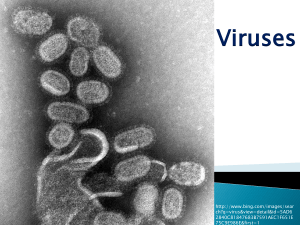
病毒概述
advertisement

Virology 病毒学 Conception Virology is a subject for study of viral structure, physical and chemical properties, the relationship between viruses and hosts, diseases caused by viruses. Virology is the study of viruses, complexes of nucleic acids and proteins that have the capacity for replication in animal, plant and bacterial cells . Viruses come in ※two basic types, those that have a genome of DNA and those that have a genome of RNA. Chapter 18 General properties of virus 病毒的基本性状 ※ This chapter will focus on Conceptions virus, virion病毒体, capsid衣壳, nucleocapsid核衣壳, naked virus裸露病毒, enveloped virus包膜病毒, viral replication病毒复制, defective viruses缺陷病毒, abortive infection顿挫感染,interference病毒的干扰现象 Questions Describe the structures of viruses. List the steps in normal viral replication What is viral interference and its application? Compare viruses with bacteria. Describe the distinctive features of virus. What is virus ? ※Viruses the smallest infectious and acellular microbe consisting only one kind of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligately严格地 replicate inside host cells. ※ Virions 病毒体 The complete mature infectious viral particle, it is the extracellular structure of virus. ※ Distinctive features 特性: Acellular microbes非细胞型 Small enough to pass through 0.2μm filters过滤器and can retain infectivity Obligatory intracellular parasites严格细胞内寄生 Contain DNA or RNA Self-replication Nonsensitive to antibiotics Differentiation of viruses from bacteria Virus Bacterium Size 0.02~0.3um 0.5~3.0um Structure Acellular microorganism DNA or RNA Prokaryotic microorganism DNA and RNA Growth on cell free medium Mode of multiplication Cannot grow Can grow Replication Binary fission Ribosome核糖体 None Has ribosome Antibiotic Resistant Sensitive Interferon干扰素 Sensitive Resistant Nucleic acid I. Size, shape and structure A. Size: The unit of measurement ? nm ( nanometer毫微米 , 纳米1/1000um微米 ) Parvoviruses 细小病毒 poxviruses 痘病毒 Comparative sizes of virions and bacteria 1. Staphylococcus aureus 2. Rickettsia立克次体 3. Chlamydia衣原体 4. Poxviruses痘病毒 5. Bacteriophage of E. coli 6. Influenza virus流感病 毒 7. Adenovirus腺病毒 8. Encephalitis B virus 乙脑病毒 B. Shape: round, rod, filamentous, tadpole蝌蚪, bullet子弹, brick砖, etc Tobacco mosaic virus烟草花叶病毒: rod-shaped HIV 人类免疫缺 损病毒 Spherical VSV: bullet-shaped子弹 (Vesicular stomatitis水泡性口炎virus): Bacteriophage T4: tadpole-shaped蝌蚪 Ebola Virus: filamentous shape C. Structure: ※Basic structure基本结构: Core核心: Viral nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) Capsid衣壳: Protein shell Capsomers壳粒 (morphological subunit) polypeptide molecules (chemical subunit) Core + Capsid → nucleocapsid 核衣壳 Envelope包膜: Spike刺突 D. Symmetry of viral nucleocapsids ※核衣壳的对称型 It is decided by arrangement of capsomers. 壳粒 Helical symmetry螺旋对称 (e.g., tobacco mosaic virus) Icosahedral symmetry 二十面体立体对称 (e.g., adenovirus) complex symmetry复合对称 (e.g., Poxviruses ) 作用:保护、鉴定、分类、 介导、免疫原性 ※ Conceptions Naked virus裸露病毒: Nucleocapsid is the virion. Enveloped virus包膜病毒: Nucleocapsid+Envelope→virion spikes or peplomers包膜子粒; Special structure特殊结构: e.g. Retrovirus has reverse transcriptase逆转录酶 结构举例: Influenza virus 流感病毒 HA - hemagglutinin NA - neuraminidase nucleocapsid lipid bilayer envelope CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF VIRUSES 病毒的化学组成 A. Viral Protein 1. The structural proteins of viruses 2. The non-structure proteins非结构蛋白 B. Viral Nucleic Acid C. Viral Envelopes D. Viral Glycoproteins: are virus-encoded II. Replication 病毒的复制 In host cell, virus replicates its nucleic acid and synthesizes its proteins, then assembles装配 them to form progeny viral particles子代 病毒颗粒 that are released mainly by budding or host cell lysis. A. ※ Normal Replication正常复制 Absorption /Attachment Penetration穿入 Uncoating脱壳 Biosynthesis生物合成 Assembly组装 Maturation and Release 1、Attachment / Absorption吸附 2、Penetration穿入: the internalization内在化of virus into the host cell Mechanisms: A. Endocytosis内吞作用 The naked viruses 裸露病毒 B. Fusion 融合between cell membrane and viral envelope The enveloped viruses 包膜病毒 C. Nucleic acid translocation 移动: Some bacteriophages and naked viruses 3、Uncoating脱壳: capsid 衣壳 is removed and viral nucleic acid is released in the host cell. 4、Biosynthesis生物合成: Biosynthesis includes: Viral genome replication 