Presentation @9:00am
advertisement

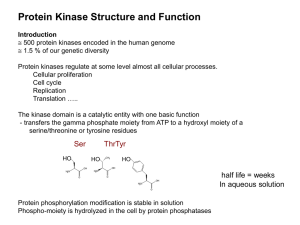
Clustering and Motif Discovery in Kinases of Yeast, Worm and Arabidopsis thaliana Sihui Zhao Background – Kinase Protein kinases play a pivotal role in the control of all cellular processes Cell proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, migration, metabolism and signal transduction A kinase superfamily in each genome, ~2% of all sequences Background Structure of Catalytic Domain Also called C-subunit Conserved among protein kinase superfamily Contains 250-300 residues 12 subdomains Background Subdomains of C-subunit Two pivital subdomains (based on PKA): Subdomain I: Sequester ATP Gly-X-Gly-X-X-Gly-X-Val Subdomain VIB: ‘Catalytic loop’ His-Arg-Asp-X-Lys-X-X-Asn Background Conserved Residues Residue Probable Function Gly50 Gly52 Val57 Sequester ATP Lys72 Glu91 Positioning triphosphate group Asp166 Lys168 Asn171 Catalytic loop Glu208 Arg280 Assembly of catalytic core Asp220 Assembly of catalytic loop Background Motif Motif is a locally conserved region Conserved due to higher selection pressure compared to non-conserved regions Importance to the biological function or structure Problem & Strategy in Motif Discovery Background Motif discovery relies on either statistical or combinatorial pattern search techqniues Problem: High noise compared to signal when facing huge number of sequences Strategy: Clustering/classification used to find sequence families first to decrease the noise ratio Objectives Cluster kinase sequences into different families Find conserved motifs from sequence families Tools Blast – Sequence alignment tool ClustalW – Multiple alignment tool HMMER – HMM-based package BAG package – Sequence clustering package BlockerMaker – Block/Motif discovery tool LAMA – Alignment tool for Blocks Perl Computational Framework – Outline Collecting and clustering kinase sequences based on similarity The iterative HMM search – To collect more kinases, especially remotely homologous sequences Motif discovery – To find blocks from each cluster and merge blocks across multiple clusters Computational Framework Collecting and Clustering Sequences Cluster kinase sequences Extract annotated kinase sequences All to all pairwise comparison Estimate best score for clustering Cluster sequences using BAG Computational Framework HMM Iterative Search Collect more sequences for each cluster Multiple alignment using CLUSTALW Build HMM/Profile Search all 3 genomes Add hits to each cluster if any Computational Framework Motif Discovery Find blocks and merge across multiple clusters Block discovery by BlockMaker All to all block comparison by LAMA Clustering blocks using BAG package Conserved sites detection Result 963 kinase from ~45,000 sequences (~2%) 159 clusters of kinase sequences containing 2 to 32 sequences each 0 to ~1000 sequences added to each cluster after HMM iterative search Result 71 sequence clusters sent to BlockMaker ID c51.seq-1 BLOCK AC c51.seq-1; distance from previous block=(79,120) DE similar to eukaryotic protein kinase domains BL EGL motif=[5,0,17] motomat=[1,1,-10] width=31 seqs=5 gi|3329644|gb|AAC ( 792) SNFNFEFHKDSLEILEPIGSGHFGVVRRGIL 99 gi|3329650|gb|AAC ( 154) YNPKYEVDLEKLEILEQLGDGQFGLVNRGLL 92 gi|3877967|emb|CA ( 836) YNNDYEIDPVNLEILNPIGSGHFGVVKKGLL 79 gi|3877968|emb|CA ( 842) YNEDYEIDLENLEILETLGSGQFGIVKKGYL 77 gi|3878749|emb|CA ( 129) YKKQYEIASENLENKSILGSGNFGVVRKGIL 100 Result 45 clusters of Blocks after LAMA comparison and BAG clustering Result Some Found Conserved Sites Cluster 11, size 29 Subdomain I: G-X-G-X-X-G-X-V Cluster 16, size 97 Subdomain VIB: H-R-D-X-K-X-X-N Result Some New Sites Cluster 20, size=8 Known: Arg280 - assembly of catalytic core Unknown: Cys, Trp, Pro Cluster 31, size=13 Alignment and motif Alignment and motif Known: Asp220 - assembly of catalytic loop Unknown: Gly, Thr, Tyr Cluster 40, size=7 Alignment and motif Known: Glu91 - positioning triphosphate group Unknown: His, Pro Conclusion This computational framework is successful Especially when no preliminary information on huge amount of sequences It’s efficient Not completely automatic Conclusion Kinases are clustered based on similarity, which provides a way to deduce the functions from other family members Some new conserved sites are found, which might indicate the specificity of kinase functions Acknowledgement Prof. Sun Kim Prof. Mehmet Dalkilic Dr. Irfan Gunduz