Pathology and Forensics PPT
advertisement

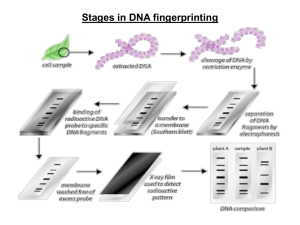
What’s wrong with me? Whenever you become ill, you can go to your doctor and by examining you and performing various tests, your doctor comes up with a diagnosis of what he feels is wrong with you and so he will know how to treat you and make you better. Careers that perform the tests that diagnose you are called Diagnostic Services. Tests such as blood, urinalysis, cultures, imaging, biopsies, home medical kits, genetic testing, and the newest, latest are noninvasive breath tests that can check for many diseases such as lung, throat, and breast cancer, MS and TB. Nuclear Medicine Technologist- operate advanced imaging machines (CT, MRI, PET) scans. Pathologists- medical doctors who specialize in the diagnosis and study of diseases and disease processes. Medical Lab Technologists and Technicianswork in lab settings performing lab tests, maintain and calibrate lab instruments. Phlebotomist- draw blood specimens. Postmortem exam to find how and why the victim died. Two types- Forensic and Clinical May be done by a Pathologist, Medial Examiner or Coroner Place body in a clean body bag and place victim’s hands in a bag to preserve evidence. Notes, photos and X-rays are taken of any marks, wounds, evidence found. External examination, body weighed and measured. Blood, oral fluid and tissue samples may be taken for toxicology analysis. Internal examination-incision cutting open the chest to reveal organs which are examined, weighed and measured for abnormalities. Tissue samples may be taken. If the brain must be examined, it is removed and put in formulin for later examination. Rigor Mortis- muscles become stiff after death, starts in 3 hours, whole body affected after 12 hours. Around 36 hours, becomes soft and supple again. Lividity- red blood cells break down after death and skin appears reddish in color on ground-side where patient was lying when they died. Entomology- study of insects. Can play a role in time of death. Stomach contents- the process of digestion can help determine time of death. Costs Religion Personal reasons- might reveal something family doesn’t want to know, medical error, etc. We all have it! A set of instructions encoded in long molecules of deoxyribonucleic acid,(DNA). Four chemicals that make up DNA are Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine. A always pairs with T, C always pairs with G. Human DNA is arranged in 23 pairs of chromosomes. Human DNA is more than 95% similar to chimpanzee DNA. Your DNA is 50% identical to your mother’s DNA and 50% identical to your father’s DNA. Unless you have an identical twin, nobody has DNA just like yours. If you have samples of body tissues such as blood, semen, saliva, skin, or hair you can test it to see if it’s DNA matches that of a particular person! In the US, The FBI maintains a database of DNA profiles for convicted criminals, some arrestees, missing persons and unidentified remains. DNA is also used to establish paternity, inheritance, immigration and other legal cases. Genetic testing can help with establishing your or your children’s chances of getting an inherited disease. Karotyping- a technique for looking at an organism’s set of chromosomes.Some genetic disorders are caused by extra, missing, or rearranged chromosomes or pieces of chromosomes. Polymerase Chain Reaction- used to make enough copies of DNA segments to the DNA can be sequenced, profiled, or tested for a particular genetic disorder. Gel Electrophoresis- a technique for separating molecules by length and charge, including DNA, RNA, and proteins. Microarrays- Microarrays can detect the presence and activity of thousands of genes at the same time. Forensic Science is the application of science and technology to establish facts in legal cases. There are many different fields and specialties of forensic science. Medical Examiner- a medical doctor or forensic pathologist in charge of death investigations. He is usually appointed by the state to investigate any suspicious or unusual deaths in which there could be foul play. They must determine cause of death! Forensic Toxicology- the investigation of drugs and poisons in the body in cases of illegal drug use, drug abuse, poisoning and death. Body fluids and tissue samples are taken and analyzed for drugs and alcohol. Forensic Pathology- medical doctors who specialize first, in pathology and second, in forensic pathology. Forensic Anthropology- application of physical anthropology archeological techniques to recover, identify and investigate skeletal remains. Forensic Odontology- application of dental science to forensic cases. Wildlife Forensic Science- applies forensic techniques to cases of nonhuman biological evidence. Medical tests, both diagnostic and forensic, are usually very accurate, but as with any test, there is also room for error! False positive- when a test shows something that isn’t there. True positive- when a test shows positive for a disease that is there. False negative- when a test fails to detect a condition that the patient really has. True negative- when a test shows negative for a disease that the patient realy doesn’t have. Sensitivity- the measure of how often a test will detect a condition when the condition is present. Specificity-the measure of how often a test will give negative results for a condition when the condition is not present. High Prevalence and Low Prevalence- See example scenarios in BMT curriculum!