Chapter 4. Long-term Potentiation as a physiological
advertisement

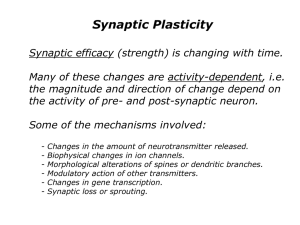
Long-term Potentiation as a Physiological Phenomenon From Mechanisms of Memory by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Memories are stored as alterations in the strength of synaptic connections between neurons in the CNS. “Hebb’s Postulate”: When an axon of cell A … excites cell B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells so that A’s efficiency as one of the cells firing B is increased. D.O. Hebb, The Organization of Behavior, 1949. From Sidney Harris Memories are stored as alterations in the strength of synaptic connections between neurons in the CNS. “Hebb’s Postulate”: When an axon of cell A … excites cell B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells so that A’s efficiency as one of the cells firing B is increased. D.O. Hebb, The Organization of Behavior, 1949. TVP Bliss, FRS The Entorhinal/Hippocampal System Entorhinal Cortex Dentate Gyrus Mossy Fiber CA3 Schaffer Collaterals Stratum Lacunosom Molecular inputs Perforant Pathway Recurrent Connections Ipsilateral CA1 Bliss and Lomo’s First Published LTP Experiment The Entorhinal/Hippocampal System Entorhinal Cortex Dentate Gyrus Mossy Fiber Lateral Septum, Contralateral CA1 CA3 Schaffer Collaterals Stratum Lacunosom Molecular inputs Perforant Pathway CA1 Axon Recurrent Connections GABAergic Interneuron Ipsilateral CA1 Entorhinal Cortex Norepinephrine, Acetylcholine, Dopamine, Amygdala, Cortex Serotonin SLM Inputs Subiculum Lateral Septum Schaffer Collaterals The Dendritic Tree The Dendritic Spine The Entorhinal/Hippocampal System Entorhinal Cortex Dentate Gyrus Mossy Fiber Lateral Septum, Contralateral CA1 CA3 Schaffer Collaterals Stratum Lacunosom Molecular inputs Perforant Pathway CA1 Axon Recurrent Connections GABAergic Interneuron Ipsilateral CA1 Entorhinal Cortex Norepinephrine, Acetylcholine, Dopamine, Amygdala, Cortex Serotonin SLM Inputs Subiculum Lateral Septum Schaffer Collaterals Electrodes in a Living Hippocampal Slice Stimulating Electrode Recording Electrode Tissue Slice Chamber Recording Configuration and Typical Responses in a Hippocampal Slice Recording Experiment Recording in Stratum Pyramidale in Area CA1 Stimulating Schaffer Collaterals in Area CA3 Recording in Stratum Radiatum in Area CA1 Stimulus Artifact Fiber Volley EPSP An Input/Output Curve and a Typical LTP Experiment In p u t/O u tp u t F ib e r V o lle y 500 250 0 0 .7 5 0 .3 0 .2 0 .1 0 .0 0 10 20 30 40 0 Normalized Initial Slope S tim ulus Intensity ( A) B In p u t/O u tp u t v s F ib e r V o lle y 0 .4 S lope fE P SP ( V /m s) Fiber V olley A m plitude ( V) 750 S lope fE P SP ( V /m s) A 10 20 30 40 0 .5 0 0 .2 5 0 .0 0 0 .0 S tim ulus Intensity ( A) 0 .1 2 1 0 0 20 40 Time (min) 0 .3 Fiber V olley Am plitude ( V ) 3 -20 0 .2 60 80 100 0 .4 From Nicoll et al. Malenka et al, Bear et al, Huganir et al. Theta Pattern in Hippocampal EEG 1-voluntary movement 2-REM sleep 3-still-alert 4-slow-wave sleep Before and after a medial septal lesion. LTP Triggered by Theta Burst Stimulation A 100-Hz 100-Hz 100-Hz 200 msec 200 msec 100-Hz … 200 msec 10 msec between pulses • 5-Hz burst frequency • 10 bursts per train • 3 trains, 20-sec intertrain interval B (% of baseline) fEPSP slope 200 175 150 125 100 75 -20 0 20 Time (min) 40 60 Voltage Clamp Cell Body Pairing LTP ASSOCIATIVE LTP German Barrionuevo and Tom Brown Back Propagating Action Potentials Pairing LTP NEURONAL INFORMATION PROCESSING MOLECULAR MECHANISMS Graham Collingridge NMDA APV = AP5 APV Block of LTP APV fEPSP slope (% of baseline) 225 Vehicle 50 M APV 200 175 150 125 100 75 -20 0 20 Time (min) 40 60 Coincidence Detection by the NMDA Receptor Synaptic Cleft + + Gly + - Cytoplasm Synaptic Cleft Gly - Ca++ + + + Cytoplasm Ca++ Mg++ Ca++ Mg++ Glu + + + + - Synaptic Glutamate Alone Glu - + + + + Glutamate plus Membrane Depolarization Back Propagating Action Potentials Timing of Back-propagating Action Potentials with Synaptic Activity The Dendritic Tree and Regulation of Action Potential Propagation A B NE 1 Synaptic Activity 2 LTP? Synapse Change in Local excitability % S lo p e p E P S P (S tan d ardiz ed to B aselin e) 200 Hz 200 175 150 125 100 75 200Hz A P -5 50 -3 0 -2 0 -1 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 T im e (m in ) Mossy Fiber TEA LTP NMDAR Independent LTP 60 % baseline fE P SP 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 -9 0 -6 0 -3 0 0 30 60 S eco n d s PPF PTP 90 120 150 180