Presentation 2
advertisement

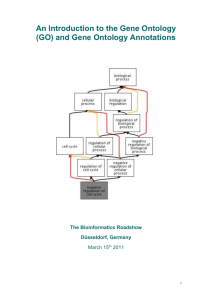
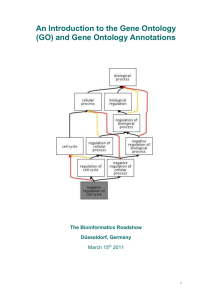
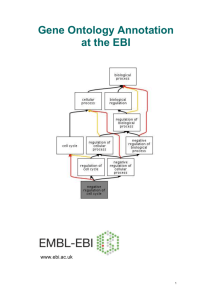
Introduction to the Gene Ontology and GO annotation resources Rachael Huntley UniProt-GOA EBI Programmatic Access to Biological Databases 3rd October 2012 What is an Ontology? What is the difference between an ontology and a controlled vocabulary? An ontology formally represents knowledge as a set of concepts within a domain, and the relationships among those concepts. It can be used to reason about the entities within that domain and may be used to describe the domain. A Controlled vocabularies provide a way to organize knowledge for subsequent retrieval but does not allow reasoning about the entities. Ontologies and CVs in Biology Ontologies/CVs are heavily used in biological databases • Allow organisation of data within a database • Enable linking between databases • Enable searches across databases www.ebi.ac.uk/ols What is GO? The Gene Ontology Less specific concepts • A way to capture biological knowledge for individual gene products in a written and computable form • A set of concepts and their relationships to each other arranged as a hierarchy More specific concepts www.ebi.ac.uk/QuickGO The Concepts in GO • • 1. Molecular Function An elemental activity or task or job protein kinase activity insulin receptor activity 2. Biological Process A commonly recognised series of events • cell division • mitochondrion 3. Cellular Component Where a gene product is located • mitochondrial matrix • mitochondrial inner membrane Anatomy of a GO term Unique identifier Term name Synonyms Definition Cross-references Ontology structure • Directed acyclic graph Terms can have more than one parent • Terms are linked by relationships is_a part_of regulates (and +/- regulates) has_part occurs_in www.ebi.ac.uk/QuickGO These relationships allow for complex analysis of large datasets Relations Between GO Terms is_a If A is a B, then A is a subtype of B part_of Wherever B exists, it is as part of A. But not all A is part of B. A B http://www.geneontology.org/GO.ontology-ext.relations.shtml All replication forks are part of a chromosome Not all chromosomes have replication forks Relations Between GO Terms Regulates • One process directly affects another process or quality • Necessarily regulates: if both A and B are present, B always regulates A, but A may not always be regulated by B B A All cell cycle checkpoints regulate the cell cycle. The cell cycle is not solely regulated by cell cycle checkpoints http://www.geneontology.org/GO.ontology-ext.relations.shtml Process-Function Links in GO • GO was originally three completely independent hierarchies, with no relationships between them • Biological processes are ordered assemblies of molecular functions • As of 2009 we have started making relationships between biological process and molecular function in the live ontology functions that regulate processes e.g. transcription regulator regulates transcription process process function functions that are part_of processes e.g. transporter part_of transport function Searching for GO terms Search GO terms or proteins http://www.ebi.ac.uk/QuickGO Exercise Search for a GO term Exercise 1 (pg.16) Why do we need GO? 17 Reasons for the Gene Ontology • Inconsistency in English language www.geneontology.org Inconsistency in English languauge • Same name for different concepts Cell or ?? • Different names for the same concept Eggplant Aubergine Brinjal Melongene Same for biological concepts Comparison is difficult – in particular across species or across databases Just one reason why the Gene Ontology (GO) is is needed… Reasons for the Gene Ontology • Inconsistency in English language • Increasing amounts of biological data available • Increasing amounts of biological data to come www.geneontology.org Increasing amounts of biological data available Search on ‘DNA repair’... get over 68,000 results Expansion of sequence information Reasons for the Gene Ontology • Inconsistency in English language • Increasing amounts of biological data available • Increasing amounts of biological data to come • Large datasets need to be interpreted quickly www.geneontology.org Aims of the GO project • Compile the ontologies - currently over 38,000 terms - constantly increasing and improving • Annotate gene products using ontology terms - around 30 groups provide annotations • Provide a public resource of data and tools - regular releases of annotations - tools for browsing/querying annotations and editing the ontology http://www.geneontology.org Reactome GO Annotation UniProt-Gene Ontology Annotation (UniProt-GOA) project at the EBI • Largest open-source contributor of annotations to GO • Provides annotation for more than 350,000 species • Our priority is to annotate the human proteome A GO annotation is … …a statement that a gene product; 1. has a particular molecular function or is involved in a particular biological process or is located within a certain cellular component 2. as determined by a particular method 3. as described in a particular reference Accession Name P00505 GO ID GO term name GOT2 GO:0004069 aspartate transaminase activity Reference PMID:2731362 Evidence code IDA UniProt-GOA incorporates annotations made using two methods Electronic Annotation • Quick way of producing large numbers of annotations • Annotations use less-specific GO terms • Only source of annotation for many non-model organism species Manual Annotation • Time-consuming process producing lower numbers of annotations • Annotations tend to use very specific GO terms Electronic annotation methods 1. Mapping of external concepts to GO terms GO:0005634: Nucleus GO:0009734: Auxin mediated signaling pathway GO:0004707: MAP kinase