ADSL - Intranet
advertisement

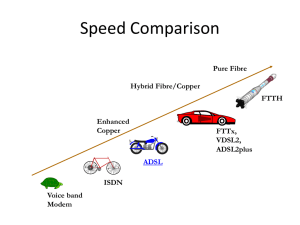
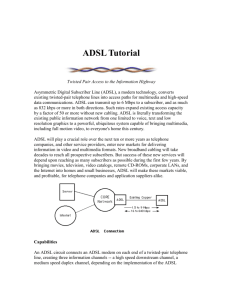
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Tutorial Slide Show Tutorial Outline What Is ADSL ? What Can ADSL Do ? How Does It Work ? Architectural Options Status of the Technology The Future ADSL Equipment Standard Telephone Lines Central Office Building Residential Customer ADSL Rack of Line Cards Customer Premises Equipment Remote ADSL Unit Data & Telephony on One Line Data as ATM Cells &/or IP Packets TV Fast Internet All in Addition to Existing Analogue Telephony “Evolution of Digital Access” Pure Fibre Hybrid Fibre/Copper FTTH Enhanced Copper FTTx + VDSL Today ADSL Voiceband Modem ISD N “Tomorrow’s Network” : ADSL Video Servers ADSL Internet Broadband Network 1.5 to 8Mbit/s 9.6 to 640kbit/s Telephone Network Live Broadcast Typical Network Construction Central Office Street Cabinet Feeder Network Distribution Network Underground Feed Overhead Feed Next Topic What Is ADSL ? What Can ADSL Do ? How Does It Work ? Architectural Options Status of the Technology The Future ADSL Applications Internet Access, etc. LAN Access (Teleworking) Distance Learning Broadcast TV Home Shopping Video On Demand Next Topic What Is ADSL ? What Can ADSL Do ? How Does It Work ? Architectural Options Status of the Technology The Future How Does ADSL Work? Functional Elements Use of Bandwidth Channel Separation & POTS Splitter Transmission Methods Discrete Multi-tone Modulation (DMT) Quadrate Amplitude Modulation (QAM) Carrierless Amplitude/phase Modulation (CAP) ADSL Modem Structure Mbit/s kbit/s Mbit/s ADSL Modem ADSL Modem Line POTS Filter POTS Filter POTS Linecard Exchange End Customer End kbit/s ADSL Modem Functions Digital Interface Transmission Convergence Physical Media Dependent Rates/multiplexing Forward Error Control (FEC) Framing/mapping Protocol processing OAM processing Line Code (modulation) Initialisation POTS splitter/interface Scrambler/descrambler Base EOC functions Alternatives Alternatives Bit Synchronous (STM) Packet Mode ATM Mode DMT QAM CAP Baseband Line Interface Growth in Bandwidth Utilization VDSL ~1997/8? Time ADSL ~1994 ~1990 ~1986 HDSL ISDN ~0.1 MHz ~0.5 MHz ~1 MHz Bandwidth (MHz) 10+ MHz Next Topic What Is ADSL ? What Can ADSL Do ? How Does It Work ? Architectural Options Status of the Technology The Future Data-Centric Architecture 10 base T Ethernet CPE ADSL or PC Remote 10 base T Ethernet ADSL Linecard 45 or 155 Mbit/s Ethernet Hub/Switch Router 10 base T or 100 base T ATM or FR ISP Telecom-Centric Architecture ATM e.g. 25 Mbit/s CPE e.g. PC or STB ADSL Remote 155 Mbit/s fibre ADSL Linecard ADSL Access Mux ATM ISP Next Topic What Is ADSL ? What Can ADSL Do ? How Does It Work ? Architectural Options Status of the Technology The Future Status of ADSL Technology Equipment Standards Trials ADSL Equipment Trends More Choice of Transceiver Chips and Equipment Increased Transceiver Integration More Transceivers Per Line Card and Equipment Rack More Customers Per Exchange Transceiver Faster Transmission Speeds Increased Embedded Internetworking Functionality Standards and Recommendations ANSI ETSI ADSL FORUM DAVIC ATM FORUM ITU ADSL Activities Throughout the World ADSL Activities in the USA ADSL Activities in Asia & Australasia ADSL Activities in Europe Next Topic What is ADSL ? What can ADSL do ? How does it work ? Architectural Options Status of the technology The Future Broadband Network Broadband Switch Network (eg. ATM) Service Providers High-Capacity Backbone Links Servers & Billing Operational Support System ADSL Access Network New Optical Cable Local Exchange VDSL POTS “Evolution of Digital Access” Pure Fibre Hybrid Fibre/Copper FTTH Enhanced Copper FTTx + VDSL Today ADSL Voiceband Modem ISD N Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Introduction Slide Show Thank You for watching!