous dominant red eyes,
what are the possible phenotypes and
genotypes of their offspring?
7) If the female fly has EE and the male
fly has EE, what are the possible
phenotypes and genotypes of their
offspring?
8) If both flies are heterozygous, then
what are the possible phenotypes and
genotypes of their offspring?
Use the following for questions 9-11:
In dogs, there is an hereditary deafness
caused by a recessive gene, “d.” A kennel
owner has a male dog (Gilbert) that she
wants to use for breeding purposes if
possible. The dog can hear.
9) What are the two possible genotypes of
Gilbert?
– DD or Dd
10) If the dog’s genotype is Dd, the owner
does not wish to use him for breeding so
that the deafness gene will not be passed
on. This can be tested by breeding the
dog to a deaf female (dd). Draw two
Punnett squares to illustrate these two
possible crosses.
11) In each case, what percentage/how
many of the offspring would be expected
to be hearing? deaf? How could you tell
the genotype of this male dog? Also, using
Punnett square(s), show how two hearing
dogs could produce deaf offspring.
Widow’s peak dominant
No widow’s peak recessive
12) If Wentworth Miller is Aa, and he and
Rihanna had children, what are the
possible phenotypes and genotypes of
their children?
13) Look at the phenotypes of Beyonce and
Jay Z. If these two had children, could they
have children with a widow’s peak?
Why or why not?
Dihybrid Cross
Can you create a punnett square to cross
these two pea plants:
TtRr x ttRr
*T=tall, t=short, R=round, r=wrinkled
Hint: the punnett square is bigger than 4
parts
Vocab chart checked
tomorrow
Punnett square quiz Friday
Bell Ringer
12/5/13
In humans, brown eyes (B) are dominant
over blue (b)*. A brown-eyed man marries
a blue-eyed woman and they have three
children, two of whom are brown-eyed
and one of whom is blue-eyed. Draw the
Punnett square that illustrates this
marriage. What is the man’s genotype?
What are the genotypes of the children?
Incomplete Dominance
In this case, neither allele is completely
dominant over the other, so the outcome
of a cross is a 3rd phenotype that is
different from either of the ones that were
crossed
Example of incomplete
dominance
When curly hair is crossed with straight hair,
sometimes wavy (a blend of the two) is the
outcome:
CC is curly (homozygous curly)
cc is straight (homozygous straight)
Cc is wavy (heterozygous)
What is the outcome of a cross between a curly
haired father and a wavy haired mother?
C
C
c
CC
Cc
C
CC
Cc
50%
CC – curly
50% Cc – wavy
0% cc - straight
Bell Ringer
12/9/13
Read page 264 in the blue book, 269
green bk. What is the difference between
a haploid cell and a diploid cell?
Read the 1st paragraph under the subtitle
“homologous chromosomes” on page 265
blue or 270 green bk. What is a
homologous chromosome?
Complete Problem-solving lab 10.2 pg 265
or 270 green bk.
Meiosis
Mitosis
Meiosis
Cell process beginning with a single
cell (2n)
Cell process beginning with a single
cell (2n)
Creates 2 body cells (daughter cells)
Creates 4 sex cells (gametes)
Results in 2 daughter cells
Results in 4 gametes
Daughter cells are diploid (2n)
Daughter cells are haploid (n)
On a clean sheet of paper:
Sketch and label the stages of meiosis
On your diagram write a summary
sentence of what happens at each stage.
Complete this for homework