Multiple Alleles (p. 475)
advertisement

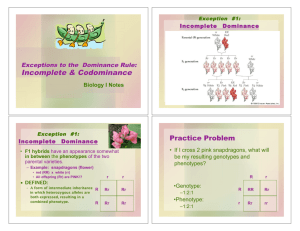
Multiple Alleles • For each trait observed by Mendel…. • Only 2 alleles existed (T & t, for example) • Many traits are controlled by multiple alleles • 2 examples include –Eye color in Drosophila (fruit flies) –Blood types in humans • • • • • Eye Color in Drosophila 4 alleles control eye color E1 = Wild E2 = Apricot E3 = Honey E4 = White 1 •E > 2 E > 3 E > 4 E Normal Fruit Fly Mutant Fruit Flies Short winged fly Normal fruit fly Curly winged fly Eye Color in Drosophila • Phenotypes Genotypes • Wild Type E1E4 • Apricot • Honey • White E1E1, E1E2, E1E3, E2E2, E2E3, E2E4 E3E3, E3E4 E4E4 Predict the phenotypic outcome if a honey colored heterozygous fly is crossed with a white fly! E3 E4 E4 E3E4 E4E4 E4 E3E4 E4E4 Phenotypes 2 Honey : 2 White Genotypes 2 E3E4 : 2 E4E4 What are the possible phenotypes of the parents in a cross which produces the following offspring? ? ? ? E1E2 E1E3 ? E2E3 E3E3 Genotpes E1E3 : E2E3 Phenotypes Wild & Apricot Another Example of Multiple Alleles Possible alleles C cch ch c Antigen type Determines Blood type Blood Types Person with A A blood type A A A A Has antigen A A A A on RBC’s A A & Antibody B (floating in plasma) Blood Typing in Humans • Another example of multiple alleles • Controlled by 3 alleles • IA, IB and i • IA and IB are said to be codominant • If a person inherits both of them, then antigen A and antigen B are on the RBC’s •i is recessive to B I A I and Blood Components Antigens A, B or Rh may be present on RBC surface Genotypes and Phenotypes for ABO Blood Types • Genotype Phenotype • • • • IAIA, IAi IBIB, IBi IAIB ii A antigen B antigen A & B antigen neither antigen Blood Type A B AB 0 Predict the phenotypic outcome if a person with blood type AB mates with a person with type O! IA IB i IAi IBi i IAi IBi Phenotypes 1 Type A : 1 Type B Genotypes 2 IAi : 2 IBi Blood Typing Problem 1 Mom Blood Type A Dad Unknown Blood Type IA IA or IA i Baby Blood Type B IBIB or IBi Must carry IB__ I BI B IBi IA IB Blood Typing Problem 1 Dad Unknown Blood Type Mom Blood Type B Must carry IB IB or IB i Baby Blood Type O i__ IBi IA i ii ii Punnet Squares for Codominance Calculate the probability of producing a son who is blood type A from the following cross! Must Use Product Rule IA IB i IAi IBi i IAi IBi Probability of producing a son = 0.5 Answer 0.5 X 0.5 = 0.25 or 25% Prob. Of producing Type A = 0.5 Blood Typing and Gender • Calculate the probability of producing a daughter who is blood type A from a cross between a Type B mother and a Type A father, given that each of these individuals have a parent with Type O. • Since parents are ii, both must be carriers for i • Mother must be IBi, Father must be IAi • Prob. of producing Type A = 0.25 • Prob. of producing a daughter = 0.50 • Therefore prob of producing Type A daughter must be found with the product rule…….. • 0.25 ( 0.5) = 0.125 or 1/8 or 13% • Diploma questions ask for answer rounded to 2 decimal places or to 2 significant digits Genetics Problem Set www.biology.arizona The Product Rule Incomplete Dominance Intermediate Inheritance Snapdragons Red X White = Pink!! Blending occurs Codominance Cattle Red X White = Roan Both genes expressed White and red hair present Red X White = Pink Gene for red (R) is incompletely dominant to gene for white (W) Incomplete Dominance: Blending/3 distinct phenotypes Predict the phenotypic outcome if a Red (RR) snapdragon is crossed with a White (WW) sd! R R W RW RW W RW RW Phenotypes All pink! Capital Letters used for both alleles since they are equally Dominant Genotypes All RW Predict the phenotypic outcome if a red (RR) snapdragon is crossed with a pink (RW) sd! R R R RR RR W RW RW Phenotypes 2 Red : 2 pink Genotypes 2 RR : 2 RW Intermediate? Or Co-dominant? Ask yourself does blending occur?? Predict the genotypes of the parents! Rr & Rr