Document
advertisement

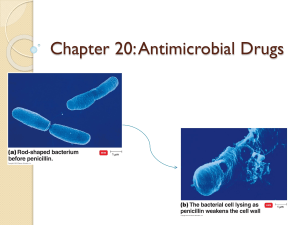
Antimicrobial Drugs Fading Miracle? Ehrlich’s Magic Bullets Fleming and Penicillin Chemotherapy • The use of drugs to treat a disease • Selective toxicity: A drug that kills harmful microbes without damaging the host Antibiotic/Antimicrobial • Antibiotic: Chemical produced by a microorganism that kills or inhibits the growth of another microorganism • Antimicrobial agent: Chemical that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms Microbial Sources of Antibiotics Antibiotic Spectrum of Activity • No antibiotic is effective against all microbes Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Action • Bacteria have their own enzymes for –Cell wall formation –Protein synthesis –DNA replication –RNA synthesis –Synthesis of essential metabolites Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Action • Viruses use host enzymes inside host cells • Fungi and protozoa have own eukaryotic enzymes • The more similar the pathogen and host enzymes, the more side effects the antimicrobials will have Modes of Antimicrobial Action Antibacterial Antibiotics Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis • Penicillin (over 50 compounds) –Share 4-sided ring (b lactam ring) • Natural penicillins • Narrow range of action • Susceptible to penicillinase (b lactamase) Prokaryotic Cell Walls Penicillins Fig 20.6 Figure 20.6 Penicillinase (b Lactamase) Figure 20.8 Semisynthetic Penicillins • Penicilinase-resistant penicillins • Carbapenems: very broad spectrum • Monobactam: Gram negative • Extended-spectrum penicillins • Penicillins + b-lactamase inhibitors Other Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis • Cephalosporins –2nd, 3rd, and 4th generations more effective against gramnegatives Figure 20.9 Other Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis • Polypeptide antibiotics –Bacitracin • Topical application • Against gram-positives –Vancomycin • Glycopeptide • Important "last line" against antibiotic resistant S. aureus Other Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis • Antibiotics effective against Mycobacteria: interfere with mycolic acid synthesis or incorporation – Isoniazid (INH) – Ethambutol Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis • Broad spectrum, toxicity problems • Examples – Chloramphenicol (bone marrow) – Aminoglycosides: Streptomycin, neomycin, gentamycin (hearing, kidneys) – Tetracyclines (Rickettsias & Chlamydia; GI tract) – Macrolides: Erythromycin (gram +, used in children) Injury to the Plasma Membrane • Polymyxin B (Gram negatives) –Topical –Combined with bacitracin and neomycin (broad spectrum) in overthe-counter preparation Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis • Rifamycin –Inhibits RNA synthesis –Antituberculosis • Quinolones and fluoroquinolones –Ciprofloxacin –Inhibits DNA gyrase –Urinary tract infections Competitive Inhibitors –Sulfonamides (Sulfa drugs) • Inhibit folic acid synthesis • Broad spectrum Figure 5.7 Antifungal Drugs • Fungi are eukaryotes • Have unique sterols in their cell walls • Pathogenic fungi are often outside the body Antiviral Drugs • Viruses are composed of nucleic acid, protein capsid, and host membrane containing virus proteins • Viruses live inside host cells and use many host enzymes • Some viruses have unique enzymes for DNA/RNA synthesis or protein cutting in virus assembly Figure 20.16a Antiviral Drugs Nucleoside and Nucleotide Analogs Figure 20.16a Analogs Block DNA Synthesis Figure 20.16b, c Antiviral Drugs Enzyme Inhibitors • Inhibit assembly –Indinavir (HIV) • Inhibit attachment –Zanamivir (Influenza) • Inhibit uncoating –Amantadine (Influenza) Antiviral Drugs Enzyme Inhibitors • Interferons prevent spread of viruses to new cells (Viral hepatitis) • Natural products of the immune system in viral infections Antiprotozoan Drugs • Protozoa are eukaryotic cells • Many drugs are experimental and their mode of action is unknown Antihelminthic Drugs • Helminths are macroscopic multicellular eukaryotic organisms: tapeworms, roundworms, pinworms, hookworms Antihelminthic Drugs • Prevent ATP generation (Tapeworms) • Alters membrane permeability (Flatworms) • Neuromuscular block (Intestinal roundworms) • Inhibits nutrient absorption (Intestinal roundworms) • Paralyzes worm (Intestinal roundworms) Measuring Antimicrobial Sensitivity • E Test • MIC: Minimal inhibitory concentration Measuring Antimicrobial Sensitivity: Disk Diffusion Antibiotic Resistance Figure 20.20 Antimicrobial Resistance • Relative or complete lack of effect of antimicrobial against a previously susceptible microbe • Increase in MIC Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance • Enzymatic destruction of drug • Prevention of penetration of drug • Alteration of antibiotic or target site • Rapid ejection of the drug Antibiotic Selection for Resistant Bacteria What Factors Promote Antimicrobial Resistance? • Exposure to sub-optimal levels of antimicrobial • Exposure to microbes carrying resistance genes Inappropriate Antimicrobial Use • Prescription not taken correctly • Antibiotics for viral infections • Antibiotics sold without medical supervision • Spread of resistant microbes in hospitals due to lack of hygiene Inappropriate Antimicrobial Use • Lack of quality control in manufacture or outdated antimicrobial • Inadequate surveillance or defective susceptibility assays • Poverty or war • Use of antibiotics in foods Antibiotics in Foods • Antibiotics are used in animal feeds and sprayed on plants to prevent infection and promote growth • Multi drug-resistant Salmonella typhi has been found in 4 states in 18 people who ate beef fed antibiotics Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistance • Infections resistant to available antibiotics • Increased cost of treatment Multi-Drug Resistant TB MRSA “mer-sah” • Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus • Most frequent nosocomial (hospital-acquired) pathogen • Usually resistant to several other antibiotics Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci Vancomycin Use USA Proposals to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance • Speed development of new antibiotics • Track resistance data nationwide • Restrict antimicrobial use • Direct observed dosing (TB) Proposals to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance • Use more narrow spectrum antibiotics • Use antimicrobial cocktails The Future of Chemotherapeutic Agents • Antimicrobial peptides –Broad spectrum antibiotics from plants and animals • Squalamine (sharks) • Protegrin (pigs) • Magainin (frogs) The Future of Chemotherapeutic Agents • Antisense agents –Complementary DNA or peptide nucleic acids that binds to a pathogen's virulence gene(s) and prevents transcription