activity Electronic annotation methods 2. Automatic transfer of manual annotations to orthologs Ensembl compara Macaque Chimpanzee Guinea Pig Rat ...and more e.g. Human Mouse Arabidopsis Cow Dog Chicken Ensembl compara …and more Brachypodium Poplar Maize Grape Rice Annotations are high-quality and have an explanation of the method (GO_REF) http://www.geneontology.org/cgi-bin/references.cgi Manual annotation by GOA High–quality, specific annotations made using: • Full text peer-reviewed papers • A range of evidence codes to categorise the types of evidence found in a paper e.g. IDA, IMP, IPI http://www.ebi.ac.uk/GOA Number of annotations in UniProt-GOA database Electronic annotations Manual annotations* 102,205,043 1,149,802 Sep 2012 Statistics * Includes manual annotations integrated from external model organism and specialist groups How to access and use GO annotation data Where can you find annotations? UniProtKB Ensembl Entrez gene UniProt vs. QuickGO annotation display UniProt QuickGO UniProt vs. QuickGO annotation display Filtering mechanism • Exclude root terms (e.g. Molecular Function) • Exclude annotations with qualifier (e.g. NOT, contributes_to) • Exclude annotations to less granular terms • Exclude annotations to GO:0005515 protein binding • Exclude lower quality assignments for same data, e.g. UniProt taken in preference to MGI • Add electronic annotations that cover ground not covered by manual annotation Gene Association Files 17 column files containing all information for each annotation GO Consortium website UniProt-GOA website Numerous species-specific files http://www.ebi.ac.uk/GOA/downloads.html GO browsers The EBI's QuickGO browser Search GO terms or proteins Find sets of GO annotations http://www.ebi.ac.uk/QuickGO Exercise Find annotations to a protein Exercise 2 (pg.16) Find annotations to a list of proteins Exercise 1 and 2 (pg.22) How scientists use the GO • Access gene product functional information • Analyse high-throughput genomic or proteomic datasets • Validation of experimental techniques • Get a broad overview of a proteome • Obtain functional information for novel gene products Some examples… Term enrichment • Most popular type of GO analysis • Determines which GO terms are more often associated with a specified list of genes/proteins compared with a control list or rest of genome • Many tools available to do this analysis • User must decide which is best for their analysis Analysis of high-throughput genomic datasets time Defense response Immune response Response to stimulus Toll regulated genes JAK-STAT regulated genes Puparial adhesion Molting cycle Hemocyanin MicroArray data analysis Amino acid catabolism Lipid metobolism Peptidase activity Protein catabolism Immune response Immune response Toll regulated genes attacked control pear son lw n3d ... lw n3d ... Color ed by cted Gene Tree: pearson Colored by:: Set_LW_n3d_5p_... List: ch color classification: Set_LW_n3d_5p_...Gene Gene List: Copy ofofCopy of(Defa... C5_RMA (Defa... Copy of Copy C5_RMA g enes allall g enes (14010) (14010) Bregje Wertheim at the Centre for Evolutionary Genomics, Department of Biology, UCL and Eugene Schuster Group, EBI. Annotating novel sequences • Can use BLAST queries to find similar sequences with GO annotation which can be transferred to the new sequence • Two tools currently available; AmiGO BLAST – searches the GO Consortium database BLAST2GO – searches the NCBI database Using the GO to provide a functional overview for a large dataset • Many GO analysis tools use GO slims to give a broad overview of the dataset • GO slims are cut-down versions of the GO and contain a subset of the terms in the whole GO • GO slims usually contain less-specialised GO terms Slimming the GO using the ‘true path rule’ Many gene products are associated with a large number of descriptive, leaf GO nodes: Slimming the GO using the ‘true path rule’ …however annotations can be mapped up to a smaller set of parent GO terms: GO slims Custom slims are available for download; http://www.geneontology.org/GO.slims.shtml or you can make your own using; • QuickGO http://www.ebi.ac.uk/QuickGO • AmiGO's GO slimmer http://amigo.geneontology.org/cgi-bin/amigo/slimmer The EBI's QuickGO browser Search GO terms or proteins Find sets of GO annotations Map-up annotations with GO slims www.ebi.ac.uk/QuickGO Precautions when using GO annotations for analysis • The Gene Ontology is always changing and GO annotations are continually being created - always use a current version of both - if publishing your analyses please report the versions/dates you used http://www.geneontology.org/GO.cite.shtml • Recommended that ‘NOT’ annotations are removed before analysis - only ~3000 out of 57 million annotations are ‘NOT’ - can confuse the analysis Precautions when using GO annotations for analysis • Unannotated is not unknown - where there is no evidence in the literature for a process, function or location the gene product is annotated to the appropriate ontology’s root node with an ‘ND’ evidence code (no biological data), thereby distinguishing between unannotated and unknown • Pay attention to under-represented GO terms - a strong under-representation of a pathway may mean that normal functioning of that pathway is necessary for the given condition Exercise Use the QuickGO web services to retrieve annotations Exercise 1 Pg.46 The UniProt-GOA group Project leader: Rachael Huntley Curators: Yasmin Alam-Faruque Prudence Mutowo Software developer: Tony Sawford Team leaders: Rolf Apweiler Claire O’Donovan Email: goa@ebi.ac.uk http://www.ebi.ac.uk/GOA Acknowledgements Members of; UniProtKB Ensembl InterPro Ensembl Genomes IntAct GO Consortium HAMAP Funding National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) British Heart Foundation EMBL