ch 12 jeopardy review Molecular Genetics
advertisement
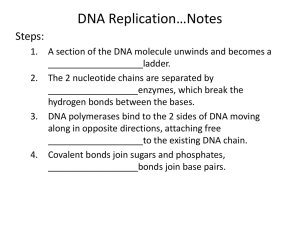
DNA Replication DNA, RNA, of DNA And Protein Gene Regulation And mutation Vocab 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 What are the 4 nitrogenous bases found in DNA compared to the 4 found in RNA? In DNA, Guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine In RNA, Guanine, adenine, cytosine and Uracil What is DNA often compared to? The shape of a Twisted ladder (double helix) What are nucleotides made out of? Sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base What did James Watson and Francis Crick discover? The used the data of other scientists to determine the shape of DNA to be in the form of a Double helix in 1953 Who had the transformation experiment that demonstrated the change of rough bacteria into smooth bacteria? Griffith in 1928 What are the 2 pairs of DNA bases bind together as a complement? 1. Adenine to Thymine Thymine to Adenine 2. Guanine to Cytosine Cytosine to Guanine What molecule is responsible for unwinding and unzipping the double helix? DNA helicase What are the stages of DNA replication? Unwinding, base pairing, joining, replication What are the 5 proteins associated in replication of DNA? DNA helicase will unwind, Single stranded Binding protein will keep the two strands separated, RNA primase adds in a RNA primer, DNA polymerase brings in the complementary DNA nucleotide, and it will remove the primer then replace it with DNA nucleotides, and DNA ligase will join or glue the lagging strand together What is the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes for the number of orgins for DNA replication? Eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication while Prokaryotes only have one What is RNA? RiboNucleic acid What is the code for TGA? ACU What is Beadle and Tatum’s hypothesis? One gene codes for one polypeptide What are the three types of RNA and their functions? mRNA- travel from the nucleus to the ribosome to direct synthesis of specific proteins. rRNA- proteins to form ribosome in the cytoplasm. tRNA- transports amino acids to the ribosome. ____codes for _____directs the synthesis of ________ DNA codes for RNA, and directs the synthesis of Proteins (this is the Central Dogma) What is a Hox gene? Crucial in development of the body plan of an organism within the embryo, and decides which part goes where. Hershey and Chase in 1952 concluded from their experiments that DNA is the genetic material of viruses, giving them strong evidence that DNA is also the genetic material of _________________? Bacteria and in Eukaryotes State the central dogma? (give the 3 steps) Transcription, translation and protein synthesis T/F– An operator is a segment of DNA that acts as an on/off switch for translation. False, an operator acts to control transcription of DNA into mRNA What blocks transcription when the operon is off? A repressor What is the difference between an exon and an Intron? Exons are the coding section of mRNA and the introns are cut out of the mRNA and do not code. What is gene regulation? Ability of an organism to control which genes are transcribed in response to the environment. What is the difference in a codon and an anticodon? A codon is a 3 base code found in DNA or in mRNA, while an anticodon is found in tRNA and is the complementary base code to a particular codon in mRNA What is a mutagen? Substance that causes mutations like chemicals, radiation, etc. What is a transcription? mRNA is written, it is formed from complementary base pairing with one side of the DNA molecule – RNA polymerase is needed to determine the correct RNA nucleotide