Development of a Diagnostic Test for Mutations in NPM1 Exon 12 in
advertisement
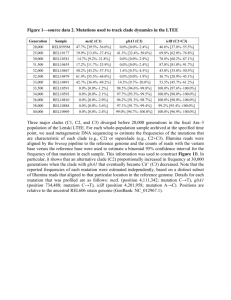
Development of a Diagnostic Test for Mutations in NPM1 Exon 12 in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML) Patients Alison Skinner Wessex Regional Genetics Laboratory NPM1 function • Implicated in leukaemia as a translocation partner for various oncogenes • Nucleolar phosphoprotein present predominantly in the nucleolus • Regulates translational activity of p53 after stress • Involved in centrosome duplication in the cell cycle via cyclin E/CDK2 phosphorylation Effect of NPM1 mutations • Gives prognostic information to the AML patients with a normal karyotype (phenotypically variable) • Favourable prognosis in the absence of the FLT3 ITD • Better response to induction therapy and have a better overall survival / longer event free survival Acquired Mutations in NPM1 Wildtype: GCTATTCAAGATCTCTGGCAGTGGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAgaaaatag -A--I--Q--D--L--W--Q--W--R--K--S--L--*--------Mutation A: GCTATTCAAGATCTCTGTCTGGCAGTGGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAgaaaatag -A--I--Q--D--L--C--L--A--V--E--E--V--S--L--R--K--*Mutation B: GCTATTCAAGATCTCTGCATGGCAGTGGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAgaaaatag -A--I--Q--D--L--C--M--A--V--E--E--V--S--L--R--K--*Mutation D: GCTATTCAAGATCTCTGCCTGGCAGTGGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAgaaaatag -A--I--Q--D--L--C--L--A--V--E--E--V--S--L--R--K--*- Results of Direct Sequencing From the original 66 samples • 41 had no visible mutation • 1 had an intronic mutation of unknown significance • 19 had a frameshift mutation: – – – – 13 had mutation ‘A’ 1 had mutation ‘B’ 3 had mutation ‘D’ 2 had novel mutations which still produced the same NES Principles of Pyrosequencing Image from www.pyrosequencing.com Designing the Pyrosequencing Assay Wildtype Mutation A Mutation B Mutation D Testing the Pyrosequencing Assay Normal Mutation A Mutation B Mutation D Further Analysis of the Pyrosequencing Results Examples of Results Using Analysis Spreadsheet Validation – 1 Retesting the Original Cohort • All 66 samples that were tested by direct sequencing were re-tested using the pyrosequencing assay • 6 / 66 failed – 1 sample failed for pyrosequencing but was normal on direct sequencing – 1 sample failed for direct sequencing but had mutation ‘A’ on pyrosequencing, – All other failures had failed for both techniques • Results of all other samples matched the results for direct sequencing Validation – 2 Normal controls • 3 / 96 failed • There was no evidence of mutations in the normal test plate • A quantification below 10% should be treated as normal / with caution (depending on the quality of the data) Validation – 3 Titration • A titration of mutational load was set up • Reliably sensitive to around 20% mutation 60 50 40 A 30 B % D Linear (A) Linear (D) 20 Linear (B) 10 0 Neat 9:1 8:2 7:3 6:4 5:5 -10 Dilution 4:6 3:7 2:8 1:9 Summary • The test is sensitive and relatively highthroughput • Identifies and quantifies the common NPM1 exon 12 mutations • Is able to identify other ‘novel’ mutations in the region • Helpful in identifying patients who have a favourable prognosis Acknowledgements • Dr Helen White – NGRL (Wessex) • Prof. Nick Cross – WRGL • Christine Waterman - WRGL