基因复制 Viral protein synthesis 蛋白质合成 Eclipse phase隐蔽期: the viral particles can not be found inside host cell and the viruses seem to have disappeared. Replication of dsDNA viruses: e.g., Herpes simplex virus单纯疱疹病毒 Cell’s DNA-dependent RNA polymerase double-strand DNA early mRNA Transcription 转录 (template) translation DNA-dependent DNA polymerase early proteins semi-conservative replication半保留复制 progeny 子代viral DNA late mRNA transcription (nonstructural proteins) translation late proteins (structural proteins) assembly 组装 progeny viral nucleocapsid 子代病毒核衣壳 5、Assembly组装: capsid + viral genome → nucleocapsid Naked virus: nucleocapsid → virion Enveloped virus: nucleocapsid + envelope包膜 → virion Site: a. DNA viruses (except poxvirus): cell nucleus细胞核; b. RNA viruses and poxvirus: cell cytoplasm细胞质; Manner: a. assemble an empty shell (procapsid 前 衣 壳 ), then viral genome fill in. b. Viral capsomers壳粒 array排列 around the viral genome to form helical symmetry nucleocapsid. 6、Maturation and Release 成熟与释放 The process of progeny viruses getting out of host cell. Naked viruses: released after the host cells lysis溶解. Enveloped viruses: Usually released by budding出芽 and acquire their envelope during budding. Traversal of cell-cell bridges细胞间横桥: e.g., defective measles virus 缺陷麻疹病毒 SSPE (Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis) 亚急性硬化性全脑炎 Host cell lysis Budding 复制的完整过程 B. ※Abnormal replication异常增殖: 1. Defective viruses缺陷病毒: are genetically deficient遗传缺陷 and incapable of producing infectious progeny virions子代病毒体. Helper viruses辅助病毒: Viruses can supplement补充 the genetic deficiency and make defective viruses replicate progeny virions when they simultaneously同时 infect host cell with defective viruses. Defective Viruses lack gene(s) necessary for a complete infectious cycle helper virus provides missing functions A A 缺陷病毒 B B example of defective virus AAV & adenovirus 腺病毒伴随病毒与腺病毒 HDV & HBV 丁肝病毒与乙肝病毒 Defective interfering particles (DIP) DIP缺陷干扰颗粒: Defective viruses which can occupy the cell machinery required for normal virus replication to prevent 防止virus production, are called "defective interfering particles" (DIP). 缺陷病毒虽不能复制,但却具有干扰同种成熟病毒体进入 细胞的作用,称缺陷干扰颗粒。 occur naturally and can cause disease e.g., DI measles virus cause SSPE. (subacute sclerosing panencephalitis)亚急性硬化性全脑炎 2. Abortive infection※顿挫感染: Virus infection which does not produce infectious progeny because the host cell cannot provide the enzyme, energy or materials required for the viral replication, is called abortive infection.因为宿主细胞不能提供酶类、能量和病毒复制的 必要成分,导致病毒感染后不能产生感染性子代。 non-permissive cells非容纳细胞 The host cells that can’t provide the conditions required for viral replication.不能提供病毒复制条件的细胞 permissive cells容纳细胞 The host cells that can provide the conditions required for viral replication. 能支持病毒完成正常增殖的细胞 III. Viral interference病毒的干扰现象 ※Viral interference When two viruses infect one cell at the same time同时 or successively先后 , the virus A may inhibit the replication of virus B, this phenomenon is called viral interference. Range of interference occurrence between the different species of virus;异种病毒 between the same species of virus;同种病毒 between the inactivated and living viruses ;灭活病毒与活病毒 between the defective virus and normal virus ;缺陷病毒与正常病毒 Viral interference Mechanisms 干扰机制 1. Virus A may inhibit virus B adsorption by blocking 防碍or destroying 破坏 receptors on host cell; 2. Virus A may compete with virus B for replication materials;竞争复制需要的物质 e.g., polymerase, translation initiation factors, etc. 3. Virus A may induce the infected cell to produce interferon干扰素 that can prevent B viral replication. Signification Viral interference干扰意义 Advantage a. Stop viral replication and lead to patients recovery. 阻止病毒复制,导致宿主康复 b. Inactivated virus or live attenuated virus can be used as vaccine to interfere with the virulent viral infection. 灭活病毒和减毒活病毒作为疫苗干扰毒性病毒感染 Disadvantage May decrease the function of vaccine 可能减低疫苗效果 IV. physical & chemical effects on viruses 理化因素对病毒的影响 Physical factors: Temperature:耐冷不耐热, 反复冰融可灭活, 保存应快速低温冷冻 pH:6~8稳定,保存可用 50%甘油缓冲盐水 radiation:X射线、γ射线、 紫外线 -196℃ IV. physical & chemical effects on viruses 理化因素对病毒的影响 Chemicals factors : Phenol 苯酚; Formaldehyde甲醛/formalin福尔马林; 70% ethanol乙醇; Oxidizing agents氧化剂; Lipid solvents脂溶剂; Biological factors: Antibiotic利于病毒分离, interferon干扰素, etc.